STEAM - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 1
Title:
STEAM
Description:
... efficient tree-based communication scheduling over time and radio frequencies ... Changes in radio connectivity. Changes in application traffic patterns. Goals ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:33
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: STEAM
1
STEAM
Umesh Shankar, Naveen Sastry, David Wagner
NEST Retreat UC Berkeley
Algorithms
Goals
- Parent Switching
- Senders switch parents if their messages are not
getting through for whatever reason. We dont
distinguish between connectivity problems,
interference, or schedule conflicts. - Nodes use EWMA estimator to decide when to
switch. - Channel Switching
- Parents need to switch channels if they are
overhearing messages that are not destined for
them. - But there is a cost to switching children must
detect that the node has switched channels and
fail over. - Compute conflict fraction f, which measures how
often a node hears messages for another node. - Compute expected conflict fraction e, which
estimates what the conflict fraction should be,
on average. - Compute cost function g(c), where c of
children - Switch channels with probability p (f e) /
g(c)
- State Exchange
- Want to communicate channel information to
neighbors using minimal number of sends/receives
of announcements. - We only need each node to have one or two backup
parents (and to have that information be
relatively recent). - Idea have each node listen or send with
exponentially decreasing probability unless new
information is needed or heard. - In the steady state, almost no energy used, but
the probability of hearing useful information is
still high. - Variable Listen Rate
- Idea If incoming message rate is low, do not
need to listen every period. - Keep estimate of message rate using EWMA
- EWMA of samples 1 if received a message, 0 if
not - Keep upper and lower thresholds if estimate goes
above upper threshold, increase listening
frequency, and if esimate goes below lower
threshold, decrease frequency. - Announce changes, but if decreasing, observe old
frequency during transition.
- Energy efficient tree-based communication
scheduling over time and radio frequencies - Handle dynamic changes
- Node joining or leaving
- Changes in radio connectivity
- Changes in application traffic patterns
Overview
- Largest time unit period
- Receivers choose channels (frequency, time
offset) on which they listen each period for
messages. - Receivers announce their choices on a special
channel no reservations with senders needed. - Senders choose some parent and send on
appropriate channel. - System converges to a good state senders switch
parents using EWMA estimator and receivers switch
channels according to a cost-benefit model. - Announcement traffic goes to near-zero in the
steady-state.
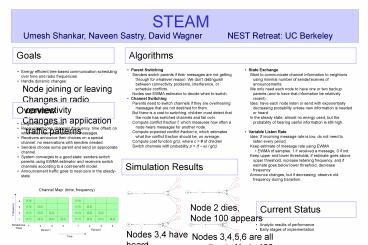
Simulation Results
Channel Map (time, frequency)
Current Status
Node 2 dies, Node 100 appears
- Analytic results of performance
- Early stages of implementation
Nodes 3,4 have heard about 100, but dont yet
know that Node 2 has died
Nodes 3,4,5,6 are all sending to Node 100