Neuromuscular Junction (NMJ) - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 13
Title:
Neuromuscular Junction (NMJ)
Description:
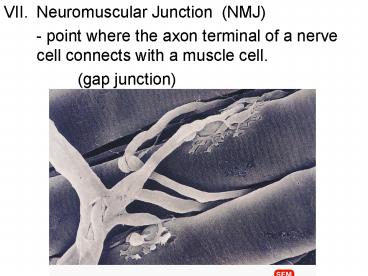
Neuromuscular Junction (NMJ) - point where the axon terminal of a nerve cell connects with a muscle cell. (gap junction) Na+ causes SR (sarcoplasmic reticulum) to ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:388
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Neuromuscular Junction (NMJ)
1
- Neuromuscular Junction (NMJ)
- - point where the axon terminal of a nerve cell
connects with a muscle cell. - (gap junction)
2
Synaptic cleft
NMJ at Rest
3
An Action Potential (AP) reaches the synaptic end
bulb. Stimulates Ca to enter into the synaptic
end bulb. Causes the Synaptic vessicles (holding
ACh) to move to the synaptic cleft. Synaptic
vessicles release Ach into synaptic cleft
4
Ach (neurotransmitter) binds to receptors on the
motor end plate. Na channels open, and Na
rushes into muscle cell. (this is the muscle
action potential)
5
AT Rest
6
- Na causes SR (sarcoplasmic reticulum) to release
Ca into the sarcoplasm. - Ca binds to T/T (troponin/tropomyosin) freeing
actin
7
- ATP on myosin head loses a P (phosphate) becoming
ADP - Myosin head then attaches to actin
8
- Myosin head will swivel and pull the actin
towards the m-line Power Stroke I. During
this, the ADP falls off the myosin head.
9
- A new ATP attaches to the myosin head causing it
to release actin - Myosin head will swivel back to its original
position
10
- ATP on myosin head loses a P (phosphate) becoming
ADP - Myosin head then attaches to actin
11
- Myosin head will swivel and pull the actin
towards the m-line Power Stroke II. During
this, the ADP falls off the myosin head.
12
- A new ATP attaches to the myosin head causing it
to release actin - Myosin head will swivel back to its original
position
13
- When the Nerve Impulse (Action Potential) stops,
the SR will take up the Ca out of the
sarcoplasm. - Without Ca, the T/T complex will block actin.
- The myosin head cant attach because ATP is on
the head and the T/T is blocked - Elastic fibers pull actin back to its original
position