Chapter 7How Cells Divide - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 22
Title:
Chapter 7How Cells Divide
Description:
http://www.gpc.edu/~vmicheli/biol107/mitosis.htm ... http://www.gpc.edu/~vmicheli/biol107/mitosis.htm (5)Cytokinesis- (division of cytoplasm) ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:34
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Chapter 7How Cells Divide
1
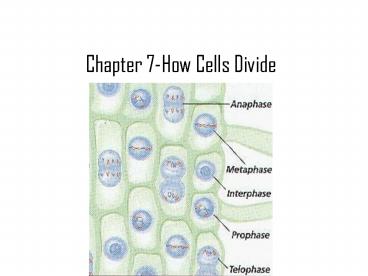
Chapter 7-How Cells Divide
2
Chapter 7-How Cells Divide
- Cell division- process which cellular material is
divided btw. two new daughter cells. - In many celled organisms, it is the way the
organism grows/repairs itself - When cell reaches certain metabolic state, it
divides. - New cells are similar to parent because it
inherits exact hereditary information - 1/2 of the parent cells cytoplasm and organelles
- Initiated when cell reaches critical size
- One-celled eukaryote, Paramecium cell division
may occur every few hours
3
http//www.sirinet.net/jgjohnso/reprod.html
4
Prokaryotes
- Most of the hereditary material is single, long,
circular molecule of DNA. (a chromosome). - 2 daughter chromosomes attach different spots of
interior of cell membrane. - As membrane elongates, chromosomes separates,
cell membrane pinches inward, new cell wall forms
5
Prokaryotes
http//www.sirinet.net/jgjohnso/reprod.html
6
Cell Division in Eukaryotes-Cell Cycle
- 1000x more DNA
- linear with distinct chromosomes (the human
somatic cells- 46), more organelles - Interphase-
- G1, S, G2- replicates and synthesizes histones/
proteins, organelles - assembly of structures
- G1-
- follows cytokinesis, intensive biochemical
activity. Cell size, enzymes, ribosomes,
mitochondria, cytoplasmic molecules increase - Some created from de novo (from
scratch)-microtubules, actin filaments,
ribosomes- protein subunits
- 2 centrioles (not found in fungi/plants)
separate begin replicating (finish job in G2) - --Mitochondria/chloroplasts replicate (own
chromosomes)
7
- Synthesis phase- DNA replication/histones
- Takes the most time to complete
- G2, newly replicated chromosomes, coil/condense
for complex movements of chromsome in mitosis - Completed contriole pair outside nuclear envelope
- Assemble special structures
- Finish replication of centrioles
8
Regulation of the Cell Cycle
- RBC 25 trillion in adult
- - produce 2.5 million each second (critical to
divide at a sufficient rate in multicellular
organismscancer) - Cells stop growing-
- 1. environmental factors (depletion of nutrients/
change in temp) - 2. Contact (density-dependent) inhibition-stop
when they are touching in late G1 phase - R restriction point? quickly to S phase
- Hypothesis- passing R point requires specific
concentration of protein in small quantities sign
of suitable size/metabolic state - Stimulatory/inhibitory growth factors,
synthesized by the cell itself
9
- Chromosome condense after S phasechromatids
joined by centromere attached to kinetochore
(microtubules attach to this) - Spindle-assembly of microtubles. Tubulin
dimerscytoskeleton - Polar fibers (each pole to center)
- Kinetochore fibers (attached kinetochores of
chromosomes) - Aster- short extend from centrioles, brace poles
of spindle against cell membrane withoutcell
wall
10
- Spindle is dissembled after cell division,
cytoskeletal network of microtublues reassembled - interchangeablility of basal bodies/centriole
(Chlamydomonas) - Staining region around centrioles, now thought to
be microtubule center
11
- Interphase- chromosomes visible thin strands of
threadlike material (chromatin) within the
nucleus under light microscope - Chromosomes- pairs of identical
replicaschromatids, held at centromere - Spindle forms (btw the centrioles, animal cells),
extend to poles - Fibers attach to chromatids at kinetochores
(protein structures with centromeres)
12
Interphase
http//www.gpc.edu/vmicheli/biol107/mitosis.htm
13
Prophase- About 10 Minutes!Longest phase of
mitosis
- (1)Prophase (longest)
- -chromatin condensed individual chromosomes
visible - - Cell is more spheroid, microtubules are
disassembled from cytoskeleton for formation of
spindle. Cell takes on a spheroid shape - -Centriole move apart form spindle (aster)
- - Ends with chromosome fully condensed,
centriole pairs at poles, polar fibers formed,
kineticore fibers formed. - -Breakdown of nuclear envelope ( resembles ER
)/disappearance of nucleoli
14
Prophase
http//www.gpc.edu/vmicheli/biol107/mitosis.htm
http//staff.jccc.net/pdecell/celldivision/mitosis
1.html
15
- (2) Metaphase chromatid pairs move to center,
arranged equatorial plane - (3) Anaphase rapid! sister chromatids separate
at centromere, - each chromatid move to opposite pole by
kinetochore fibers. - (4) Telophase chromosomes opposite ends
- tublin dimers disperse, nuclear envelope forms.
Spindle breaks down, chromosomes uncoil and
extend, nucleoli reappear. - Theories of Movement in Chromosomes -
- --kinetochore fibers lengthen in prophase,
shorten in anaphase - --Material added-pushing/pulling together
- --Microtubles are protein arms with enzyme energy
reactions
16
Metaphase
http//www.gpc.edu/vmicheli/biol107/mitosis.htm
http//staff.jccc.net/pdecell/celldivision/mitosis
1.html
17
Anaphase
http//www.gpc.edu/vmicheli/biol107/mitosis.htm
http//staff.jccc.net/pdecell/celldivision/mitosis
1.html
18
Telophase
http//www.gpc.edu/vmicheli/biol107/mitosis.htm
http//staff.jccc.net/pdecell/celldivision/mitosis
1.html
19
- (5)Cytokinesis- (division of cytoplasm)
- Animal- constrictions by actin filaments to form
a furrow - Plants- cytoplasm divided by vesicles
(polysaccharide-containing vesicles from Golgi
complex) to form cell plate. - -Layer of polysachharides impregnated with
pectins (forming the middle lamella), cellulose
against outer surface - Spindle might play a role division of cytoplasm.
- Actin filaments-constriction, purse string to
pinch apart. - Exact copy parent cell, half cytoplasm/organelles
20
Cytokinesis
http//www.sirinet.net/jgjohnso/reprod.html
21
Liver cells
- Are capable of dividing to replace liver mass
that has been surgically removed
http//www.pennhealth.com/hup/transplant/liver/abo
ut_liv_don.html
22
Chloroplast Mitochondria
- Have their own chromosomes
http//www.agen.ufl.edu/chyn/age2062/lect/lect_04
/lect_04.htm