Lymphatic System - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 44
Title:
Lymphatic System
Description:
Efferent lymphatics carry lymph from nodes. Lymph Circulation. Afferent, Efferent Lymphatics and Valves. Lymph ... Efferent Lymphatic Lymphatic Trunks ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:171
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Lymphatic System
1
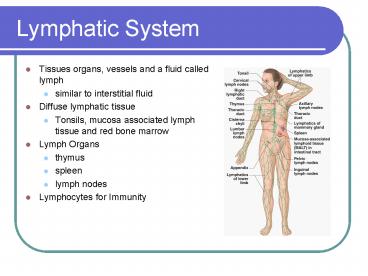
Lymphatic System
- Tissues organs, vessels and a fluid called lymph
- similar to interstitial fluid
- Diffuse lymphatic tissue
- Tonsils, mucosa associated lymph tissue and red
bone marrow - Lymph Organs
- thymus
- spleen
- lymph nodes
- Lymphocytes for Immunity
2
Functions of the Lymphatic System
- Draining excess interstitial fluid plasma
proteins from tissue spaces - Transport of some nutrients and hormones
- Immunity specific defense
- recognize microbes or abnormal cells responding
by killing them directly or secreting antibodies
that cause their destruction
3
Formation Flow of Lymph
- Some fluid proteins Filtered from blood
capillaries are collected by lymphatic
capillaries returned to the blood - Muscle contraction and breathing promote flow of
lymph - Lymphatic vessels empty into subclavian veins in
shoulders
4
Lymph Circulation
- Lymph capillaries
- Capillaries are closed-ended tubes in tissues
- Have one-way minivalves
- Pickup fluid (lymph) from Tissues (interstitial
fluid)
5
Lymph Capillaries
- Comparison of Lymph and Blood Capillaries
Minivalve
6
Lymph Circulation
- Lymphatic Vessels (lymphatics)
- Lymph passes from capillaries into lymph vessels
- Resemble veins with thin walls valves
- Afferent lymphatics carry lymph to nodes
- Efferent lymphatics carry lymph from nodes
7
Lymph Circulation
- Afferent, Efferent Lymphatics and Valves
8
Lymph Circulation
- Lymph trunks drain lymph into ducts
- Lymph ducts - largest lymph channels
- Two ducts drain lymph into subclavian veins
- Larger thoracic duct drains most of body
- Smaller right duct drains right side head, right
shoulder and right arm into right subclavian vein
9
Lymph Ducts
Right Lymphatic Duct
Thoracic Duct
10
Lymph circulation
- Drainage Pattern of Lymphatic Ducts
11
Summary of Lymphatic Flow
- Interstitial fluid ? Lymph Capillaries ?
- Afferent Lymphatics ? Lymph Nodes ?
- Efferent Lymphatic ? Lymphatic Trunks
- ? Lymphatic Ducts ? Subclavian Veins of
cardiovascular system (CVS)
12
Which are the larger lymphatic structures?
Question
- (A) lymphatics
- (B) trunks
- (C) capillaries
- (D) ducts
13
Lymph Tissues
- Lymphatic nodules MALT (Mucosa Associated Lymph
Tissues) - lymphatic nodules within the digestive and
respiratory systems - Small intestine
- Appendix
- Bronchi of respiratory tract
14
Lymph Tissues
- Tonsils
- Located in and around throat
- Tonsilar crypts
- Functions
- Crypts Trap microbes such as bacteria
- Mount immune response against inhaled and
ingested microbes
15
Lymph Organs
- Lymph nodes
- Structure
- Location
- Throughout body but concentrated in groin, neck,
armpit - Functions
- Filter lymph
- Provide immunity
16
Lymph Node Distribution
Cervical Nodes
Axillary Nodes
Inguinal Nodes
17
Vessels that enter lymph nodes are called ______
lymphatics.
Question
- (A) efferent
- (B) afferent
- (C) enter
- (D) endo
18
Lymph Organs
- Thymus
- Located in mediastinum above heart
- Large in infants atrophying with age
- Function
- Thymosin hormones for
- T-cell lymphocyte maturation
19
Spleen
- Located in upper left quadrant to left of stomach
- Functions
- Filters blood
- Provides immunity
- Stores iron and platelets
20
Question
Which of the following are located within the
intestinal lining?
- (A) tonsils
- (B) lymph nodes
- (C) thymus glands
- (D) MALT
21
What lymphatic structure contains hormones for
T-cell lymphocyte maturation?
