Molar - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Molar
Description:
... PIH Congenital defects Siamese twins Pre term Labor Need for C-S Additional parental responsibilities family needs additional support encouragement/ help The ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:181
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Molar
1
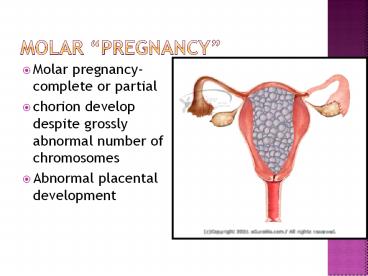
Molar pregnancy
- Molar pregnancy- complete or partial
- chorion develop despite grossly abnormal number
of chromosomes - Abnormal placental development
2
- Molar pregnancy is an abnormal form of pregnancy
in which a non-viable fertilized egg implants in
the uterus and converts a normal pregnancy into
an abnormal one - A molar pregnancy can develop when an egg that is
missing its nucleus is fertilized and that may or
may not contain fetal tissue. It is characterized
by the presence of a hydatidiform mole - Mole as used here simply indicates clump of
growing tissue, or a 'growth'.
3
Risk factors
- Age gt 40 yrs
- Previous miscarriages or ectopic pregnancy
- Mexico, Phillippines, Southeast Asia
- Incidence
- 80 non-aggressive
- 15 aggressive
- 2 cancerous
4
Signs and symptoms
- Abnormally high Hcg levels
- Brownish vaginal discharge
- Abdominal pain, distention
- Hydropic vesicles may be passed
- Uterine enlargement may be greater than expected
with pregnancy - Hyperemesis/anemia
- Diagnosed with transvaginal ultrasound, Hcg
(quantitative) testing
5
Treatment of Molar pregnancy
- D and C or D and E microscopic examination
- Risk for choriocarcinoma
- Serum Hcg q 2 weeks X 3 months, then q 1 months
for up to 1 year - Advised not to conceive for 1 year, contraception
provided - With no increased Hcg for 1 year, low risk of
recurrence or choriocarcinoma - Methotrexate agent used for carcinoma
6
Abortion- Termination of pregnancy prior to age
of viability
- Spontaneous 20 of all pregnancies prior to
week 20. May be unknown to patient. - Etiology ? Fetal/placental growth abnormalities
- Chromosomal defects
- Faulty implantation
- Drugs/ Infection
- Endocrine/ reproductive tract problems
7
- THREATENED AB
- Unexplained vaginal bleeding, cramping. May or
may not have fetal demise. - Membranes remain intact and cervical os remains
closed - Rx limit activities
- bedrest
- no sexual relations
- IMMINENT or INEVITABLE AB
- Bleeding increases, Os dilates
- COMPLETE AB
- All products of conception are expelled
8
- INCOMPLETE AB
- Products of conception are retained
- Pt will need D C
- MISSED AB
- Fetal demise in utero
- May or may not abort spontaneously
- May need induction of labor or D C
- SEPTIC AB
- Pt presents with uterine infection, elevated
temp, malodorus bleeding, abdominal tenderness. - Often due to missed abortion, serious condition
- Recurrent Pregnancy Loss may signal chromosomal
or hormonal abnormality
9
Nursing Interventions
- Emotional Support for Family
- Help mother and family through grieving process.
This can take 6-24 months - shock, disbelief, grief, sadness, anger, guilt
- mourning
- resolution, acceptance
- Be available, listen, encourage family to
verbalize. Provide family opportunity to hold
aborted fetus, foot prints, photo (if applicable) - Refer to Support Group- Resolve through Sharing,
Spiritual Counsel - Maternal care same as post partum, Rhogam
10
Incompetent or Dysfunctional Cervix
- When 2 or more spontaneous abs occur in the 2nd
trimester - Usually a result of weak, torn, or absent
sphincter muscle at cervical os - Causes include Cervical trauma, infection,
multiple gestation, cone bx, late term abortion - Premature dilation is painless. S/S contraction,
bleeding, leaking amniotic fluid - Treatment Bedrest, possible cerclage
11
Cerclage
- Cerclage- surgical suture around internal os
around week 13-15 - Suture must be opened for delivery, usually
around 37 weeks - Mom must notify if SROM occurs
- Risks to fetus not 100 effective
12
Premature Rupture of Membranes
- Many predisposing risk factors
- Maternal Sequelae Abruption, Intra-amniotic
infection, post-partum infection of endometrium - Fetal sequelae Respiratory distress, sepsis,
prolapsed cord - Diagnoses nitrazine paper, microscopic test of
amniotic fluid - No digital examination!!!
