Demands of Performance (Psychology of Sport) - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 36
Title:
Demands of Performance (Psychology of Sport)
Description:
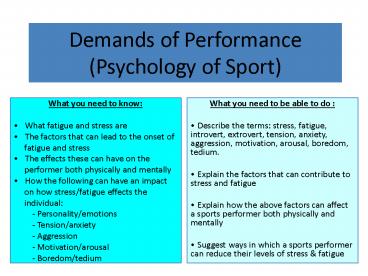
Demands of Performance (Psychology of Sport) What you need to be able to do : Describe the terms: stress, fatigue, introvert, extrovert, tension, anxiety, aggression ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:162
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Demands of Performance (Psychology of Sport)
1
Demands of Performance (Psychology of Sport)
- What you need to be able to do
- Describe the terms stress, fatigue, introvert,
extrovert, tension, anxiety, aggression,
motivation, arousal, boredom, tedium. - Explain the factors that can contribute to
stress and fatigue - Explain how the above factors can affect a
sports performer both physically and mentally - Suggest ways in which a sports performer can
reduce their levels of stress fatigue
- What you need to know
- What fatigue and stress are
- The factors that can lead to the onset of
- fatigue and stress
- The effects these can have on the
- performer both physically and mentally
- How the following can have an impact
- on how stress/fatigue effects the
- individual
- Personality/emotions
- Tension/anxiety
- Aggression
- Motivation/arousal
- Boredom/tedium
2
Prior to the Germany game
World Cup 2010 England boss Fabio Capello The
pressure has got to Wayne Rooney but he will
bounce back
"Sometimes the pressure is so big for all the
important players.
Almost half a century since they won their only
major tournament, England burdens its players
with a crippling level of expectation and
pressure, and pays no heed to the enormous body
of evidence that they cannot handle it.
England and Germany Face Possible Early World Cup
Exits
England players faced harsh criticism from their
media and fans after their scoreless draw against
Algeria last Friday.
England's football World Cup is in the balance
with everything up for grabs Wednesday for all
the four teams in Group C.
After the match against Algeria, England players
were booed by their own fans.
3
Andy Murray is hoping to get the royal seal of
approval at Wimbledon on Thursday when he plays
in front of the Queen.
"I hope it doesn't affect me in the match," said
Murray. "I think it's one of those things that
when you get out there you're aware of it, but
then it is our job to be able to concentrate and
to focus, not let things that are going on off
the court distract you.
Murray insisted last weekend that he loved the
game, and despite the enormous expectations he
faces each year at Wimbledon, he maintained that
the fortnight was his favourite time of the year.
I dont mind it, he said of the expectations.
Theres definitely more pressure on me to play
well.
4
Objectives
- All Describe the following arousal,
personality type, stress - Most Explain how can these factors affect
performance? - Some Suggest ways in which a sportsman/woman
could overcome these factors and deal with
stressful situations positively.
5
What is stress?
- It is the bodys reaction to a change that
requires physical, mental or - emotional adjustment or response
- Some people may become more aggressive, others
may find their level of - arousal is increased when they are stressed.
- Excitement can lead to tension. Tension can then
lead to tight muscles that will in turn effect
performance (this is a form of stress) - Anxiety can be make you feel apprehensive before
and during a performance. Mistakes increase if
you are over anxious. Most athletes need some
degree of anxiety to help them focus, but too
much anxiety can make a person argumentative, for
example (more on anxiety next lesson) - Nervousness can also lead to increased tension
levels some performers experience shakiness and
sickness - Motivation often decreases when any of the above
three reactions are witnessed.
6
Personality types
- Introverts
- Reserved, less outgoing, less sociable, enjoy
time on their - own. Likely to have smaller circles of friends.
- Not necessarily shy.
- Suited to individual sports/repetitive sports
e.g. - Marathon running, gymnastics, golf, cycling
- Extroverts
- Assertive, interested in seeking out excitement,
enjoy social - interactions, enthusiastic, talkative, loud,
outgoing, enjoy - new/un familiar situations.
- Suited to team sports e.g. Football, rugby,
netball
7
Arousal
- The level of readiness of an individual to
perform a task - What happens to your performance if your not up
for it? - What happens if you are too up for it?
- Inverted U Theory
- As arousal increases you get better - up to
- a certain point, after which you get worse
8
Type of person?
The individual can affect the placement of the
curve
9
Type of Sport?
Performance
Surfing
Archery
Kick boxing
Arousal
The sport can affect the placement of the curve
10
Increasing / decreasing arousal
Ways to increase Ways to decrease/control
11
Starter
- With a partner discuss and be ready to define
and explain at least two of the following terms
Stress - Arousal - Introvert - Extrovert -
The bodys reaction to a change that requires
physical, mental or emotional adjustment of change
The level of readiness of an individual to
perform a task. (How psyched up the performer
is)
Reserved, less outgoing, prefer being in small
groups suited to individual/repetitive sporting
activities
Assertive, thrill seeking, enjoy social
interactions, suited to games based activities
Further Q Can you explain the link between
personality and arousal levels?
