Mechanisms of Microevolution - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 10
Title:
Mechanisms of Microevolution
Description:
Mechanisms of Microevolution There are 5 mechanisms that affect real populations resulting in microevolution or changes to allele frequencies within a population. – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:174
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Mechanisms of Microevolution
1
Mechanisms of Microevolution
2
There are 5 mechanisms that affect real
populations resulting in microevolution or
changes to allele frequencies within a
population.
- 1. Mutations
- are only important to evolution if the mutated
DNA is in a gamete and passed on to offspring - the new mutation may provide an advantage for
natural selection - Ex) Daphnia adapted to warmer water
3
2. Genetic Drift
- Definition Chance changes in allele
frequencies due to a small population size. The
smaller the population the less likely all of the
alleles in the parent gene pool will be reflected
in the offspring gene pool - a) Bottleneck Effect
- reduction of alleles in a population resulting
from a disaster that drastically reduces
population size. - Example) earthquakes, volcanoes
- b) Founder effect
- occurs when a few individuals separate from a
large population and establish a new one
4
3. Gene Flow
- The gain or loss of alleles from a population
by the movement of individuals or gametes. This
could result from immigration or emigration. - Ex) pollen blowing in the wind and fertilizing
other plants
5
4. Non-random Mating
- in-breeding or mating between closely related
partners results in fewer heterozygotes and more
homozygotes - ex. self fertilization in plants
- assortative mating where a similar partner is
chosen like toads choosing a same size partner,
or dog breeding
6
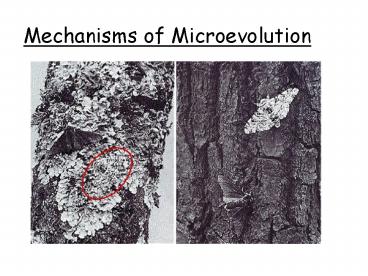
5. Natural Selection
- Individuals with favorable traits that make them
better suited for their environment are more
likely to survive to reproductive age and leave
more offspring. - http//www.pbs.org/wgbh/evolution/library/11/2/qui
cktime/e_s_4.html
7
Darwins 5 points About Natural Selection
- Population has variations.
- Some variations are favorable.
- More offspring are produced than survive
- Those that survive have favorable traits.
- A population will change over time.
8
Three Ways Natural Selection Can Affect a
Population
- 1) Directional selection
- One extreme phenotype is favoured over all other
forms. - Ex. Increasing horse body size
9
2) Stabilizing Selection
- Intermediate phenotypes are favoured.
- Ex) average human birth weight is around 7
pounds (3-4 kg)
10
3) Disruptive Selection
- Two extreme phenotypes are favoured.
- Ex) mimicry in butterflies
- Most African Swallowtails exhibit one of two
forms. Each form looks like another species that
tastes offensive to birds