I. Allelic, Genic, and Environmental Interactions - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
I. Allelic, Genic, and Environmental Interactions
Description:
Sex Determination and Sex Linkage A. Sex Determination Environmental Sex Determination a. Temperature Winter ... ZW female Birds Some fish Some reptiles Some ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:98
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: I. Allelic, Genic, and Environmental Interactions
1
I. Allelic, Genic, and Environmental
Interactions II. Sex Determination and Sex
Linkage
2
- I. Allelic, Genic, and Environmental Interactions
- II. Sex Determination and Sex Linkage
- A. Sex Determination
- Environmental Sex Determination
- a. Temperature
MT FT
3
- I. Allelic, Genic, and Environmental Interactions
- II. Sex Determination and Sex Linkage
- A. Sex Determination
- Environmental Sex Determination
- a. Temperature
MT FT
4
- I. Allelic, Genic, and Environmental Interactions
- II. Sex Determination and Sex Linkage
- A. Sex Determination
- Environmental Sex Determination
- a. Temperature
MT FT
5
- I. Allelic, Genic, and Environmental Interactions
- II. Sex Determination and Sex Linkage
- A. Sex Determination
- Environmental Sex Determination
- a. Temperature
Winter Melon (Benincasa hispida)
- flowers begin as perfect in bud - male or
female parts aborted as flower develops
monoecious plants with separate male and female
flowers - at lower temps, ratio of
Abcissic/Indole Acetic Acid declines influences
development more female flowers
(Huang et al. 2012, Grubben 2004)
6
- A. Sex Determination
- Environmental Sex Determination
- a. Temperature
- b. Size/Nutrition
Arisaema triphyllum Jack-in-the-Pulpit
Small plants - male Large plants - female
7
- A. Sex Determination
- Environmental Sex Determination
- a. Temperature
- b. Size/Nutrition
Benefit of being male quantity of
offspring Benefit of being female regulate
quality of offspring
Cervus elaphus Red deer
Starving pregnant females selectively abort male
embryos. Small daughters may still mate small
sons will not acquire a harem and will not mate.
Selection has favored females who save their
energy, abort male embryos when starving, and
maybe live to reproduce next year.
8
- A. Sex Determination
- Environmental Sex Determination
- a. Temperature
- b. Size/Nutrition
- c. Social Environment
Sexually mature female
(Inhibits development of males)
Sexually mature male
Immature males
Wouldnt the species do better if there were more
females/group? Yes, but selection favors
individual reproductive success.
9
- A. Sex Determination
- Environmental Sex Determination
- a. Temperature
- b. Size/Nutrition
- c. Social Environment
Midas cichlid
Brood
10
- A. Sex Determination
- Environmental Sex Determination
- a. Temperature
- b. Size/Nutrition
- c. Social Environment
Midas cichlid
Brood
Add Larger juveniles
female
11
- A. Sex Determination
- Environmental Sex Determination
- a. Temperature
- b. Size/Nutrition
- c. Social Environment
Midas cichlid
Brood
Add smaller juveniles
male
12
- A. Sex Determination
- Environmental Sex Determination
- a. Temperature
- b. Size/Nutrition
- c. Social Environment
These are still undoubtedly GENETIC effects,
likely caused by the activation of different
genes under different conditions. MUTATIONS in
single genes can influence sex determination.
ts homozygotes tassle develops female
flowers At other loci sk (silkless) ba (barren
stalk)
No female flowers in silk
But these loci that influence sex are not all on
the same chromosome.
