Framework for Commensal Evaluation - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 17
Title:
Framework for Commensal Evaluation
Description:
ABR transfer to pathogen density, available mechanisms, nutrition, selection ... Intersection of Soil Chemistry and Microbiology ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:18
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Framework for Commensal Evaluation
1
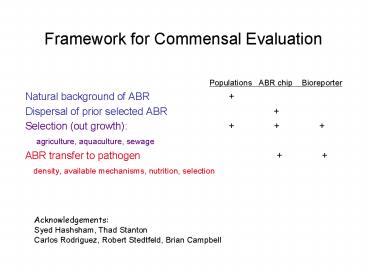
Framework for Commensal Evaluation
- Populations ABR chip Bioreporter
- Natural background of ABR
- Dispersal of prior selected ABR
- Selection (out growth)
- agriculture, aquaculture, sewage
- ABR transfer to pathogen
- density, available mechanisms, nutrition,
selection
Acknowledgements Syed Hashsham, Thad
Stanton Carlos Rodriguez, Robert Stedtfeld, Brian
Campbell
2
83 of total since 2000 67 of total since 2003
Of only 7 soil studies, 84 of unique
isolate/gene combinations in soil come from 2
studies (published in 2007 and 2008) Despite only
7 studies, isolate/gene combinations unique to
soil isolates represent 17 of the total
isolate/gene combinations from environmental and
animal sources much unexplored diversity!
3
Molecular functional analysis in
soil microcosms
100 g of water-saturated soil
located next to manured soil, same soil type
4
Quantification of tet (36) in soil microcosms
5
Tetracycline Resistant Bacterial Isolates from an
Agricultural Field in Michigan
Screened for A, B, C, D, E, G, H, J, X, Y, Z, 30,
and 31
- Expanding the spectrum of genes found in
isolates - Identification of tet(Y) in Pseudomonas, tet(C)
and tet(31) in Stenotrophomonas, tet(A) in
Microbacterium, and tet(A) and tet(C) in
Thermomonas - Second identification of tet(X) in
Sphingobacterium - Moore et al., 2005 show that Tigecycline is
modified by TetX - Although modification was slight perhaps
mutation could enhance activity?
Unpublished
6
PCR amplification of class 1 integrons
variable region from manured soil DNA
7
Amplification of class 1 integron variable region
(manured wheat field, 1 week after application)
temp gradient 65-54oC
control soil (no manure)
manured soil
Amplification of class 1 integron variable region
(manured wheat field, 4 weeks after application)
manured soil
control soil (no manure)
M 65o 64o 63o 62o 61o 60o 59o58o 57o 56o 55o
54o M
1636 bp
1636 bp
1018 bp
1018 bp
8
Abundance of RPP genes in clone libraries after 1
month of application
Abundance of integron-associated ABR genes in
clone libraries after 1 month of application
after 1 month
after 1 week
GTP-binding (2)
cation transporters (4)
ribosomal protection (7)
metabolism (6)
hypothetical/putative (31)
14 of retrieved sequences corresponded to RPP
genotypes (N 50)
9
Assessment of integron diversity by comparative
sequence analysis of conserved regions among
integron encoded integrases
Integrons are classified on the basis of the
divergence among their integrase genes
(Rowe-Magnus and Mazel, 2001).
hep35/hep36 Degenerate primers designed to
hybridize to a conserved region (approximately
500bp long) among integron encoded integrase
genes intl1, intl2 and intl3 (White et al,
2000).
10
Diversity of environmental integrases
11
Biotrove OpenArray Used for ABR Chip
12
Success rate of primer design Validation of 110
VMG Assays
Stedtfeld et al., AEM 2008
13
QPCR of AB resistance genes Experimental approach
Primer Design Approach
- Download aligned nucleotide sequences from FGPR
- Group sequences based on similarity and construct
consensus sequences. - Design primers from conserved regions of
consensus sequence using Primer Express. - Blast and select primers based on theoretical
specificity of 3 end.
Experimental Approach
- Overall, 336 primer sets targeting 176 ABR genes,
and 39 virulence genes. - Used multiple displacement amplification to
increase DNA for each sample. - SYBR based QPCR was performed on all samples,
which were tested simultaneously (in triplicate)
using 3 BioTrove plates.
14
QPCR results Genes amplified in 1 or more samples
Collaboration with Thad Stanton. Natl Animal
Disease Cntr
15
Intersection of Soil Chemistry and Microbiology
Does tetracycline contamination in soil enhance
the development, maintenance, and transfer of
resistance genes?
- Tetracycline is commonly found in soils at
concentrations ranging from 200 300 ppb. In a
complex matrix such as soil, is tetracycline at
environmentally relevant concentrations
bioavailable to drive resistance gene expression?
What factors control the bioavailability of
tetracycline in environmental matrices? - To begin to answer these questions
- Characterize bioavailability of tetracycline
complexed with environmentally relevant cations
in solution phase. - Quantitatively measure promoter activity using a
tetracycline inducible bioreporter and model
equations developed by Leveau Lindow, 2001. - Explain results in context of tetracycline
solution chemistry - Use this base knowledge and collaboration with
soil chemists to expand to tetracycline cation
mineral phase systems (e.g. smectite clays)
Courtesy of Dr. Lars Hansen (University of
Copenhagen)
16
TC Bioavailability (LB)
1 mM Mg2
0.1 ug/mL TC
n/a
1 mM Mg2
0.1 ug/mL TC
n/a
7.5 mM Mg2
5 mM Mg2
2.5 mM Mg2
7.5 mM Mg2
5 mM Mg2
2.5 mM Mg2
10 mM Mg2
10 mM Mg2
17
10 mM MgCl2 Added
10 mM EDTA Added