Gastrointestinal Tract of Poultry Simple Stomached - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 32
Title:
Gastrointestinal Tract of Poultry Simple Stomached
Description:
Vitamin B12 is digested and released from dietary proteins and rapidly bound to ... The binding proteins are digested within the intestine, releasing Vitamin B12 ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:286
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Gastrointestinal Tract of Poultry Simple Stomached
1
(No Transcript)
2
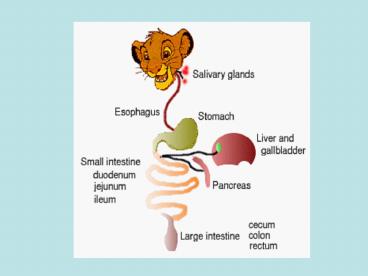
Gastro-intestinal Tract of Poultry (Simple
Stomached)
3
Gastro-intestinal Tract of the Horse (Simple
Stomached Non-ruminant Herbivore)
4
Gastro-intestinal Tract of the Pig (Simple
Stomached)
5
Gastro-intestinal Tract of the Cow (Ruminant)
6
(No Transcript)
7
(No Transcript)
8
Phases of Digestion - Stomach
- Cephalic phase seeing, smelling, anticipating
food
9
Phases of Digestion - Stomach
- Cephalic phase seeing, smelling, anticipating
food - Gastric Phase meal enters the stomach,
distension, mucosal irritation
10
Experiments and observations on gastric juice
and physiology of digestion
- W.W. Beaumont, 1829
- .patient with a gastric fistula, gastric acid
follows ingestion of a meal
11
Late 19 th Century, nervism or exclusive role of
nerves in control of digestive secretion
- Lectures on Conditioned Reflexes Ivan Pavlov,
1926 - Nobel Prize, 1904
- . the essential role of the central nervous
system and vagal nerves in the stimulation of
gastric secretion, sham feeding and ordinary
feeding
12
- .the exploration of new biological agents
discharged by particular tissue cells directly
into blood, they were called hormones, the name
coined by English physiologists William Bayliss
(1860-1924) and Ernest Starling (1866-1927) from
the University College in London.
13
First discovery of hormonal control of pancreatic
secretion by non-nervous substance, Secretin
- Bayliss and Starling, 1902.
- The mechanism of pancreatic secretion.
- J. Physiology (London)
- 22325-330.
14
The control of gastric secretionGASTRIN
- J. Edkins, 1906
- The chemical mechanisms of gastric secretion.
- J. Physiology (London)
- 34133-144.
15
In 1916, Popielski discovered the role of
histamine as an agent increasing the secretion of
the hydrochloric acid
The results of his study pointed that histamine
increased secretion of the gastric juice in
humans, causing soon after its subcutaneous
injection a rapid increase of the rate of acid
juice secretion in the stomach with the peak
after 30-55 minutes.
16
Controversy in the halls of science
- Popielski strongly objected to the hormonal
theory, he challenged Edkins' concept according
to which the secretion of the stomach juice is
stimulated by the "stomach secretion" (gastrin).
17
- acetycholine and histamine became the focal
points as the principal regulators of acid
secretion.
18
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1936
- Sir Henry Dale
Otto Leowi - "for their discoveries relating to chemical
transmission of nerve impulses and
appreciation for acetylcholine and histamine as
physiological regulators"
19
Parietal Cells
- The stomach secretes HCl in direct proportion to
the number of parietal cells (oxyntic cells) - Resulting pH of 0.8 (160 mM)
- Enzymatically driven carbonic anhydrase
- Carbonic anhydrase, H/K ATPase (proton pump)
- Excessive secretion of acid is a major problem in
humans
20
(No Transcript)
21
Intrinsic Factor
- Intrinsic factor is a glycoprotein secreted by
parietal cells (humans) or chief cells (rodents)
22
Intrinsic Factor
- Intrinsic factor is a glycoprotein secreted by
parietal cells (humans) or chief cells (rodents) - Vitamin B12 is digested and released from dietary
proteins and rapidly bound to two Vitamin B12
binding proteins.
23
Intrinsic Factor
- Intrinsic factor is a glycoprotein secreted by
parietal cells (humans) or chief cells (rodents) - Vitamin B12 is digested and released from dietary
proteins and rapidly bound to two Vitamin B12
binding proteins. - The binding proteins are digested within the
intestine, releasing Vitamin B12
24
Intrinsic Factor, contd
- The vitamin becomes bound to intrinsic factor in
the intestine and there are receptors for the
vitamin-IF complex on mucosal cells.
25
Intrinsic Factor, contd
- The vitamin becomes bound to intrinsic factor in
the intestine and there are receptors for the
vitamin-IF complex on mucosal cells. - Vitamin B12 is need for erythrocyte maturation
and a deficiency leads to anemia.
26
Intrinsic Factor, contd
- The vitamin becomes bound to intrinsic factor in
the intestine and there are receptors for the
vitamin-IF complex on mucosal cells. - Vitamin B12 is need for erythrocyte maturation
and a deficiency leads to anemia. - Cobalt is a key co-factor in the activity of this
vitamin.
27
Enterochromaffin-Like Cells
- Distinctive type of endocrine cell within the
mucosa prevalent in acid secreting regions. - ECL cells synthesize and secrete histamine in
response to gastrin. - Histamine and gastrin become the primary
regulators of acid secretion by parietal cells.
28
Intestinal Feedback
- Enterogastric reflex - chemical and osmotic
irritation of the mucosa sends gastric-inhibitory
impulses via the enteric nervous system - Enteric hormones cholecystokinin and secretin
are released from cells in the small intestine,
suppress gastric activity
29
Enterochromaffin-Like Cells
- Distinctive type of endocrine cell within the
mucosa prevalent in acid secreting regions.
30
Enterochromaffin-Like Cells
- Distinctive type of endocrine cell within the
mucosa prevalent in acid secreting regions. - ECL cells synthesize and secrete histamine in
response to gastrin.
31
Enterochromaffin-Like Cells
- Distinctive type of endocrine cell within the
mucosa prevalent in acid secreting regions. - ECL cells synthesize and secrete histamine in
response to gastrin. - Histamine and gastrin become the primary
regulators of acid secretion by parietal cells.
32
- Komarow, 1938.
- ..evidence that a histamine free extract was
effective in the stimulation of gastric secretion
in cats, effect was not influenced by neural
blockers