Family Characteristics (Applied Research Bulletin) - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Family Characteristics (Applied Research Bulletin)
Description:
Family Characteristics (Applied Research Bulletin) Effect of parental separation on children's behavior 13.8% of children born in 1983-84 experienced parental ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:47
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Family Characteristics (Applied Research Bulletin)
1
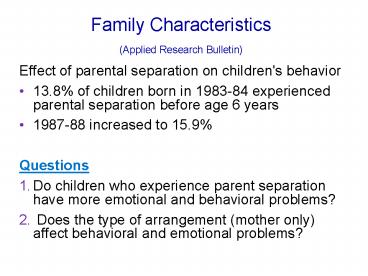
Family Characteristics (Applied Research
Bulletin)
- Effect of parental separation on children's
behavior - 13.8 of children born in 1983-84 experienced
parental separation before age 6 years - 1987-88 increased to 15.9
- Questions
- Do children who experience parent separation have
more emotional and behavioral problems? - Does the type of arrangement (mother only)
affect behavioral and emotional problems?
2
- Method
- Used NLSCY data of children 2-11 years of age
- Emotional and behavioral disorders anxiety,
emotional disorder, hyperactivity, inattention,
conduct disorder, aggression, unsocial. - Results Rates of Problems
- More behavioral and emotional problems in
children living with parental separation than
those living with both parents. - Small difference 32.5 vs 28
- Majority (2/3rds) of children have no problems
3
(No Transcript)
4
- Results
- Gender, number of siblings, and SES are better
predictors of behavioral/emotional problems - Being male increased chance of problems
- Prevalence for girls 38 less than boys
- More siblings increases chance of problems
- Each additional sibling increases chance of
problems by 7 - Mothers education, age, and income are strongly
related to problems - Those with no high school are 42 more likely to
report problems in their children - Each year older the mother is, the odds of her
child having a problems decrease by 8 - Higher income associated with less problems
5
- Results Custody Arrangement
- Custody arrangement did not have an effect on the
rates of problems - Conclusions
- Conclude that behavioral and emotional problems
are the result of a number of processes - Resiliency in children
- Time since separation is important in healing
6
Children in Lone-Parent Families
- Almost 16 of Canadian children live in single
parent families - Research suggests they are at risk for mental and
physical health problems, poorer well being,
competence, and attainment. - US data indicates that they are 2x as likely to
drop out of school and have kids before age 20,
and 1.5x more likely to be out of work and school
in late adolescence and early adulthood. - But, Canadian data suggests children in single
parent families grow up healthy
7
- Canadian researchers looked at outcomes of
children from single parent families - Measured vulnerability (health, behavior,
emotional and academic outcomes) among 2-11 yr
olds. - Found that the majority of children in single
parent families were not vulnerable to poor
outcomes - Differences are due to a small number of children
with extreme scores - Parenting style was most related to vulnerability
- More than income, parental and community
resources, and family characteristics
8
(No Transcript)
9
Family Characteristics and School
- How do family characteristics affect school
success? - Researchers used NLSCY data of 4300 6-11 yr olds
to see how families affect school achievement. - Family School Relationships (FSR) Model
characteristics of the family that are most
connected to school will have the greatest effect
on school success - Childs personal characteristics have the largest
effect, then what families do at home to promote
school success
10
(No Transcript)
11
- SES directly positively related to achievement
- Above and beyond family characteristics
- SES associated with positive attitudes towards
school, which is related to school achievement - SES associated with more social support, which is
related to less depression, which decreases
family dysfunction and ineffective parenting,
which are associated with more positive school
attitudes and higher achievement. - Policy implications improve SES
- Target parents (psychological services, education
programs, parenting classes)
12
Working Mothers and Learning
- NLSCY 25 of Canadian preschoolers have some
delays in vocabulary, 10 very low - At risk for school problems
- Researchers hypothesize that both family labor
force and income both predict vocabulary - Labor force leads to more income (positive), but
reduces time mothers spend with children
(negative) - Used NLSCY data for 3000 4-5 yr olds.
