Chapter 2: Carbon Compounds - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 20
Title:
Chapter 2: Carbon Compounds
Description:
Chapter 2: Carbon Compounds Hydrocarbons Consist of only Carbon and Hydrogen Atoms Alkanes Contain the Maximum # of H Atoms Alkenes Hydrocarbons w/ Double Bond(s) – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:354
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Chapter 2: Carbon Compounds
1
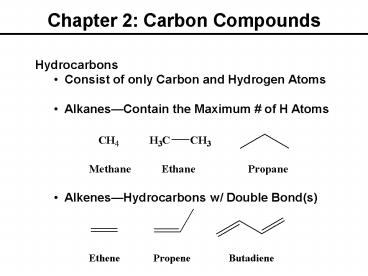
Chapter 2 Carbon Compounds
- Hydrocarbons
- Consist of only Carbon and Hydrogen Atoms
- AlkanesContain the Maximum of H Atoms
- AlkenesHydrocarbons w/ Double Bond(s)
2
Hydrocarbons Continued
- AlkynesHydrocarbons w/ Triple Bond(s)
- Alkanes Referred to as Saturated Compounds
- (Contain Maximum of Hydrogen Atoms)
- Alkenes/Alkynes Unsaturated Compounds
- Can React w/ H2 (Hydrogenation Reactions)
3
Aromatic Compounds Benzene
- Benzene/Aromatics are Special Class
- Understood in Terms of Kekulé Structures or MOs
4
Polar Covalent Bonds
- Electronegativity Difference Pulls Electron
- Density Toward More Electronegative Atom
- This Creates What is Called a Dipole
- Unit of Dipole Moment Measure Debye
HCl HBr C-O
For Bonds, Dipole Moment is Indicated w/ Arrow
From Least to Most Electronegative What About
Molecular Dipoles?
5
Polar and Nonpolar Molecules
Polar Nonpolar
NH3 CO2
H2O BH3
CH3Cl CH4
CH2Cl2 CCl4
CH3CH2OH Benzene
H3C-O-CH3 Diatomics (Cl2, Br2, etc.)
- Look at Individual Dipole Moments Check for Net
6
Polar and Nonpolar Molecules (2)
7
Functional Groups
1. Alkyl Groups (R)
Parent HC Alkyl Group Abbreviation
Methane methyl Me
Ethane ethyl Et
Propane propyl Pr
isopropyl iPr
Alkanes can be Generally Represented as R-H
8
Functional Groups
2. Alkyl Halides
- Look at Carbon w/ Halide attached
- 1 C AttachedPrimary 2 C AttachedSecondary
- 3 C Attached--Tertiary
9
Functional Groups
3. Alcohols
- Look at Carbon w/ Alcohol attached
- 1 C AttachedPrimary 2 C AttachedSecondary
- 3 C AttachedTertiary
- Replace O with S now have a Thiol
10
Functional Groups
4. Ethers
- Name sides of ether in alphabetical order
11
Functional Groups
5. Amines
- Note amines are utile as bases in organic
reactions
12
Functional Groups
6. Hydrazines
- Note hydrazines react with aldehydes/ketones
13
Functional Groups
7. Carbonyls Aldehydes and Ketones
- Note CO common link between aldehydes/ketones
14
Functional Groups
8. Carboxylic Acids
- Question What helps makes this functionality
acidic?
15
Functional Groups
9. Esters
- Note CYCLIC esters are a special case called
LACTONES
16
Functional Groups
10. Amides
- Note CYCLIC amides are a special case called
LACTAMS - Amides have restricted rotation about the C-N
bond. Why?
17
Functional Groups
11. Nitriles (Cyano)
- See Table 2.3 for a Good Summary of Functional
Groups
18
Multiple Functional Groups 1 Molecule
19
Intermolecular Forces
- Van der Waals Interactions
- Dipole-Dipole Interactions
- Consider how molecules with permanent dipoles
align - Hydrogen Bonding
- Very strong electron delocalizations
- Ionic
- Very strong electrostatic interactions
20
Hydrogen Bonding
- H-Bonds nearly linear (O-H-O)
- Electrons from an O lone pair ? s(OH)