12
You have 5mins to revise for a TEST on everything
you have studied in GCSE PE so far.
Now complete the SCAT test
13
Objectives
- All Describe the following anxiety, SCAT test,
intrinsic and extrinsic motivation. - Most Explain how anxiety and motivation can
affect performance? - Some Suggest ways in which a sportsman/woman
could overcome or reduce their anxiety.
14
Anxiety
It was your homework to find out what this it and
how it affects performers
- When a person is uneasy or troubled, often
caused by fear of underperforming - All performers experience some degree of anxiety
before or during a performance. The level of
anxiety will depend on the nature of the activity
(if the stakes are high or if the crowd is large)
and the personality of the individual
- How do you feel before competing for your team in
a PE lesson? - When competing for the school?
- If you were competing for the county?
- If you were representing the country?
15
Motivation
- Motivation is
- the driving force that compels people to do
something. - .is why people do what they do
- the direction and intensity of ones effort
- What motivates you take part in sport? Take
GCSE PE? Play for the school team? Play sport
outside of school etc? - Motivation can take 2 forms Intrinsic and
Extrinsic
16
What motivates them?
17
Intrinsic or Extrinsic Motivation?
So, David Beckham, what persuaded you to sign
that 128m deal with LA Galaxy? Los Angeles
Reporter Pain is temporary. It may last a
minute, or an hour, or a day, or a year, but
eventually it will subside and something else
will take its place. If I quit, however, it lasts
forever.Lance Armstrong Every kid around the
world who plays soccer wants to be me. I have a
great responsibility to show them not just how to
be like a soccer player, but how to be like a
man.Pele Champions aren't made in the gyms.
Champions are made from something they have deep
inside them -- a desire, a dream, a
vision.Muhammad Ali 'Success is not final,
failure is not fatal it is the courage to
continue that counts' Winston Churchill I'm
tired of hearing about money, money, money,
money, money. I just want to play the game, drink
Pepsi, wear Reebok.Shaquille O'Neal I'm
motivated by trophies - not money - and that's
why I joined Manchester CityGareth Barry The
key to immortality is living a life worth
remembering. Bruce Lee
Intrinsic motivation comes from the activity
itself for the love of the game You enjoy the
sport regardless of the rewards. Extrinsic
motivation comes from rewards and outside factors
like winning, prize money, rankings and
sponsorship
18
Intrinsic or Extrinsic Motivation?
- Consider this question
- Would you rather play badly and your team
win, or you play well and your team lose? - What does the answer say about your motivation?
19
TASK
- Create a psychological profile for yourself.
- As a minimum you must do the following
- ALL of you must
- Identify whether you are an introvert or
extrovert (explain why) - Explain how you cope with anxiety in sport
- Identify whether you are intrinsically or
extrinsically motivated (explain why) - Most of you should
- Explain how these factors link to affect how you
deal with stress in a sporting situation and how
this affects your performance overall - Explain the arousal theory in relation to your
own personality/sport - Some of you could
- Suggest how your arousal levels/reaction to
stress is different in varying situations - Suggest ways to control your levels of
stress/anxiety in competition - BEGIN IN DRAFT ON FLIP CHART PAPER, A4 OR
A3 PAPER, then complete in best for homework. Due
this Thursday.
20
Example
My SCAT score is 18 indicating that I have an
average (low average) level of anxiety. I know
this to be true as I often get a little nervous,
but I enjoy the nerves and they help me perform
better.
I am more extroverted than introverted. I can be
loud, I enjoy interacting with team mates and I
enjoy the excitement of winning in team sports.
But I also enjoy quieter sports/activities, like
going to the gym and cycling (they give me me
time, which is typical introvert behaviour)
- Mr Boaler
I am predominantly intrinsically motivated which
means
This would often have a positive impact on my
performance within martial arts competitions. My
hands would shake a little and my heart rate
would rise, but this actually helped me as I felt
a heightened sense of awareness and up for it.
My arousal level .
To deal with this I could
21
Boredom, Feedback, Aggression
Bronze Define and explain
boredom and feedback Silver
Explain how boredom and feedback can affect
motivation and performance
Gold Suggest ways in which a
coach could prevent boredom and
provide effective feedback to help a performer to
improve
22
Boredom
- You are totally uninterested in what you are
doing, your concentration lapses and the chances
are you will try very little if at all. - Boredom is also referred to as Tedium
- How many of you experienced this during the first
task? - What was changed to make it more
interesting/challenging? - How do you think boredom effects motivation and
performance? Can you think of a situation in
sport where this has applied to you?
