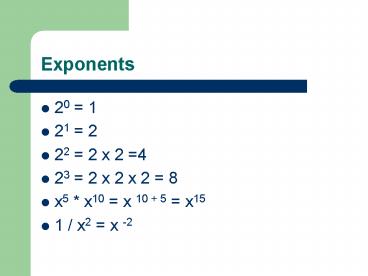Exponents - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 43
Title: Exponents
1
Exponents
- 20 1
- 21 2
- 22 2 x 2 4
- 23 2 x 2 x 2 8
- x5 x10 x 10 5 x15
- 1 / x2 x -2
2
Decimal Numbering systems
- Base 10
- Digits 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9
- Representation
- 5234
- Thousands Hundreds Tens Units
- 5 2 3 4
3
Decimal Numbering systems
- Example 523410
- 103 1000 102 100 101 10 100 1
- 5 2 3 4
- 5,234 5 x 1000 2 x 100 3 x 10 4 x 1
4
Binary Numbering systems
- Base 2
- Digits 0, 1
- binary number 1101012
- positional powers of 2 25 24 23 22
21 20 - decimal positional value 32 16 8 4 2
1 - binary number 1 1 0
1 0 1
5
Binary to Decimal Conversion
- To convert to base 10, add all the values where a
one digit occurs. - Ex 1101012
- positional powers of 2 25 24 23 22
21 20 - decimal positional value 32 16 8 4 2
1 - binary number 1 1 0
1 0 1 - 32 16 4 1 5310
6
Binary to Decimal Conversion
- Ex 1010112
- positional powers of 2 25 24 23 22
21 20 - decimal positional value
- binary number
7
Binary to Decimal Conversion
- Ex 1010112
- positional powers of 2 25 24 23 22
21 20 - decimal positional value 32 16 8 4 2
1 - binary number 1 0 1
0 1 1 - 32 8 2 1 4310
8
Decimal to Binary Conversion
- The Division Method. Divide by 2 until you reach
zero, and then collect the remainders in reverse. - Ex 1 5610 1110002
- 2 ) 56 Rem
- 2 ) 28 0
- 2 ) 14 0
- 2 ) 7 0
- 2 ) 3 1
- 2 ) 1 1
- 0 1
9
Decimal to Binary Conversion
- Ex 2 3510
- 2 ) Rem
- 2 )
- 2 )
- 2 )
- 2 )
- 2 )
- Answer 3510
2
10
Decimal to Binary Conversion
- The Subtraction Method
- Subtract out largest power of 2 possible (without
going below zero) each time until you reach 0.
Place a one in each position where you were able
to subtract the value, and a 0 in each position
that you could not subtract out the value without
going below zero.
11
Decimal to Binary Conversion
- Ex 1 5610
- 56 26 25 24 23 22 21 20
- - 32 64 32 16 8 4 2 1
- 24 1 1 1 0 0 0
- - 16
- 8
- - 8
- 0
- Answer 5610 1110002
12
Decimal to Binary Conversion
- Ex 2 3810
- 38 26 25 24 23 22 21 20
- Answer 3810 2
13
Character Representation ASCII Table
Rightmost Leftmost Three Bits Four
Bits 000 001 010 011 100 101 110 111 0000 NUL DLE
Space 0 _at_ P p 0001 SOH DC1 ! 1 A Q a q 0010 STX
DC2 " 2 B R b r 0011 ETX DC3 3 C S c s 0100 EOT
DC4 4 D T d t 0101 ENQ NAK 5 E U e u 0110 ACK
SYN 6 F V f v 0111 BEL ETB ' 7 G W g w 1000 BS C
AN ( 8 H X h x 1001 HT EM ) 9 I Y I y 1010 LF SUB
J Z j z 1011 VT ESC K k 1100 FF FS , lt
L \ l 1101 CR GS - M m
1110 SO RS . gt N n 1111 SI US / ? O _ o DEL
14
Character Representation
- Ex Find the binary ASCII and decimal ASCII
values for the character.
Rightmost Leftmost Three Bits Four
Bits 000 001 010 011 100 101 110 111 0000 NUL DLE
Space 0 _at_ P p 0001 SOH DC1 ! 1 A Q a q 0010 STX
DC2 " 2 B R b r 0011 ETX DC3 3 C S c s 0100 EOT
DC4 4 D T d t 0101 ENQ NAK 5 E U e u 0110 ACK
SYN 6 F V f v 0111 BEL ETB ' 7 G W g w 1000 BS C
AN ( 8 H X h x 1001 HT EM ) 9 I Y I y 1010 LF SUB
J Z j z 1011 VT ESC K k 1100 FF FS , lt
L \ l 1101 CR GS - M m
1110 SO RS . gt N n 1111 SI US / ? O _ o DEL
15
Character Representation ASCII Table
- From the chart
- 0100110 (binary ASCII value)
- Convert the binary value to decimal
- 01001102 32 4 2 3810
- Therefore
- 38 (decimal ASCII value)
16
Octal Numbering systems
- Base 8
- Digits 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7
- Octal number 12468
- powers of 84 83 82 81 80
- decimal value 4096 512 64 8 1
- Octal number 1 2 4 6
17
Octal to Decimal Conversion
- To convert to base 10, beginning with the
rightmost digit multiply each nth digit by
8(n-1), and add all of the results together. - Ex 12468
- positional powers of 8 83 82 81
80 - decimal positional value 512 64 8 1
- Octal number 1 2 4
6 - 512 128 32 6 67810
18
Octal to Decimal Conversion
- Ex 103528
- positional powers of 8 84 83 82
81 80 - decimal positional value
- Octal number
19
Decimal to Octal Conversion
- The Division Method. Divide by 8 until you reach
zero, and then collect the remainders in reverse. - Ex 1 433010 103528
- 8 ) 4330 Rem
- 8 ) 541 2
- 8 ) 67 5
- 8 ) 8 3
- 8 ) 1 0
- 0 1
20
Decimal to Octal Conversion
- Ex 2 81010
- 8 ) 810 Rem
- 8 )
- 8 )
- 8 )
- Answer 81010 8
21
Decimal to Octal Conversion
- The Subtraction Method
- Subtract out multiples of the largest power of 8
possible (without going below zero) each time
until you reach 0. Place the multiple value in
each position where you were able to subtract the
value, and a 0 in each position that you could
not subtract out the value without going below
zero.