13
- A. Sex Determination
- Environmental Sex Determination
- Chromosomal Sex Determination
- a. Protenor sex determination
The presence of 1 or 2 sex chromosomes determines
sex
Order Hemiptera True Bugs Family Alydidae
Broad-headed bugs
14
- A. Sex Determination
- Environmental Sex Determination
- Chromosomal Sex Determination
- a. Protenor sex determination
- b. Lygaeus sex determination
The type of sex chromosomes determines sex
15
- A. Sex Determination
- Environmental Sex Determination
- Chromosomal Sex Determination
- a. Protenor sex determination
- b. Lygaeus sex determination
Which sex is the heterogametic sex varies
XX female, XY male Most mammals, including
humans Some insects Some plants
ZZ male, ZW female Birds Some fish Some
reptiles Some insects (Butterflies/Moths) Some
plants
16
- A. Sex Determination
- Environmental Sex Determination
- Chromosomal Sex Determination
- a. Protenor sex determination
- b. Lygaeus sex determination
- c. Balanced sex determination
The ratio of Xs to autosomal sets determines sex
Human genotype and sex 2n 46, XX
female 2n 46, XY male 2n1 47, XXY
male 2n-1 45, X female Have a Y
male No Y female
Drosophila genotype and sex 2n 8, XX
female 2n 8, XY male 2n1 9, XXY
female 2n-1 7, X male Ratio of autosomal
setsX 21 male Ratio of autosomal setsX
11 female
17
- A. Sex Determination
- Environmental Sex Determination
- Chromosomal Sex Determination
- a. Protenor sex determination
- b. Lygaeus sex determination
- c. Balanced sex determination
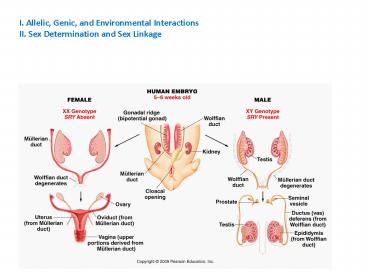
- d. Human sex determination SRY gene
18
- A. Sex Determination
- Environmental Sex Determination
- Chromosomal Sex Determination
- a. Protenor sex determination
- b. Lygaeus sex determination
- c. Balanced sex determination
- d. Human sex determination SRY gene
The presence of the Y, regardless of the number
of Xs, determines maleness
Klinefelters Male
Turners Female
19
- A. Sex Determination
- Environmental Sex Determination
- Chromosomal Sex Determination
- a. Protenor sex determination
- b. Lygaeus sex determination
- c. Balanced sex determination
- d. Human sex determination SRY gene
SRY gene produces the protein called the testis
determining factor, which stimulates the
undifferentiated gonadal tissue to become a
testis. It is a transcription factor that binds
to other genes, stimulating their expression.
20
- A. Sex Determination
- Environmental Sex Determination
- Chromosomal Sex Determination
- a. Protenor sex determination
- b. Lygaeus sex determination
- c. Balanced sex determination
- d. Human sex determination SRY gene
X X
X XX male XX male
Y- XY- female XY- female
21
- Sex Determination
- Sex Linkage Genes of interest are one of the sex
chromosomes (X or Y) - 1. For Comparison heredity for sex (as a trait)
and an autosomal dominant trait (A,a). - Autosomal genes NECESSARILY assort independently
from sex-linked genes
RECIPROCAL CROSSES
MALE AAXY MALE AAXY
FEMALE aa XX A X A Y
FEMALE aa XX a X AaXX AaXY
FEMALE aa XX a X AaXX AaXY
MALE aa XY MALE aa XY
FEMALE AA XX a X a Y
FEMALE AA XX A X Aa XX Aa XY
FEMALE AA XX A X Aa XX Aa XY
All offspring, regardless of sex, express the A
trait in both reciprocal crosses
22
- Sex Determination
- Sex Linkage
- 1. For Comparison heredity for sex (as a trait)
and an autosomal dominant trait. - 2. Sex Linkage example red-green coloblindness
in humans
MALE MALE
FEMALE Xg Y
FEMALE XG XGXg XGY
FEMALE XG XGXg XGY
MALE MALE
FEMALE XG Y
FEMALE Xg XGXg XgY
FEMALE Xg XGXg XgY
100 G, for all offspring 50 G daughters, 50
g sons Now, the sex of the parent that expresses
the G trait matters the transmission of this
gene correlates with the sex of the offspring,
because this trait and sex are influenced by
the same chromosome.
23
Queen Victoria of England
Her daughter Alice
X-linked recessive traits are expressed in males
more than females, because females get a second X
that may carry the dominant allele.
24
- Sex Determination
- Sex Linkage
- Dosage Compensation
- - Females have two doses of X-linked genes,
while males have one dose. Since protein
concentration is often important in protein
function, how is this imbalance corrected?
25
- Sex Determination
- Sex Linkage
- Dosage Compensation
- - Females have two doses of X-linked genes,
while males have one dose. Since protein
concentration is often important in protein
function, how is this imbalance corrected? In
females, one X in each cell condenses.
Barr Body
26
- Sex Determination
- Sex Linkage
- Dosage Compensation
Actually, in all humans and mammals, all but one
X condenses, regardless of sex or number of Xs.
27
- Sex Determination
- Sex Linkage
- Dosage Compensation
Random X-inactivation leads to tortoiseshell
heterozygote females
28
- Sex Determination
- Sex Linkage
- Dosage Compensation
Calico determined by a different autosomal gene
that affects rate of melanocyte migration to the
skin surface.
Melanocytes
XBXb, pp
White
No migration of melanocytes to skin
Slow migration
Calico
XBXb, Pp
Inactivation before proliferation
Fast migration
XBXb,PP
Torty
Proliferation before inactivation
29
- Sex Determination
- Sex Linkage
- Dosage Compensation
- This happens in humans, too so that females are
really a mosaic, with some cells in a tissue
expressing one X (and its X linked traits) and
some cells in that tissue expressing the other X.
Females heterozygous for red-green
colorblindness have patches of retinal cells that
cant distinguish red from green.
30
Anhidrotic ectodermal dysplasia