23
Feedback
- It is through feedback that progress and
learning occur (think about the feedback we give
at the end of the leadership sessions). Without
feedback improvements would be limited. - There are 2 main forms of feedback
- Internal (Intrinsic) from inside the body
what it feels like. Can you think of examples of
this? - External (extrinsic) this comes from outside
the body through sound and vision and provides
information about the performance knowledge of
performance and about results knowledge of
results e.g. video recording/verbal feedback
from a teacher/coach
24
- Knowledge of performance
- Feedback about how to improve the
skill/technique - e.g. keep your arms straight in the
handstand - keep your head up when dribbling with the
ball so you can see where the defender is - Knowledge of results
- Feedback about how well the sportsperson
performed. - e.g. You saved 5 goals and only let in 1
well done - You finished the race in 58.58
- REMEMBER
- Feedback should always motivate the
- performer as well as correct the
- technique/performance
25
Starter Boredom and Feedback
- With a partner How many of these can you answer
in 2 mins??? - What is intrinsic feedback?
- Define boredom
- Give 2 ways a coach could alleviate boredom in a
training session - What is knowledge of results?
- Give an example of feedback given as knowledge
of performance - Give 2 effects on performance that you would
expect if the performer is bored?
Start the computers!!
26
Todays lesson What level are you happy with?
Bronze (C/D) Describe the difference between
direct and indirect aggression and give examples
of this. Define fatigue and describe basic
effects this can have on performance Silver
(B/C) Give examples of how fatigue can affect
performance and explain how it could be
reduced Gold (A/A) Explain how performers in
a high level sporting context have been effected
by fatigue. If you were there coach what would
you do to a) help them perform to their best
despite fatigue b) try to prevent this occurring
again
27
Aggression
- What is aggression? Discuss this with you
partner. - Aggression is defined as behaviour aimed at
causing harm or pain, psychological harm, or
personal injury or physical distraction. - or
- Acting with intent to injury someone
- When does this occur in sport?
- Do we really want players to play with more
aggression? - There are 2 types aggression
- Direct players make contact with each other
- Indirect aggression directed towards a
ball/other object - When may some aggression be a positive?
- When would it be a negative? What may be the
dangers of uncontrolled aggression?
28
Direct Aggression
- Contact sports involve physical contact.
29
Indirect Aggression
- You can still be aggressive in non-contact sports.
30
Direct or Indirect Aggression
31
Aggression
Controlled and uncontrolled aggression Extroverte
d people are often involved in sports which
require a degree of aggression. Aggression can be
a negative, although as long as it is controlled,
it can also become a positive. Aggression can
sometimes be the same as being assertive and
determined, in non-contact sports especially,
this is usually a good thing. In contact sports,
aggression, if uncontrolled, can lead to rule
breaking and injuring the opponent
32
- Examples of aggression. Consider the
following - Are they examples of direct/indirect
aggression.? - Justify your answer.
- http//www.youtube.com/watch?vvF4iWIE77Ts
- http//www.youtube.com/watch?vSszJZNB0XsMfeature
fvw
33
Fatigue
Fatigue is a feeling of extreme physical or
mental tiredness brought on by extreme exertion.
It can result in temporary loss of strength and
energy. It can be caused by a lack of sleep, but
this is not the only cause. What else do you
think could cause fatigue? Overtraining (too
much, too long) Lack of variety in training
(tedium) Insufficient rest between training
sessions
Research Task Use a search engine to find
examples from sport where fatigue has had
dramatic consequences.
34
Fatigue
- Discussion carousel based on fatigue articles
- 1 min summarise to a partner what you found out
- 1 min partner explains to you what they found
out - Swap partners
- 45 secs summarise to your partner swap over
- 30 secs summarise what you first partner said,
swap over - Swap partners
- 3 mins summarise what you have discussed so far
How do you think fatigue can affect your
performance?
35
Fatigue
- Effects of fatigue
- Your body or parts of your body may not be able
to carry on with what you are doing due to local
muscular fatigue. (You may need to stop
altogether) - Concentration levels will decrease and you are
more likely to make mistakes of judgement - Skill level decreases
- You may be forced to stop
- In games based activities what is in place to
help prevent injuries from fatigue occurring?
36
Scenario Task
- Read the three profiles on the handout.
- Remember this task covers arousal, stress,
anxiety, personality types (introvert/extrovert),
motivation, aggression and fatigue. - TIPS
- Recognise the difficulty of the questions (Gold,
Silver, Bronze) - Be aware of how many marks the question is worth
- Objectives of this activity
- A/A - to ensure your knowledge is applied in the
context of a real sporting scenario, which
enables you to show your depth of knowledge and
understanding.. - C/B - familiarisation with the format of the
terminal GCSE exam and practise answering
questions to earn the available marks. - D/C - to revise the key words and definitions
associated with the Demands of Performance
(Sports Psychology) module. To allow anyone who
has missed lessons to be able to catch up.