Chapter 19: Magnetism - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 21
Title: Chapter 19: Magnetism
1
Chapter 19 Magnetism
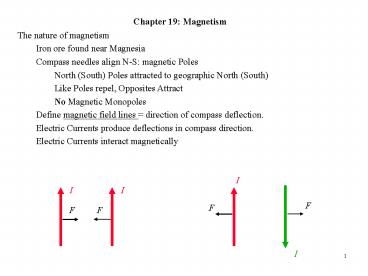
The nature of magnetism Iron ore found near
Magnesia Compass needles align N-S magnetic
Poles North (South) Poles attracted to geographic
North (South) Like Poles repel, Opposites
Attract No Magnetic Monopoles Define magnetic
field lines direction of compass
deflection. Electric Currents produce deflections
in compass direction. Electric Currents interact
magnetically
I
I
I
F
F
F
F
I
2
Magnetic Fields in analogy with Electric Fields
- Electric Field
- Distribution of charge creates an electric field
E in the surrounding space. - Field at charges location exerts a force Fq E on
a charge q - Magnetic Field
- Moving charge or current creates a magnetic field
B in the surrounding space. - Field exerts a force F on a charge moving q
- F qvB sin? ? is angle between B and v.
- F is perpendicular to B an v
3
Right Hand Rule (1-2-3) v, B, F
4
Units of Magnetic Field Strength B
F/(qv) N/(C m s-1)
Tesla actually defined in terms of force on
standard current CGS Unit 1 Gauss 10-4
Tesla Earth's field strength 1 Gauss Direction
direction of velocity which generates no force
5
J. J. Thomsons Measurement of e/m Electron
Gun
???????????????????????????????
E
???????????????????????????????
Example 19.2 Electrons are accelerated through
a potential difference of 1000 V. The electrons
then enter a region where there is a magnetic
field and a crossed electric field (E and B are
perpendicular), both of which are perpendicular
to the beam. What magnitude magnetic field must
be applied to exactly cancel the effect of the
Electric field of 104 V/m?
6
Field of a long straight wire
I
Magnetic field circulates around the wire use
Right hand rule for direction Thumb in direction
of the current, fingers curl around in direction
of B
B
s
Example 19.2 Find the magnetic field 10 mm from
a wire that carries a current of 1.0 A.
7
(No Transcript)
8
Magnetic Field in a Solenoid Close packed stacks
of coils form cylinder
Fields tend to cancel in region right between
wires. Field Lines continue down center of
cylinder Field is negligible directly outside of
the cylinder
9
Example 19.3 A solenoid 20 cm long and 40 mm in
diameter with an air core is wound with a total
of 200 turns of wire. The solenoid is to be used
to exactly cancel the Earth's magnetic field
where it is 3.0x10-5 T in magnitude. What should
the current in the solenoid be for its field to
exactly cancel the earths field inside the
solenoid?
10
Magnetic Materials
Microscopic current loops electron
orbits electron spin
Quantum Effects quantized angular momentum L,
Pauli Exclusion Principle, etc. are important in
macroscopic magnetic behavior.
11
Magnetic Materials Microscopic magnetic moments
interact with an external (applied) magnetic
field and each other, producing additional
contributions to the net magnetic field B.Types
of Materials Diamagnetic Magnetic field
decreases in strength. Paramagnetic Magnetic
field increases in strength. Ferromagnetic
Magnetic field increases in strength! Diamagneti
c and Paramagnetic are often approximately linear
with a relative permeability KM, ? KM ? 0
12
Ferromagnetism Greatly increases field Highly
nonlinear, with Hysteresis Hysteresis
magnetic record Magnetization forms in Magnetic
Domains
Saturation
Permanent Magnetization
13
More on the magnetic force on a moving charge
For a charged particle moving perpendicular to
the Magnetic Field
- Circular Motion!
14
Example 19.5 A mass spectrometer
velocity selector circular trajectory
E 40.0 kV/m B .0800 T Velocity Selector uses
crossed E and B, so that Electric and Magnetic
Forces cancel for a particular velocity. (a)What
is the speed of the ions pass through the
velocity selector? (b) If the radius of the path
of the ions is 390 mm, what is the mass of the
ions?
15
In a non-uniform field Magnetic Mirror Net
component of force away from concentration
of field lines.
v
F
Magnetic Bottle
Van Allen Radiation Belts
16
Magnetic Force on a Current Carrying Wire
B
I
A
vd
?L
Fi
17
Example 19.6 (almost) A wire carries 100 A due
west, suspended between two poles 50 m apart.
The Earths field is 5.0 x 10-5 T, directed
north. What is the magnitude and direction of
the magnetic force on the wire.
18
Force between two long parallel current carrying
wires (consider, for this example, currents in
the same direction)
I2
I1
F12 I1 Bdue to I2 ?L I1 (?oI2/(2?r)) L F/L
?oI1 I2 /(2??r) force on I1 is towards I2 force
is attractive (force is repulsive for currents in
opposite directions!)
Bdue to I2
Fdue to I2
Example Two 1m wires separated by 1cm each carry
10 A in the same direction. What is the force
one wire exerts on the other
19
Torque on a Current Loop (from force on wire
segments) Rectangular loop in a magnetic field
(directed along z axis) short side length a, long
side length b, tilted with short sides at an
angle with respect to B, long sides still
perpendicular to B.
B
Fb
Fa
Fa
Fb
Forces on short sides cancel no net force or
torque. Forces on long sides cancel for no net
force but there is a net torque.
20
Torque calculation Side view
moment arm a/2 cos ?
Fb IBb
?
Fb
??? Fb a/2 cos ?????Fb a/2 cos ?? ??????Iab B
cos ?? I A B cos ?? ??????? I N A B cos ??with N
loops Magnetic Dipole Electric Dipole Switch
current direction every 1/2 rotation gt DC
motor Torque for armature of Galvanometer
21
Magnetic Poles Magnetic dipoles from electric
current No isolate magnetic poles, they are
always present in pairs! No magnetic monopoles!