The Strategy Design Process - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
The Strategy Design Process
Description:
Strategy Implementation and Evaluation ... There are significant benefits to gain through an explicit process of formulating strategy to insure that at ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:390
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: The Strategy Design Process
1
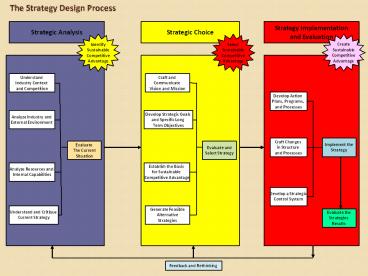
The Strategy Design Process
Strategic Analysis
Strategic Choice
Strategy Implementation and Evaluation
Identify Sustainable Competitive Advantage
Create Sustainable Competitive Advantage
Select Sustainable Competitive Advantage
Craft and Communicate Vision and Mission
Understand Industry Context and Competition
Develop Action Plans, Programs, and Processes
Analyze Industry and External Environment
Develop Strategic Goals and Specific Long Term
Objectives
Implement the Strategy
Craft Changes in Structure and Processes
Evaluate The Current Situation
Evaluate and Select Strategy
Analyze Resources and Internal Capabilities
Establish the Basis for Sustainable Competitive
Advantage
Develop a Strategic Control System
Generate Feasible Alternative Strategies
Understand and Critique Current Strategy
Evaluate the Strategies Results
Feedback and Rethinking
2
Situation Analysis
Identify Strategic Options for the Company
Select the Best Strategy for the Company
3
Question 4 Which Companies are in
Strongest / Weakest Positions?
- A strategic group is a group of firms in an
industry following the same or similar strategy.
- Identifying strategic groups
- Identify principal strategic variables that
distinguish firms. - Position each firm in relation to these
variables. - Identify clusters.
4
Strategic Groups Within the World Petroleum
Industry
Statoil
INTEGRATED DOMESTIC OIL COMPANIES
PRODUCTION COMPANIES
INTEGRATED INTERNATIONAL MAJORS
DIVERSIFIED MAJORS
PDVSA
Kuwait
0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0
Exxon
Vertical Balance
Shell
Amoco
BP
Chevron
Unocal
Arco
Total
Mobil
Texaco
Phillips
Indian Oil
Petrobras
ENI
ENI
Elf
Elf
INTERNATIONAL DOWNSTREAM OIL COMPANIES
Repsol
Neste
Petrofina
Nippon
Sun
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80
NATIONALLY-FOCUSED DOWNSTREAM COMPANIES
Geographical Scope
5
How to Start a Revolution
- Re-conceive your product or service
- Radically improve the value equation
- Separate form and function
- Achieve joy of use
- Re-define the market space
- Push the bounds of universality
- Strive for individuality
- Increase accessibility to your products
- Re-draw industry boundaries
- Rescale the industry
- Compress the supply chain
- Drive convergence between industries
6
- What is a competitive advantage?
- How do you know if you have one (or not)?
- How can you create one?
7
Sources of Competitive Advantage
COST ADVANTAGE
Similar product
at lower cost
COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE
Price premium
from unique product
DIFFERENTIATION ADVANTAGE
8
The Porter Value Chain
SUPPORT ACTIVITIES
FIRM INFRASTRUCTURE HUMAN RESOURCE
MANAGEMENT TECHNOLOGY DEVELOPMENT PROCUREMENT IN
BOUND OPERATIONS OUTBOUND MARKETING SERVICE LOGIST
ICS LOGISTICS SALES
PRIMARY ACTIVITIES
9
Using the Value Chain to Identify Differentiation
Potential on the Supply Side
IS that supports fast response capabilities
Training to support customer service excellence
FIRM INFRASTRUCTURE HUMAN RESOURCE
MANAGEMENT TECHNOLOGY DEVELOPMENT INBOUND
OPERATIONS OUTBOUND MARKETING SERVICE LOG
ISTICS LOGISTICS SALES
Unique product features. Fast new product
development
Customer technical support. Consumer credit.
Availability of spares
Quality of components materials
Defect free products. Wide variety
Fast delivery. Efficient order processing
Building brand reputation
10
Creating Competitive Advantage
- Industry structure matters, but success does not
come just from industry attractiveness - Value difference between buyers willingness to
pay and sellers opportunity cost - Added value marginal value created by the firm
(value that would be lost by its absence) - The larger the added value, the larger the
potential profit for the seller - CA is achieved by driving a wedge between buyer
willingness to pay and value added by the firm
(scarcity)
Ghemawat Rivkin, 2006
11
Activity Analysis of Value Creation
- Catalog activities (along the value chain)
- Use activities to analyze relative costs and cost
drivers - Use activities to analyze relative willingness of
customers to pay - Who is the real buyer?
