Some Transport Types - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 17
Title:
Some Transport Types
Description:
Facilitated diffusion (Down a chemical or electrical potential gradient) ... GluT1 (erythrocytes) Kt ~ 1.5 mM. GluT2 (liver and other) Kt ~ 66 mM ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:108
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Some Transport Types
1
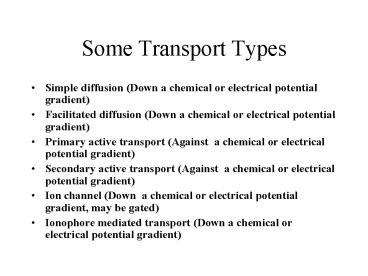
Some Transport Types
- Simple diffusion (Down a chemical or electrical
potential gradient) - Facilitated diffusion (Down a chemical or
electrical potential gradient) - Primary active transport (Against a chemical or
electrical potential gradient) - Secondary active transport (Against a chemical
or electrical potential gradient) - Ion channel (Down a chemical or electrical
potential gradient, may be gated) - Ionophore mediated transport (Down a chemical or
electrical potential gradient)
2
Classes of Transport
- Uniport
- Cotransport
- Symport
- Antiport
3
Fig 12-43
4
Aquaporin
- Six helices per chain
- Four chains form a pore
- Single file, 5? 108 molecules per second
- Cf. 4? 107 s-1 turnover number for catalase
- Water flows in the direction of the osmotic
gradient
5
Glucose Transporter
- 12 transmembrane helices per chain
- 5 chains form a pore
- GluT1 (erythrocytes) Kt 1.5 mM
- GluT2 (liver and other) Kt 66 mM
- GluT4 (myocytes and adipocytes) insulin
stimulates installation in membrane
6
Figure 12-27
7
Box 12-2 figure 1
8
Chloride-Bicarbonate Exchanger
- In respiring tissues
- CO2 in by simple diffusion, then HCO3- out, Cl-
in - In lungs
- HCO3- in, made into CO2, Cl- out
- Antiport
9
Fig 12-28
10
Active Transport
- The hydrolysis of ATP or other energy-releasing
reaction is required. - ATP H2O ? ADP Pi
- The energy is required to move against a chemical
(concentration) gradient or an electrical
(voltage) gradient (the latter usually means both)
11
Fig 12-30
12
ATPases
- P-type
- Cation transporters
- V-type
- Proton transporters (acidifiers)
- F-type
- Proton transporters in bacteria, mitochondria,
and chloroplasts (also ATP synthases) - Multidrug transporter (tumor cells)
13
NaK ATPase
- P-type
- 3 Na for every 2 K in
- Fig 12-33
14
Other P-type systems
- Plasma membrane Ca pump
- SERCA pump
- Cotransport systems
15
Fig 12-36
Cotransporter can pump to a 30,000 to 1 glucose
level!
16
Other Ion Channels
- Ligand and Voltage gated
- Na, K, and Ca
- On-off operations
- Neurons, etc.
17
Ionophores (Fig 12-37)