22
Decimal to Octal Conversion
- Ex 1 201810
- 2018 84 83 82 81 80
- - 1536 4096 512 64 8 1
- 482 3 7 4 2
- - 448
- 34
- - 32
- 2
- - 2
- 0 Answer 201810 37428
23
Decimal to Octal Conversion
- Ex 2 76510
- 765 84 83 82 81
80 - Answer 76510 13758
24
Hexadecimal Numbering systems
- Base 16
- Digits 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7,8,9,A,B,C,D,E,F
- Hexadecimal number 1F416
- powers of 164 163 162 161
160 - decimal value 65536 4096 256 16 1
- Hexadecimal number 1 F 4
25
Hexadecimal Numbering systems
- Four-bit Group Decimal Digit Hexadecimal Digit
- 0000 0 0
- 0001 1 1
- 0010 2 2
- 0011 3 3
- 0100 4 4
- 0101 5 5
- 0110 6 6
- 0111 7 7
- 1000 8 8
- 1001 9 9
- 1010 10 A
- 1011 11 B
- 1100 12 C
- 1101 13 D
- 1110 14 E
- 1111 15 F
26
Hexa to Decimal Conversion
- To convert to base 10, beginning with the
rightmost digit multiply each nth digit by
16(n-1), and add all of the results together. - Ex 1F416
- positional powers of 16 163 162 161
160 - decimal positional value 4096 256 16
1 - Hexadecimal number 1
F 4 - 256 240 4 50010
27
Hexa to Decimal Conversion
- Ex 7E16
- positional powers of 16 163 162 161
160 - decimal positional value
- Hexa number
28
Decimal to Hexa Conversion
- The Division Method. Divide by 16 until you
reach zero, and then collect the remainders in
reverse. - Ex 1 12610 7E16
- 16) 126 Rem
- 16) 7 14E
- 0 7
29
Decimal to Hexa Conversion
- Ex 2 81010
- 16 ) 810 Rem
- 16 )
- 16 )
- Answer 81010 16
30
Decimal to Hexa Conversion
- The Subtraction Method
- Subtract out multiples of the largest power of 16
possible (without going below zero) each time
until you reach 0. Place the multiple value in
each position where you were able to subtract the
value, and a 0 in each position that you could
not subtract out the value without going below
zero.
31
Decimal to Hexa Conversion
- Ex 1 81010
- 810 163 162 161 160
- - 768 4096 256 16 1
- 42 3 2 A
- - 32
- 10
- - 10
- 0 Answer 81010 32A16
32
Decimal to Hexa Conversion
- Ex 2 15610
- 156 162 161 160
- Answer 15610 16
33
Binary to Octal Conversion
- Since the maximum value represented in 3 bit is
equal to - 23 1 7
- i.e. using 3 bits we can represent values from 0
7 - which are the digits of the Octal numbering
system. - Thus, three binary digits can be converted to one
octal digit and visa versa.
34
Binary to Octal Conversion
- Three-bit Group Decimal Digit Octal Digit
- 000 0 0
- 001 1 1
- 010 2 2
- 011 3 3
- 100 4 4
- 101 5 5
- 110 6 6
- 111 7 7
35
Octal to Binary Conversion
- Ex
- Convert 7428 2
- 2 010
- 4 100
- 7 111
- 7428 111 100 0102
36
Binary to Octal Conversion
- Ex
- Convert 101001102 8
- 110 6
- 100 4
- 010 2 ( pad empty digits with 0)
- 101001102 2468
37
Binary to Hexa Conversion
- Since the maximum value represented in 4 bit is
equal to - 24 1 15
- i.e. using 4 bits we can represent values from 0
15 - which are the digits of the Hexadecimal numbering
system. - Thus, Four binary digits can be converted to one
Hexadecimal digit.
38
Binary to Hexa conversion
- Four-bit Group Decimal Digit Hexadecimal Digit
- 0000 0 0
- 0001 1 1
- 0010 2 2
- 0011 3 3
- 0100 4 4
- 0101 5 5
- 0110 6 6
- 0111 7 7
- 1000 8 8
- 1001 9 9
- 1010 10 A
- 1011 11 B
- 1100 12 C
- 1101 13 D
- 1110 14 E
- 1111 15 F
39
Hexa to Binary Conversion
- Ex
- Convert 3D916 2
- 9 1001
- D 1101
- 3 0011
- 3D916 0011 1101 10012
40
Binary to Hexa Conversion
- Ex
- Convert 101001102 16
- 0110 6
- 1010 A
- 101001102 A616
41
Octal to Hexa Conversion
- To convert between Octal to Hexadecimal
numbering systems and visa versa convert from one
system to binary first then convert from binary
to the new numbering system
42
Hexa to Octal Conversion
- Ex
- Convert E8A16 8
- 1110 1000 10102
- 111 010 001 010 (group by 3 bits)
- 7 2 1 2
- E8A16 72128
43
Octal to Hexa Conversion
- Ex
- Convert 7528 16
- 111 101 0102 (group by 4 bits)
- 0001 1110 1010
- 1 E A
- 7528 1EA16