18'1 Galvanic series - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 22
Title:
18'1 Galvanic series
Description:
Electromotive force: DC voltage needed to halt the ionization of a metal in a standard electrolyte. 2 ... Electromotive force series. Reactive metals -0.13. Pb ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:486
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: 18'1 Galvanic series
1
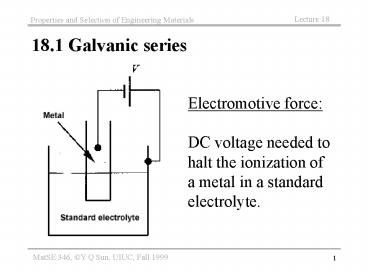
18.1 Galvanic series
Electromotive force DC voltage needed to halt
the ionization of a metal in a standard
electrolyte.
2
Electromotive force series
Reactive metals
3
Electromotive force series
Noble metals
4
18.2 Galvanic two-metal corrosion
Fe anode, corrodes
Cu cathode, Does not corrode
Introduction to Materials Science for Engineers,
J.F. Shackelford, Prentice-Hall, 1994.
5
Galvanic cell
- Fe dissolves in electrolyte because of Fes low
electrode potential (-0.44 V), leaving electrons
on the anode. - Cu deposits on the cathode because of Cus high
electrode potential (0.33 V), consuming electrons
that flow to the cathode. - Voltage driving dissolution of Fe 0.77 V.
6
Electro-chemical corrosion
- Involves two different metals.
- The two metals are in electrical contact
- The two metals are immersed in a electrolyte.
7
Example of Galvanic corrosion
8
Importance of relative areas
- Slow corrosion of plate
- Rapid corrosion of bolt
9
18.3 Galvanic series in sea water
Pt?Au ? Ti ? Ag ? Sn ? Pb ? High Ni cast iron ?
SS ? Cast iron ? PC steel ? 2024 Al ? Zn ? Mg
10
18.4 Microscopic Galvanic cell
- Two phase alloys (e.g. Cu-Zn).
- Microscopic chemical inhomogeneity.
- Grain boundaries.
11
18.5 Gaseous reduction corrosion
O2 depleted region anode
O2 rich region cathode
Introduction to Materials Science for Engineers,
J.F. Shackelford, Prentice-Hall, 1994.
12
O2 concentration cell
- Anode low oxygen. Fe dissolves as Fe, leaving
electrons on the anode. - Cathode high oxygen. Oxygen reacts with H2O to
form hydroxide ions OH-, consuming an electron - O2 2H2O 4e- ? 4OH-
- Electrons are pulled from O2-depleted region to
O2-rich region.
13
Examples of gaseous corrosion
14
Examples of gaseous corrosion
15
Examples of gaseous corrosion
16
Materials Selection Project
- Start Oct. 11
- White paper (5) due Oct. 18
- Report due Nov. 22
- One week delay for off-campus
- No Late submission.
17
White paper
- Less than one page single space
- Title
- Name and concentration.
- Engineering issue
- Importance of materials and selection
- Proposed activities.
18
Content of project
- Focus on selection and use of materials in one
engineering issue in your area of specialization. - In-depth examination of one material.
- Comparative study of competing materials.
19
Content of project
- Discussion of properties covered in this course
- i.e. mechanical, thermal, treatment, failure
(oxidation and corrosion, friction and wear,
fatigue, fracture) - Do not discuss properties not covered in this
course. - e.g. optical, biological, electrical, magnetic,
liquids, gases.
20
Misc on report
- Check course web for grading guide of report.
- Must be individual effort and shown to be so.
- No late submission
21
Possible selection topics
- Landing gear
- Fuel tanks
- Wings
- Turbine blades
- Helicopter rotor blades
- Shuttle exterior panel
- Brakes
22
Possible selection topics
- Body panel
- Engine block
- Engine valve
- Exhaust system
- Brakes
- Bearings
- Transmission shaft
- Steering wheel