- What do buyers want and what are they willing to
pay for? - What is the relative success of our firm and
competitors in fulfilling customer needs - Relate success back to activities are the
activities customers need the ones we are good
at? - Explore options and make choices
- Understand competitors, their likely reactions,
the bundle of benefits to customers, and the role
of scope and scale
Ghemawat Rivkin, 2006
12
Value NetworksA non-linear model of value
creation
13
Porters Generic Strategies
SOURCE OF COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE
Low cost Differentiation Industry-wide
COST DIFFERENTIATION COMPETITIVE
LEADERSHIP SCOPE Single
Segment FOCUS
14
The Evolution of Competitive Advantage
How does competitive advantage evolve?
- External sources of
- change e.g.
- Changing customer demand
- Changing prices
- Technological change
Internal sources of change
Some firms have greater creative and
innovative capability
Resource heterogeneity among firms means
differential impact
Some firms faster and more effective in
exploiting change
15
Drivers of Cost Advantage
- Indivisibilities
- Specialization and division of labor
ECONOMIES OF SCALE
- Increased dexterity
- Improved coordination/ organization
ECONOMIES OF LEARNING
- Mechanization and automation
- Efficient utilization of materials
- Increased precision
PRODUCTION TECHNIQUES
- Design for automation
- Designs to economize on materials
PRODUCT DESIGN
- Location advantages
- Ownership of low-cost inputs
- Bargaining power
- Supplier cooperation
INPUT COSTS
CAPACITY UTILIZATION
- Ratio of fixed to variable costs
- Costs of installing and closing capacity
MANAGERIAL/ ORGANIZATIONAL EFFICIENCY
- Organizational slack
16
Identifying Differentiation Potential The
Demand Side
What needs does it satisfy?
THE PRODUCT
What are key attributes?
- FORMULATE DIFFERENTIATION STRATEGY
- Select product positioning in relation to
product attributes - Select target customer group
- Ensure customer / product compatibility
- Evaluate costs and benefits of differentiation
Relate patterns of customer preferences to
product attributes
By what criteria do they choose?
THE CUSTOMER
What price premiums do product attributes command?
What motivates them?
What are demographic, sociological, psychological
correlates of customer behavior?
17
The Evolution of Honda A Strategy Based on
Resources and Capabilities
50cc 2-cycle engine
Related products ground tillers, marine engines,
generators, pumps, chainsaws
Founding of Honda motor company
405cc motor cycle
Insight Hybrid
4 cycle engines
1948 1950 1955 1960 1965 1970
1975 1980 1985 1990 1995 2005
First product clip-on engine for bicycles
The 50cc super -cub
N360 mini car
1000cc Goldwing touring motor cycle
Acura Car division
18
Core Competence Three Tests
- Provides potential access to a wide variety of
markets and products - Makes a significant contribution to perceived
customer benefits of the end product - Is difficult for competitors to imitate
19
Strategic Intent
- Global leadership over a long time horizon
- An obsession with winning at all levels of the
firm - A sustained, challenging, focused BHAG
- Stable over time
- Attracts personal effort and commitment
- Guide for resource development and allocation
- Avoiding recipes for imitation
- Creating competitive advantages faster than
competitors can imitate them, creating new
space - Layers of competitive advantage
- Changing the terms of engagement
20
The Relationships Between Resources,
Capabilities and Competitive Advantage
INDUSTRY KEY SUCCESS FACTORS
COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE
STRATEGY
ORGANIZATIONAL CAPABILITIES
- RESOURCES
- TANGIBLE INTANGIBLE HUMAN
- Financial
- Physical
- Specialized skills
- and knowledge
- Communication
- interactive abilities
- Motivation
- Technology
- Reputation
- Culture
21
The Profit Potential of Resources and
Capabilities
Scarcity
THE EXTENT OF THE COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE
ESTABLISHED
Relevance
Durability
THE PROFIT EARNING POTENTIAL OF A RESOURCE
OR CAPABILITY
SUSTAINABILITY OF THE COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE
Transferability
Replicability
Property rights
Relative bargaining power
APPROPRIABILITY OF RETURNS
Embeddedness of resources
22
Preparing for the Future The Role of Scenario
Analysis
- Stages in undertaking multiple Scenario Analyses
- Identify major forces driving industry change
- Predict possible impacts of each force on the
industry environment - Identify interactions between different external
forces - Among range of outcomes, identify 2-4 most
likely/ most interesting scenarios
configurations of change forces and outcomes - Consider implications of each scenario for the
company - Identify key signposts pointing toward the
emergence of each scenario - Prepare contingency plan
23
Perspectives on Strategic Planning
- The essence of strategic planning is the
systematic identification of opportunities and
threats that like in the future to provide a
basis for making better current decisions
(George Steiner) - There are significant benefits to gain through
an explicit process of formulating strategy to
insure that at least the policies (if not the
actions of functional departments) are
coordinated and directed at some common set of
goals (Michael Porter) - Planning is the substitution of error for chaos
(Anonymous) - Most corporate planning is like a ritual rain
dance It has no effect on the weather that
follows, but it makes those who engage in it feel
they are in control (Russell Ackoff)