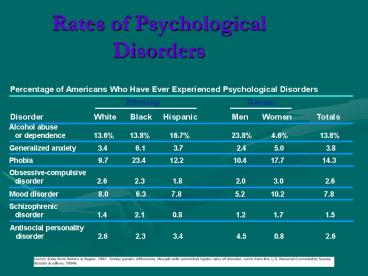
Rates of Psychological Disorders - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 33
Title:
Rates of Psychological Disorders
Description:
Schizophrenic Disorders Theories of Schizophrenia Genetic Relationships and Schizophrenia The risk of developing schizophrenia in one s lifetime increases as ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:60
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Rates of Psychological Disorders
1
Rates of Psychological Disorders
2
Psychosis
3
Psychosis
- Psychosis is a loss of contact with reality,
typically including delusions (false ideas about
what is taking place or who one is) and
hallucinations (seeing or hearing things which
aren't there). - Psychosis is a symptom, not a disease, and can
have many underlying causes.
4
Psychosis is a severe mental condition
characterized by a loss of contact with reality.
There are numerous potential causes
- Alcohol and certain drugs can induce psychosis
- Bipolar disorder (manic depression)
- Brain tumors
- Epilepsy
- Psychotic depression
- Schizophrenia
- Dementia (Alzheimer's and other degenerative
brain disorders) - Stroke
5
Symptoms of Psychosis
- Loss of touch with reality
- Seeing, hearing, feeling, or otherwise perceiving
things that are not there (hallucinations) - Disorganized thought and/or speech
- Emotion is exhibited in an abnormal manner
- Extreme excitement (mania)
- Confusion
- Depression and sometimes suicidal thoughts
- Unfounded fear/suspicion
- Mistaken perceptions (illusions)
- False beliefs (delusions)
6
Schizophrenia
- Disorganized Schizophrenia
- Catatonic Schizophrenia
- Paranoid Schizophrenia
- Delusional Disorder
7
Schizophrenia
- Schizophrenia
- literal translation split mind is misleading.
Has no connection to multiple personality. - a group of severe disorders characterized by
- disorganized and delusional thinking
- disturbed perceptions
- inappropriate emotions and actions
8
Schizophrenic Disorders The Symptoms of
Schizophrenia
- Incoherent Thinking
- Delusions
- False beliefs
- Hallucinations
- Sensory experiences that occur in the absence of
actual stimulation - Disturbance of Affect
- Bizarre Behavior
9
Schizophrenic Disorders Positive and Negative
Symptoms
- Positive Symptoms include cognitive, emotional,
and behavioral excesses. - Examples of positive symptoms are hallucinations,
delusions, thought disorders, and bizarre
behaviors. - Negative symptoms include cognitive, emotional,
and behavioral deficits. - Examples of negative symptoms are apathy,
flattened affect, social withdrawal, inattention,
and slowed speech or no speech.
10
Schizophrenic Disorders Types of Schizophrenia
- Disorganized Exhibit signs of illogical
thinking and speech - Catatonic Exhibit extremes in motor behavior
- Paranoid Delusions or hallucinations often
include extreme suspiciousness and hostility - Undifferentiated Do not clearly fit into a type
- Residual Experienced prior episodes of
schizophrenia but are not currently exhibiting
symptoms
11
Schizophrenia
12
Who is affected?
- Estimates of how many people are diagnosed with
this disorder vary. The illness affects about 1
of the population. More than 2 million Americans
suffer from schizophrenia at any given time, and
100,000-200,000 people are newly diagnosed every
year. Fifty percent of people in hospital
psychiatric care have schizophrenia. - Schizophrenia is usually diagnosed in people aged
17-35 years. The illness appears earlier in men
(in the late teens or early twenties) than in
women (who are affected in the twenties to early
thirties).
13
- Delusions
- false beliefs, often of persecution or grandeur,
that may accompany psychotic disorders - Hallucinations
- false sensory experiences such as seeing
something without any external visual stimulus
14
Positive Symptoms
- Delusions Beliefs with little or no basis in
reality (e.g. beliefs that you are being
persecuted or beliefs that you are the Messiah) - Hallucinations Unreal perceptual or sensory
experiences (e.g. hearing, seeing, or feeling
things that are not there.) - Disorganized thought and speech Grossly
disorganized pattern of speech (e.g. complete
incoherence, linking together words because of
sound instead of meaning) - Disorganized or catatonic behavior Behavior
that is highly unpredictable, bizarre, and/or
shows a complete lack of responsiveness to the
outside world (e.g. becoming completely
motionless for long periods, sudden, untriggered
outbursts.)
15
Delusions
- Persecutory delusions False beliefs that ones
self or ones loved ones are being persecuted,
watched, or conspired against by others. - Delusions of being controlled Belief that ones
thoughts, feelings, or behaviors are being
imposed or controlled by some external force - Thought broadcasting Belief that ones thoughts
are being broadcast from ones mind for others to
hear - Thought insertion Belief that another person or
object is inserting thoughts into ones head - Thought withdrawal Belief that thoughts are
being removed from ones head by another person
or object - Delusions of guilt or sin False belief that one
has committed a terrible act or is responsible
for come terrible event - Somatic delusions False belief that ones
appearance or part of ones body is diseased or
altered - Grandiose delusions False belief that one has
great power, knowledge, or talent or that one is
a famous and powerful person
16
Negative Symptoms
- Negative, or Type II symptoms of schizophrenia
involve losses or deficits in certain areas of
functioning. There are three types of negative
symptoms recognized by the DSM-IV as core
symptoms of schizophrenia - Affective flattening A severe reduction or
complete lack of emotional responses to the
environment. - Alogia A severe reduction or complete lack of
speech. - Avolition An inability to persist at common,
goal-oriented tasks.
17
Schizophrenic Disorders Theories of
Schizophrenia Genetic Relationships and
Schizophrenia
- The risk of developing schizophrenia in ones
lifetime increases as the genetic relatedness
with a diagnosed schizophrenic increases.
18
Schizophrenia
19
(No Transcript)
20
Is There a Connection between Creativity and
Mental Illness?
- The rate of mental illness (in general) is
slightly higher among those in the arts than
those in other professions.
21
(No Transcript)
22
(No Transcript)
23
(No Transcript)
24
(No Transcript)
25
(No Transcript)
26
(No Transcript)
27
(No Transcript)
28
(No Transcript)
29
(No Transcript)
30
(No Transcript)
31
(No Transcript)
32
(No Transcript)
33
(No Transcript)