13
Treatment options
- Assess fetal well-being, gestational age
- Give antibiotics
- lt 37 weeks gestation, minimal options
- gt 34 weeks, assess lung maturation of fetus,
possibly single dose betamethasone may be
administered - Monitor for signs and prevent premature labor
- Provide psychological support for mother and
family
14
Pre-term Labor
- Onset of Labor from 20-37 weeks
- Rarely due to a single cause
- Common problem 11.6 of all births are premature
- Multiple causes
- Maternal renal, CV, DM, PIH, Placental problems,
Trauma, PROM - Effect to fetus
- Maturational deficiencies- no body fat
- Respiratory Distress
- Poor glucose, heat regulation
15
- Strongest predictors hx of previous bacterial
vaginosis, abnormal cervical length or
funneling, fetal fibronectin screening - Dx based on cervical dilation gt 1cm, effacement
or gt 80 - Greater than 4 contractions in 20 minutes or
greater than 8 in one hour
16
- TOCOLYTIC DRUGS
- Maternal Steroid Injection (24-36 weeks)
- In hospital Continuous FHR, monitoring of
contractions, hydration, treatment of any
causative infections
17
Patient education
- Braxton Hicks versus Labor greater than 4 cx
per hour - New low back pain
- Spotting or bleeding
- Increase in vaginal discharge
- Pelvic pressure
- Bedrest side-lying position, adequate hydration,
frequent voiding, avoid nipple stimulation and
sexual activity, other self care measures.
18
ABO and Rh Incompatibility
- Preventing maternal sensitization and risks to
the fetus
19
Rh Incompatibility
- Blood entering maternal circulation from Rh
positive fetus causes immune reaction. Mother
produces antibodies to babys blood. - Result? Agglutination and hemolysis of the babys
rbcs
20
(No Transcript)
21
Rh Immune globulin
- RhoGAM helps prevent maternal sensitization in
the Rh negative mom - Initial Rh and ABO testing antepartally followed
by Rh antibody screening at 28 weeks - RhoGAM given after abortion, ectopic pregnancy,
amniocentesis and within 72 hrs after birth
22
ABO Incompatibiltiy
- O positive mother has A, B or AB fetus with
antigens causing maternal antibody reaction - Rarely causes significant hemolysis, unlike Rh
incompatibility, therefore requires no antepartal
treatment usually
23
TORCH Infections Perinatal infections affecting
the fetus
- Toxoplasmosis
- O ther
- Rubella
- Cytomegalovirus
- Herpes simplex virus
- Cause fetal loss, IUGR, anomalies, premature
birth, chronic post-natal infection
24
TORCH INFECTIONS
- Toxoplasmosis (also an opportunistic infection in
HIV) - Produces flu like symptoms, lymphadenopathy
- Fetal demise, AB, retardation, blindness and
other anomalies - Treated with Sulfa/ clindamycin
- Avoid Eating Raw/ improperly cooked meat
- Stay away from Kitty litter
- Wear gloves when gardening- animal feces
25
- Other- Hepatitis A,B, C, D, E, Syphilis,
Chlamydia, Trichomonas, Gonorrhea, Condyloma,BV,
Urinary tract infections, - Hep A- Due to poor sanitation, hand washing,
foodborne - Maternal flu like symptoms
- Fetal anomalies
- Vaccination post partum
- Hep B- blood borne/ sexually transmitted
- Maternal flu like symptoms, jaundice
- Fetal like Hep A
- Rx Prevention with Hep B Vaccine which also
prevents Hep D
26
- Urinary Tract Infections,
- Need early detection Tx
- Urine CS
- NO TETRACYCLINE
- If untreated can ascend to pyelonephritis
- High fevers, pain, NV, ? GFR
- Hospitalization with IV Antibiotics
- Premature delivery, IUGR
- SYPHILIS- CROSSES THE PLACENTA
- VDRL
- Can cause fetal disease/ demise/ miscarriage