- Vocabulary (PPVT), Labor (weeks a mother works
per year), income (family income) - Amount a mother works has little effect on
vocabulary - Those who work more have children with higher
vocabulary scores
13
(No Transcript)
14
- Mothers who work more read just as much to their
kids as those who work less - Reading correlated with vocabulary
- Mothers education more important predictor of
preschool vocabulary than income - Mothers with more education may talk more with
their children and also have innate skills that
they pass on to their children - Income not as strongly related to vocabulary, and
mainly for the very poor, so increasing income
for these individuals may make a difference
15
Parenting Teti Huang
- For infants parenting competency can be defined
by the security of the infant-mother attachment - Ainsworth attachment research parental
sensitivity is the most important feature for
having a secure attachment - Mothers ability to perceive and interpret signs
in her infants behavior - Awareness of signals, alertness
- Ability to interpret the signals (empathy and no
distortion) - Responding to the signals promptly and
appropriately
16
- Instrumentally competent child independent,
responsible, achievement, friendly, cooperation - Parenting Styles
- Authoritarian high control and maturity demands,
low nurturance and clarity of communication - Permissive high nurturance and clarity, low
control and maturity demands - Authoritative high on all dimensions, nurturing
but have firm consistent control, clear rules - Children from authoritative homes are the most
instrumentally competent - Independent, assertive, achievement oriented,
friendly, and cooperative
17
- Authoritarian hostile, less achievement
oriented, more dependent - Permissive dependent, poor self-control
- Neither teach children how to cope with stress
and adapt to life situations - Control and Discipline
- Power assertion threat or use of force, physical
punishment, and withdrawing privileges - Love withdrawal ignoring or showing
disappointment - Reasoning/Explanation communicating to the child
what was done wrong and showing how it affected
others rights and feelings - Best for fostering internalization, but can be
used with other methods
18
Spanking Children (Kazdin Benjet, 2003)
- Spanking children is a broad area interest in
many disciplines - Using corporal punishment for discipline in the
home has been banned in some counties (Austria,
Croatia, Denmark, Norway, Sweden) - UN is against all forms of physical violence to
children - In the US, there are laws against being hit by
others for adults, some organizations lobby for
the same laws for children
19
- In the US 74 of parents say the spank their
children (aged 17 and under). - Of those parents with 3-4 yr olds, 94 say they
use corporal punishment - What is considered spanking?
- hitting a child with an open hand on the
buttocks or extremities with the intent to
discipline without leaving a bruise or causing
physical harm - What is Physical abuse?
- corporal punishment that is harsh and excessive,
involves the use of objects (belts, paddles) is
directed towards parts of the body other than
extremities, and causes or has the potential to
cause physical harm
20
- Views of Spanking
- Pro-corporal punishment not supported in
academic research writings, but occurs in
society - Biblical quote spare the rod and spoil the
child - Promotes spanking and states that negative
consequences result from not spanking - Anti-corporal punishment Focuses on the negative
consequences of corporal punishment - Violence begets violence, modelling and social
learning - Morality of inflicting pain
- Conditional corporal punishment spanking is not
negative or positive, but depends on the
conditions - Spanking varies across dimensions (frequency and
intensity) and contexts. Does not advocate or
refute.
21
- Gershoff (2002) conducted a meta-analysis of 88
studies on corporal punishment - Looked at relation between corporal punishment
and child outcomes (compliance, moral
internalization, aggression, criminal and
antisocial behaviour, parent-child relationship,
mental health, and abuse). - Spanking tended to lead to immediate compliance
of the child, but - Associated with decreased internalization of
morals, poorer parent-child relationships, poorer
mental health of child and adult, more
delinquency and antisocial behaviour. - At risk for abuse or abusing ones child or
spouse - More angry, aggressive and stressed
22
- The review had studies with more harsh
punishments or even physical abuse and these
studies had more negative outcomes - Another review (Larzelere, 2000) found that mild
spanking, as a back up, may not be detrimental - Key Issues for Research
- Different definitions of spanking
- Most research on the effects of spanking on child
outcomes are retrospective, with ratings
completed by the same person (parent) - Difficult to say that spanking actually preceded
the outcome (e.g. child deviance) - Spanking may be a proxy for other variables
related to negative child outcomes. - Parents who spank tend to do less reading,
playing, and hugging with children - They have more stress and major life events,
marital dysfunction, mental illness and substance
abuse
23
- Goal of discipline is to decrease some behaviors
(negative) and develop others (positive) - Not a lot of research to show punishment is the
best strategy - Positive reinforcement techniques work
- Child abuse has many serious negative effects
(changes in the brain), but it is not clear if
how the brain distinguishes between abuse
spanking - Need research on how spanking affects other
psychological processes (attachment, emotion reg) - Harsh frequent spanking has negative outcomes,
but effects of mild occasional spanking are
unclear - Caution against use of spanking other good
methods and may lead to more harsh punishment