Bivariate Data and Scatter Plots - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 21
Title:
Bivariate Data and Scatter Plots
Description:
Scatter Plots Bivariate Data: The values of two different variables that are obtained from the same population element. While the variables may be either categorical ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:192
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Bivariate Data and Scatter Plots
1
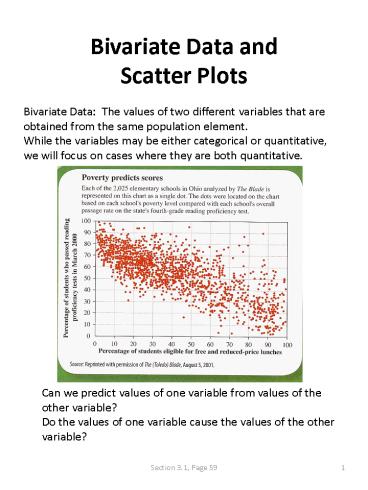
Bivariate Data and Scatter Plots
Bivariate Data The values of two different
variables that are obtained from the same
population element. While the variables may be
either categorical or quantitative, we will focus
on cases where they are both quantitative.
Can we predict values of one variable from values
of the other variable? Do the values of one
variable cause the values of the other variable?
2
Scatter Plot ExampleTI-83
Scatter Plots always have and explanatory
variable and a response variable. The choice is
arbitrary. The explanatory variable is always
plotted on the x-axis, and the response variable
is always plotted on the y axis.
STAT EDIT ENTER Enter x data in L1, and y in
L2 2nd STAT PLOT ENTER -1 Plot 1 Highlight
ONType Highlight first icon XList 2nd L1 YList
2nd L2 ZOOM 9 ZoomStat TRACE Use arrows to
move to points and display values.
3
Linear Correlation
Linear Correlation A measure of the strength of
a linear relationship between two variables. The
closer to a straight line the dots are, the
stronger the relationship.
If there correlation, then we say the two
variables are associated. Changes in the value
of one variable are associated with changes in
the value of the other variable.
4
Coefficient of CorrelationMeasure of Strength
perfect straight line negative slope
no relationship at all
perfect straight line with positive slope
Also known as the Pearson Correlation Coefficient.
5
Problems
6
Correlation CoefficientTI-83 Add-In Program
Finding r. STAT EDIT ENTER Enter data in L1
and L2 PRGM-CORRELTN 2nd LI Comma 2nd
L2 SCATTER PLOT? 1YES (Displays scatter
plot) ENTER (Displays r.8394) This is a
moderately strong positive relationship.
7
Association and Causality
Elementary School StudentsReading Scores
8
Grade Level
4
1
1
4
8
Shoe Size
Is this a reasonable association? Does giving
students bigger shoes cause reading scores to
improve? What explains this association? Lurking
Variable A third variable, often unexpressed,
that has an effect on either or both x and y
variables making it appear they are
related. Association alone can never establish
causality!
8
Problems
9
Problems
10
Problems
11
Linear Regression
Line of Best Fit If a straight line model seems
appropriate, the best fit straight line is found
by using the method of least squares. Suppose
that is the equation of a
straight line, where (read y-hat) represents
the predicted value of y that corresponds to a
particular value of x. The least squares
criteria requires that we find the constants, a
and b such that is as small as
possible.
12
Line of Best Fit
The best line will be the one where the sum of
the squares of the misses is at a minimum.
Calculus procedures are used to find the
coefficients, a and b such that the line y a
bx has the least squares.
r is the correlation coefficient, sy is the
standard deviation of y-values and sx is the
standard deviation of the x values
13
Linear RegressionTI-83 Add-In Program
- For the above data, make a scatter plot, and
comment on the suitability of the data for
regression analysis.
STAT EDIT Enter Height in L1, and Weight in
L2. PRGN REGBASIC X LIST2ND L1 Y LIST2ND
L2 SCATTER PLOT 1YES
The pattern looks positive, linear, and no
outliers which could cause problems.
Scatter Plot
14
Linear RegressionTI-83 Add-In Program
- Find the regression equation and r.
- ENTER The program is paused to view graph,
hitting ENTER moves the program along.
The equation is -186.4706 4.7059x
r, the coefficient of correlation .7979, a
relatively strong relationship.
c. Check the plot of the regression line versus
the scatter plot. ENTER 1YES
15
Linear RegressionTI-83 Add-In Program
- What is the value of the slope of the line, and
what does it mean? - b 4.7095 is the slope of the line. It
indicates the number of units change in the y
value for every one unit increase in the x value.
In this problem, for each one inch increase in
height, weight increases by 4.7095 lbs. Its
units are lbs/inch. - What is the value of the intercept of the line,
and what does it mean?a -186.4706 is the y
intercept. It has no meaning in this problem.
It would be the weight of a person of zero
height. - What is the value of r2?It is called the index
of determination. It measures the strength of
the model, 1 being perfect and 0 being useless.
r2 .6367 indicating a relative strong positive
correlation.
16
Linear RegressionTI-83 Add-In Program
g. Check the residual plot and explain what it
means
ENTER 1 YES
The horizontal line represents the regression
line. For each actual value of x, the residual is
the actual y-value predicted y-value. The dots
show the misses or residuals. If the
residuals show some kind of a pattern, it means
that the linear regression model is not
appropriate for the data, so other model, i.e.
quadratic, may be better. Since there is not
pattern is this plot, the linear model is
appropriate for this data.
17
Linear RegressionTI-83 Add-In Program
h. Use the model to predict the weight of a woman
who is 65 inches tall.
PREDICTED Y 1 YES X65 Answer 119.4 lbs
i. Use the model to predict the weight of a woman
who is 77 inches tall. ENTER 1
YES X77 Answer 175.9 lbs.
Notice that the range of the x values is from 61
to 69 inches. 77 inches is too far above the
actual values used to develop the model. While
the result is mathematically correct, the result
is not valid in the context of the problem.
18
Problems
19
Problems
- Construct a scatter diagram.
- Does the pattern appear linear?
- Find the equation of best fit.
- What is the value of r and what does it mean?
- What is the slope? What are its units?
Interpret its meaning. - What is the y-intercept value? What does it
mean? - What does the residual plot show? What does it
mean? - Estimate the the stride rate for a speed of 19.2
ft/sec. Is the estimate reliable? Why? - Estimate the stride rate for a speed of 31
ft/sec. Is the estimate reliable? Why?
20
Problems
- What is the value of r and what does it mean?
- What is the slope? What are its units?
Interpret its meaning. - What is the y-intercept value? What does it
mean? - What does the residual plot show? What does it
mean? - Estimate the of intersections for a state with
450 miles. Is the estimate reliable? Why? - Estimate the of intersections for a state with
950 miles. Is the estimate reliable? Why?
21
Problems
- Construct a scatter diagram. What does it
indicate to you? - Find the equation of best fit.
- What is the value of r and what does it mean?
- What is the slope? What are its units?
Interpret its meaning. - What is the y-intercept value? What does it
mean? - What does the residual plot show? What does it
mean? - Estimate the price of an 8 year old car. Is the
estimate reliable? Why? - Estimate price of a 22 year old car. Is the
estimate reliable? Why?