- TX Penicillin or Erythromycin
27
- Gonorrhea/ Chlamydia
- Usually exist together/ treat pt. For both
- Can affect newborn at birth/ vision
- Usual TX
- Erythromycin for Chlamydia Newborn eyes treated
with Erythromycin opthalmic ointment - B.Hemolytic Strep-
- 30 of women harbor Gr. B. Strep
vaginally/rectally/ can enter amniotic fluid - Can cause respiratory distress, sepsis,
meningitis in newborn - RX with Ampicillin, Amoxicillin, Erythromycin
28
- R Rubella or German Measles
- A Virus if contracted in 1st trimester can cause
multiple congenital anomalies. Heart, vision,
hearing, retardation - Diagnosed by blood
- Ideal to immunize all women before child bearing
, Offer post partum - C Cytomegaly virus-CMV
- A virus spread by close contact. Common in HIV.
Can cross the placenta - Can cause fetal cognitive and hearing impairment
- Prevention with Standard precautions
29
- H Herpes (HSV 1 2)
- Painful blisters(vessicles) on genitalia
- Neonatal mortality high if fetus exposed to
active disease after ROM or in Vaginal delivery - Brain damage, fever, jaundice, seizures poor
feeding, skin lesions can occur in the neonate - Moms treated with antivirals if active
lesions, must have C/S - Healthcare workers with HSV1 should wear face
mask around newborns to prevent transmission and
avoid direct contact - Good handwashing
30
Herpetic Lesions
31
Advanced Maternal AgePregnancy gt35 years
- For a woman in good health gt35 who gets prenatal
care early risks are similar to younger women - As biologic clock runs out conception may
become more difficult - Increased risk of genetic disorders can be
detected early with Amniocentesis - Fatigue may be greater prenatal and postpartum
32
Multiple Pregnancy
33
Multiple Pregnancy
- Twins- 1 in 90 births
- Triplets1 in 7600 births
- Familial tendency/ fertility drugs
- Monozygotic twins- Identical
- from one fertilized egg- always same sex
- one placenta, two amnions
- Dizygotic- Fraternal
- from 2 fertilized eggs- gender can vary
- 2 placentas
34
- All multiple pregnancies carry increased risk to
mom and fetus - High risk for
- spontaneous abortions, placenta previa, placenta
abruptia, PIH - Congenital defects
- Pre term Labor
- Need for C-S
- Additional parental responsibilities
- family needs additional support encouragement/
help
The Dionne Quintuplets born 1934
35
Post-term pregnancy
- Pregnancy that goes beyond 42 weeks
- Most common cause
- Miscalculation of dates
- After 42 weeks
- decreased placental function/ amniotic fluid
- decrease rate of fetal growth
- fetal distress
- Fetal changes
- Increase scalp hair, long thin body, less subcu
fat, long nails, decrease vernix, dry skin - Rx Fetal surveillance, Induction or C-S
36
ABUSE DURING PREGNANCY
- 4-14 of Adult pregnant women are physically by
an intimate partner - 20 of adolescents say they are abused during
pregnancy - Pts must be assess for this at every prenatal
visit. - A safe trusting relationship must be built
- Look for bruises, abrasions, cuts, burns.
Injuries to the abdomen, breasts, neck, head - Ask the questions when pt. Is alone and in a
soundproof, intrusion proof area
37
- If a woman discloses abuse
- Be non-judgmental
- Give the patient time
- Offer Support and reassure her that she is not
responsible for the abusive behavior/ and does
not deserve it - Discuss safety plan and refer to legal, social
service, and healthcare providers. - Document your findings carefully. Use pts own
words. Record your interventions, referrals