Heart - External View - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 9
Title:
Heart - External View
Description:
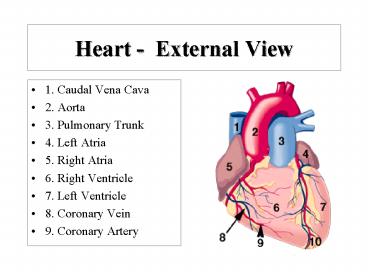
Heart - External View. 1. Caudal Vena Cava. 2. Aorta. 3. Pulmonary Trunk. 4. Left Atria ... 1. Caudal Vena Cava. 2. Right Atria. 3. Tricuspid Valve. 4. Right ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:33
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Heart - External View
1
Heart - External View
- 1. Caudal Vena Cava
- 2. Aorta
- 3. Pulmonary Trunk
- 4. Left Atria
- 5. Right Atria
- 6. Right Ventricle
- 7. Left Ventricle
- 8. Coronary Vein
- 9. Coronary Artery
2
Heart Internal View
- 1. Caudal Vena Cava
- 2. Right Atria
- 3. Tricuspid Valve
- 4. Right Ventricle
- 5. Papillary Muscle
- 6. Aorta
- 7. Pulmonary Trunk
- 8. Left Atria
- 9. Bicuspid Valve
- 10. Septum
3
Starting with the right atria list in order the
blood flow through the heart.
10
9
4
4
5
5
6
3
8
1
7
2
10
4
Heart Functioning
- Aorta
- Inferior vena cava
- Coronary artery
- Ductus Arteriosus
- Left atrium
- Left ventricle
- Pulmonary artery
- Pulmonary vein
- Right atrium
- Right ventricle
- Marks the beginning of systemic circulation
- Returns blood from the body
- Supplies the heart tissues with blood
- Used only in fetal life bypasses lungs
- Receives blood from lungs
- Pumps blood to body
- Carries blood to the lungs
- Carries blood from lungs to heart
- Receives blood from body
- Pumps blood to the lungs
5
Short Answer
- How is the fetal heart different from an adult
heart? - Ductus Arteriosus bypasses the lungs because the
fetus depends on the mother for oxygen - Why is the circulatory said to have double
circulation? - Blood passes through the heart twice on each
circuit.
6
Vocabulary
- Systolic
- Diastolic
- Heart attack
- White cells
- Red blood cells
- Platelets
- Hypertension
- Atherosclerosis
- Pacemaker
- Stroke
- Cardiac Cycle
- Blood pressure during ventricular contraction
- Blood pressure between contractions
- Results of a clogged coronary artery
- Defends against invaders
- Erythrocytes
- Aids in blood clotting
- High blood pressure
- Hardening of arteries
- Sinoatrial node
- Results of a blood clot in the brain
- Alternation of contraction and relaxation of
heart chambers
7
Types of Circulation
- Pulmonary
- Systemic
- Renal
- Portal
- Hepatic
- To the lungs
- To the body
- To the kidneys
- To the digestive system
- To the liver
8
Blood and Vessels
- Hemoglobin
- Plasma
- Capillaries
- Arteries
- Veins
- Universal Donor (O)
- Universal Receiver (AB)
- A,B,AB,O
- Oxygen carrier in blood
- Liquid part of blood
- Smallest vessels exchange of materials
- Carry blood away from heart
- Carry blood toward heart
- Can give blood to anyone
- Can get blood from anyone
- The four blood types
9
Two Closely Related Systems
- Circulatory System
- Lymphatic System
- Name 4 functions of the circulatory system.
- 1. Transport oxygen and carbon dioxide
- 2. Distribution of nutrients
- 3. Transport of wastes
- 4. Regulation of body temperature
- 5. Distribution of hormones
- 6. Protection from bacteria and viruses
- Name 3 functions of the lymphatic system.
- Remove excess fluid that leaks from capillaries
- Transport of fats from small intestine to blood
stream - Defends the body by exposing bacteria and viruses
to white blood cells