PLATE TECTONICS review - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 22
Title:
PLATE TECTONICS review
Description:
PLATE TECTONICS review REVIEW Plate Tectonics Plates are made up of the crust and top part of the mantle They move due to convection currents that occur in the ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:479
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: PLATE TECTONICS review
1
PLATE TECTONICSreview
- REVIEW
2
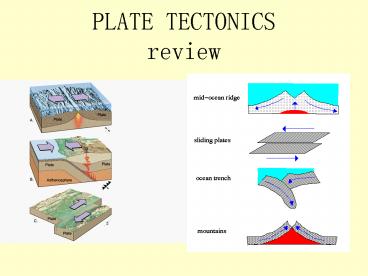
Plate Tectonics
- Plates are made up of the crust and top part of
the mantle - They move due to convection currents that occur
in the asthenosphere - Plates can converge, diverge, or slide past
eachother
3
(No Transcript)
4
Diverging Plates
- Where plates diverge, a rift valley is formed
- Magma rises up to fill the space
- Younger rock is closest to the boundary, older
rock is farther away - Ridges occur as the sea floor spreads
5
Converging Plates
- Oceanic crust is more dense than continental
crust, so it subducts (plunges under) - The result is volcanic mountains or islands above
the subduction zone (lots of melting and pressure)
6
Converging Plates
- Once there is no longer any oceanic crust (and
subduction stops), two continental plates will
collide and the rock will crumple (deform and
uplift) forming mountain ranges
7
Transform (Sliding) Boundaries
- plates slide horizontally past each other
- Friction of rock causes stress to build, which
can result in an earthquake
8
Volcanoes
- Volcanic activity can take place in many
locations on the crust (shown below), due to hot
magma rising to the surface
9
Types of Eruptions and Volcanoes Formed
- Rift (quiet) eruptions occur at spreading
boundaries and release lava - They result in broad cones called shield
volcanoes
10
Types of Eruptions and Volcanoes Formed
- Subduction (explosive) eruptions occur at
subduction zones - They result in steeper cone shaped volcanoes
(strata or cinder cone) and release ash and other
pyroclastics
11
Igneous Intrusions
- When magma solidifies in the crust in various
locations, batholiths, sills, dikes, laccoliths,
stocks result
12
Earthquakes
- Earthquakes are common at subduction zones and
transform boundaries (friction, stress!) - They occur when stress builds and then is
suddenly released - Tsunamis can be caused by underwater earthquakes
Elastic-rebound theory
13
Earthquake Waves
- There are three wave types released during an
earthquake primary, secondary and body (L) waves
14
Recording Earthquakes
- P waves travel fastest and through all materials
- S waves travel slower and do not pass through
liquids - The difference in the arrival of the p and s
waves helps geologists determine how far away the
earthquake is
15
Recording Earthquakes
- A minimum of 3 seismograph stations are required
to pinpoint the epicenter of an earthquake
(triangulation)
16
Magnitude and Intensity
- The energy released by an earthquake (magnitude)
is measured on the Richter Scale - Intensity (how much damage caused) is measured on
the Mercalli scale (subjective!)
17
Continental Margins
- Active continental margins occur at plate
boundaries and have lots of tectonic activity
(earthquakes, volcanoes) - Passive continental margins do not occur at plate
boundaries, and mostly consist of the
accumulation of sediment.
18
Faults-Three Types
- Strike-Slip sides move horizontally past
eachother (shearing force) - Normal one side drops with respect to the other
(tension force) - Reverse one side is pushed up with respect to
the other (compression force)
19
Fault Block Mountains
- When whole blocks of crust have been faulted and
thrust upwards, fault block mountains result
20
Folding of Rock Layers
- When compressional forces act on sedimentary rock
layers, folding occurs - Anticline-upfold, syncline-downfold
- Folding causes the tilting of rock layers
- Layers can also be overturned
21
Plate Tectonics-A Summary
22
(No Transcript)