Minor Connectors - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 25
Title:
Minor Connectors
Description:
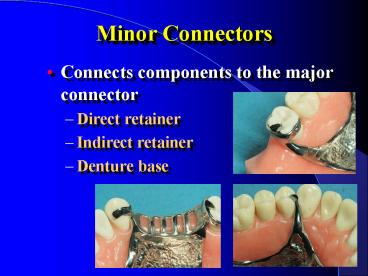
Minor Connectors Connects components to the major connector Direct retainer Indirect retainer Denture base Functions of Minor Connectors Unification and rigidity ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:660
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Minor Connectors
1
Minor Connectors
- Connects components to the major connector
- Direct retainer
- Indirect retainer
- Denture base
2
Functions of Minor Connectors
- Unification and rigidity
- Stress distribution
- Bracing through contact with guiding planes
- Maintain a path of insertion
3
Types of Minor Connectors
- Embrasure Minor Connectors
- Between two adjacent teeth
4
Types of Minor Connectors
- Embrasure Minor Connectors
- Triangular shaped in cross section
- Joins major connector at right angles
- Relief placed so connector not directly on soft
tissue
5
Types of Minor Connectors
- Embrasure Minor Connectors
- Contact teeth above height of contour
- Prevents wedging tooth mobility
- Alternatively, difficult to seat
6
Gridwork Minor Connectors
- Connect the denture base and teeth to the major
connector
7
Gridwork Minor Connectors
- Adjacent edentulous spaces
- Usually connect major connector to direct
retainers - Open lattice work or mesh types
8
Gridwork Minor Connectors
- Mesh type
- Flatter
- Potentially more rigid
- Less retention for acrylic if openings are small
9
Gridwork Minor Connectors
- Lattice Type
- Potentially superior retention
- Interferes with setting of teeth, if struts are
too thick - Both types are acceptable if correctly designed
10
Gridwork Relief
- Mechanical retention of denture base resin
- Allows the acrylic resin to flow under the
gridwork
11
Gridwork Relief
- Relief wax is placed in the edentulous areas
- 1 mm of relief
12
Relief Under the Gridwork
- Should begin 1.5 - 2 mm from the abutment tooth
13
Relief Under the Gridwork
- Creates a metal to tissue contact adjacent tooth
- Preferable since it wears less
- Less porous, (hygiene)
14
Junction With Major Connector
- Butt joint with slight undercut in metal
- Maximum bulk of the acrylic resin
- Prevents thin, weak edges fracturing
15
Mandibular Gridwork Design
- Extend 2/3 of the way from abutment tooth to
retromolar pad - Never on the ascending portion of the ridge
Stewart's, Fig. 2-55
16
Maxillary Gridwork Design
- Gridwork
- 2/3 of the length of from abutment to the hamular
notch - Major connector
- extends fully to the hamular notch
17
Gridwork Design
Facially just over the crest of the residual ridge
18
Position of Major Connector Junction
- Should be 2 mm medial to lingual surface of
denture teeth - Ensures bulk of resin around teeth
19
Mandibular Tissue Stops
- Contact of metal with cast at posterior of distal
extension gridwork - Prevents distortion at free end during hydraulic
pressure of processing
20
No Tissue Stops In Maxilla
- Maxillary major connector acts as a tissue stop
(no relief)
21
Proximal Plates
- Minor connectors originating from the gridwork in
an edentulous area - Broad contact with guiding planes
- May or may not terminate in an occlusal rest
22
Proximal Plates
23
Proximal Plates
- Shifted slightly lingually
- Increases rigidity
- Enhances reciprocation
- Improves esthetics
- Often a triangular space below the guiding plane
(an undercut)
24
Proximal Plates
- Rigid, cannot be placed in undercut
- Block-out placed in undercuts prior to waxing and
casting the framework
25
Zero Degree Block-Out
- Does not deviate from path of insertion
- Instructions to the laboratory should state Use
zero degree blockout