Question
- (A) Tonsils
- (B) Thymus gland
- (C) Spleen
- (D) MALT
22
Defense
- Non-specific Defense
- First Line Defense External
- Skin
- Mucous Membranes
- Tears
- Saliva
- Stomach acid
23
Non-specific Defense
- Second Line Defense Internal
- Antimicrobial proteins
- Interferons antiviral
- Complement immunity and inflammation
- Natural killer (NK) cells
- Lymphocytes
- Kill microbes and tumor cells
- Phagocytes
- Wandering phagocytes
- Fixed phagocytes
24
Internal Defense
- Inflammation
- Mast cells and basophils release chemicals
including histamine - Arterioles vasodilate more blood to site
- Increased capillary permeability more fluid
into tissues
25
Internal Defense
- Results in
- Redness
- Heat
- Swelling (edema)
- Pain
- Healing
26
Question
- Which of the following is a first-line of
non-specific defense? - Interferons
- mucous membranes
- NK cells
- Inflammation
- none of the above
27
Specific Defense Immunity
- Study of immunity is immunology
- Immunity versus non-specific defense
- Specificity responds to specific invaders
- Destroys invaders by various means such as
___________________________ - Memory Second exposure to antigen causes a
stronger response
28
- Antigens
- Foreign (non-self) cells or chemicals that
produce an immune response (stimulate antibody
production) - Are microbes, parts of microbes, blood cells,
transplant tissues, and a variety of chemicals
29
Immunity
- B-cell and T-cell lymphocytes responsible for
immunity - Two types of immune responses
- Cell mediated immunity T-cells respond to
intracellular antigens such as virus infected
cells and tumor cells - Antibody mediated immunity B-cells respond to
extracellular antigens - Antibodies combat the antigen
30
Cell Mediated Immunity
- T-cells originate in the red bone marrow and are
processed (undergo maturation) in the thymus
gland - Matured T-cells then pass into other lymph
tissues where they are ready to respond to
antigens
31
Immunity
- Two types of T-cell lymphocytes
- CD8 cells
- Activated by contact with virus infected body
cell - Onr type develops into killer T-cells and memory
cells - CD4 cells
- Activated when antigen presented by antigen
presenting cell (APC) cell - Develops into helper T-cells and memory cells
- Helper T-cells must activate CD8 cells before
they can become fully activated killer Ts
32
Cell Mediated Immunity continued
- Killer Ts leave lymphatic tissue to search for
and destroy virus infected cells, tumor cells and
tissue transplant cells on contact
33
Cell Mediated Immunity Diagram
34
Question
- Which of the following activate Killer
- T-cells?
- B-cells
- plasma cells
- Helper T-cells
- antibodies
- none of the above
35
Antibody Mediated Immunity
- Antigen causes production of antibodies
- B-cell lymphocytes stay in lymph tissues
- Antigen enters lymph tissue and binds to B-cell
receptors - B-cells become activated
- B-cells divide (clone) to form identical plasma
cells and memory cells - Helper T-cells bind to antigen on compatible
B-cells and help stimulate plasma cell and
memory cell formation
36
Antibody Mediated Immunity
- Plasma cells secrete various types of antibodies
- Antibodies then bind to the specific antigen that
activated its parent B-cells - Antibodies then cause the destruction of the
antigen in several ways
37
Antibody Mediate Immunity Diagram
38
Question
- Which cells secrete most of the
- antibodies?
- Plasma cells
- T-cells
- B-cells
- NK cells
- none of the above
39
Antibody Mediated Immunity
- Antibodies destroy antigens by
- Neutralizing antigens such as toxins
- Agglutinating (clumping) and precipitating
(removing from solution) antigen bearing cells - Activating the complement proteins that destroy
the antigen by various means - Enhancing phagocytosis by covering a microbe with
antibodies
40
Antibody Mediated Immunity
- There are five classes of antibodies
- IgG, IgM, IgA, IgE and IgD
- The IgG antibody is most common
- Study Table 22-1, page 807 in text and earn some
extra credit on exam by learning the functions
for each type. - What does the Ig stand for?
41
Summary of Immunity
42
Immunological Memory
- What is meant by the terms primary response and
secondary response? - What causes the secondary response?
43
Question
- What does the Ig in the antibody symbol
- stand for?
- Interferon globulin
- Immunoglobin
- Immunogenic
- Immunoglobulin
- none of the above
44
Disorders of the Immune System
- To earn extra credit on your exam, study Immune
Disorders on pages 815-817 in your text.