Somatic Sensory Pathways - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 14
Title:
Somatic Sensory Pathways
Description:
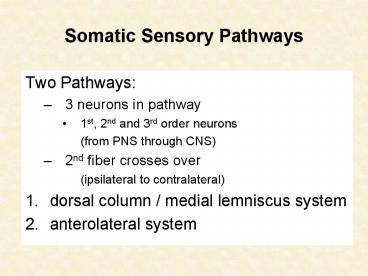
Somatic Sensory Pathways Two Pathways: 3 neurons in pathway 1st, 2nd and 3rd order neurons (from PNS through CNS) 2nd fiber crosses over (ipsilateral to contralateral) – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:153
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Somatic Sensory Pathways
1
Somatic Sensory Pathways
- Two Pathways
- 3 neurons in pathway
- 1st, 2nd and 3rd order neurons
- (from PNS through CNS)
- 2nd fiber crosses over
- (ipsilateral to contralateral)
- dorsal column / medial lemniscus system
- anterolateral system
2
Somatic Sensory Pathways
Fig. 7- 2 Ganong
Fig. 13.4
3
Dorsal Column / Medial Lemniscus System
- Signals ascend spinal cord via the dorsal (white)
columns. - large myelinated fibers (types I and II)
- fine touch and proprioception
- rapid transmission
- high degree of spatial orientation
Fig. 13.5
4
Posterior Column / Medial Lemniscus System
- 1st order sensory fibers ascend ipsilaterally in
dorsal (posterior) columns to the medulla, and
synapse in the medulla. - 2nd order fibers cross over in the medulla and
travel through the brain stem via the medial
lemniscus to the thalamus. - 3rd order fibers project to the somatosensory
areas of the cerebral cortex. - post central gyrus of the parietal lobe
5
Anterolateral System
- Signals ascend the spinal cord via the anterior
and lateral spinothalamic tracts. - small myelinated and unmyelinated fibers
- (types III and IV)
- crude touch, pain, temperature
- slow transmission
- high volume of information
- low spatial orientation
Fig. 13.5
6
Anterolateral System
- 1st order sensory neurons enter spinal cord and
synapse in the posterior horn. - 2nd order fibers cross over in the spinal cord,
and ascend spinal cord to the thalamus via the
anterior (ventral) and lateral spinothalamic
tracts. - 3rd order fibers project to the somatosensory
areas of the cerebral cortex. - post central gyrus of the parietal lobe
7
Parietal LobePost Central Gyrus
- homunculus
- visual representation of the human body on the
cerebral cortex - Because of crossover, the left side of the body
projects to the right side of the cerebrum and
vice versa.
Fig. 14.21
8
Somatic Sensation
- Perception depends less on the source of the
signal and more on what part of the brain is
stimulated. - 2 examples from pain perception
- phantom pain
- referred pain
9
Phantom Pain
- Amputees feel pain in their (missing) limbs.
- filling of cerebral cortical vacuum by other
afferent signals? - activation of cut nerve endings?
10
Referred Pain
- Pain from viscera is perceived as coming from the
skin. - e.g., heart attack pain in left arm and shoulder
- related to dermatomes
Fig. 7-7 Ganong
Fig. 16.4
11
Regulation of Pain Sensation
- Gate Theory
- In the dorsal horn, the synapse between the first
and second order neuron is a gateway for pain. - Pain may be blocked by closing this gate.
- counter irritants
- brains analgesia system one of its sites of
action
gate
Fig. 16.5
- collateral
- from touch
- receptor
Fig. 7-2 Ganong
12
Sensory Collaterals to the Brain Stem Stimulate
the Reticular Activating System
Fig. 16.3
13
Subconscious Proprioception
- via spinocerebellar pathways
Fig. 13.4
14
Video AssignmentThe Brain Parts 1 and 2
- Part 1 The Enlightened Machine
- Part 2 Vision and Movement
- DVD and VHS versions are available.
- Each part lasts about an hour.
- See p.13 of Lecture Outlines for checkout
information. - As you watch the videos, pay attention to who has
what diseases.