T Cell Activation - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 42
Title:
T Cell Activation
Description:
T cell trafficking and activation by APC's ... 'Two-signal' model of lymphocyte activation ... T cell activation is aided by accessory receptors ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:60
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: T Cell Activation
1
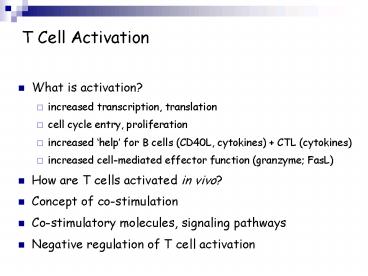
T Cell Activation
- What is activation?
- increased transcription, translation
- cell cycle entry, proliferation
- increased help for B cells (CD40L, cytokines)
CTL (cytokines) - increased cell-mediated effector function
(granzyme FasL) - How are T cells activated in vivo?
- Concept of co-stimulation
- Co-stimulatory molecules, signaling pathways
- Negative regulation of T cell activation
2
Overview of TCR/CD3 Signaling Pathways
1
3
2
IP3
AP-1
Transcription Factors
NF-kB
3
Global changes in transcription upon T cell
activation
4
Gene Induction after Ag recognition
5
Gene Induction after Ag recognition
6
Gene Induction after Ag recognition
7
T cell trafficking and activation by APCs
8
Dendritic cells sample antigens in peripheral
tissues, mature and migrate to lymph nodes
9
T Cell Circulation
10
Selectin Proteins Help Direct T Cell Traffic in
vivo
Naive T Cells
11
Integrins also help direct T cell traffic
and coordinate binding to different cell types
12
Accessory and Co-Stimulatory Moleculesin T Cell
Activation
13
Strength (Affinity) of Various Receptor/Ligand
Systems
14
Accessory Molecules Help Stabilize T Cell/APC
Interactions
Immunological synapse Supra-molecular
activation cluster (SMAC)
15
Inside-out signaling upregulates T cell
adhesion to APC
16
APC Phenotypes
17
Two-signal model of lymphocyte activation
- Burnet - clonal selection hypothesis - B cells
(1950s) - self-reactive cells must be removed during
development - Bretscher and Cohn (1970)
- what about hypermutation?
- helper cell (overlapping Ag specif.) for B cell
responses - Lafferty and Cunningham (1975)
- second signal for helper cell (from APC)
- Janeway and Medzhitov (1989-1992)
- activation signal for APC (pattern-recog.
receptor) - PRRs bind to conserved structures on pathogens
18
Roles for Co-Stimulation in T Cell Responses
- Increases efficiency of T cell activation
- increases proliferation, cytokine production
- signaling effects both quantitative qualitative
- Increases T cell survival
- Helps ensure activation by appropriate cells
- i.e. by cells w/ligands for costim. molecules
- professional APC
- particularly important for naive cells
19
Co-stimulation T cell activation
20
B Cell activation through surface Ig is aided
by a co-receptor complex
21
Molecules with T cell co-stimulatory activity
Mucin domain
TIM-1 (upregulated)
TIM-4
Yes
Yes
?
?
No
22
CD28
- 44 kD surface glycoprotein
- Cloned in Brian Seeds lab (1984)
- Later shown to augment T cell proliferation
- Also shown to increase IL-2 production
- Shown by Allison and colleagues and Jenkins and
Schwartz to prevent anergy in T cell clones
stimulated through TCR alone - Cytoplasmic domain required (signaling)
23
T Cell Clone Experiments Demonstrating the
Importance of Co-stimulation
Note No IL-2 produced
24
Co-stimulation Can Be Provided In Trans
Fixed APC untreated APC Fixed APC
anti-CD28 Ab
25
Function of IL-2 in T Cell Priming/Expansion
26
IL-2 is a critical growth factor for expansion of
effector T cells and is a target of co-stimulation
27
Generation of Effector CTL w/T Cell Help
28
CD28 Signaling
29
CD28 cytoplasmic domain
30
CD28 - downstream signaling
31
Some MAPK pathways are targets for
co-stimulatory signals
CD28
32
NF-kB activation by TCR and CD28
CD28
PI-3K
CARMA1
Akt
33
Contribution of CD28 to NFAT Activation
34
Negative Regulation of T Cell Activation
35
CD28 and CTLA-4
- After a T cell becomes activated, it up-regulates
expression of CTLA-4 on the cell surface. - CTLA-4 binds B7 with about 10x higher affinity
than does CD28 - This appears to act as a damper on activation
36
(No Transcript)
37
Regulation of CTLA-4 Expression
38
Lack of CTLA-4 Disrupts Normal T Cell Homeostasis
wild-type knockout
This suggests that there is probably some
low-level activation happening all the time in
vivo, which CTLA-4 normally dampens
1 cm
Lymphadenopathy
39
CTLA4-Ig Suppresses Immune Responses
CTLA4-Ig in the clinic -transplants -autoimmune
diseases
Also evidence that CTLA4-Ig binding to B7 on APC
can result in production of an inhibitory factor
(IDO).
40
CD28 and B7 Family Members
41
Speculative model for PD-1 Function
42
Summary
- T cell activation is aided by accessory receptors
- Activation results in global changes in gene
expression - Co-stimulatory molecules are important for
activation and function of T cells - Related inhibitory molecules play a role in
limiting immune responses