Typical Prokaryotic Cell - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 41
Title:
Typical Prokaryotic Cell
Description:
Movement across membrane for many substances is controlled ... Prevents osmotic lysis. In some cases recognized by host immune system. Target for antibiotics. ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:112
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Typical Prokaryotic Cell
1
Typical Prokaryotic Cell
2
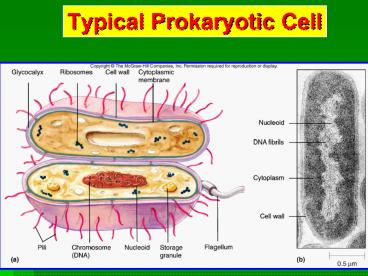
ProkaryoticCell Structures
3
Functions of Cell Membrane
- 1. Selective barrier (selectively permeable)
- 2. Secretes exoenzymes
- amylases
- lipases
- peptidases
4
Functions of Cell Membrane
- 3. E.T.S. is located here
- 4. Enzymes for cell wall synthesis
- 5. If photosynthesis, enzymes are located on
membranous structures called thylakoids - 6. Mesosomes - invagination of cell membrane
attached to DNA (Binary Fission)?
5
Cytoplasmic Membrane
- Movement across membrane for many substances is
controlled by membrane proteins. - Escherichia coli has gt200 membrane proteins.
- Many of these proteins are involved in transport
across membranes. - Others of these proteins allow a bacterium to
sense its surrounding environments (e.g., as in
chemotaxis). - Movement is via
- Simple Diffusion (including osmosis)
- Facilitated Diffusion (with concentration
gradient no energy expended) - Active Transport (against concentration gradient
energy expended)
6
Simple Diffusion - Osmosis
7
Cytoplasmic Membrane
8
Protein-Mediated Transport
9
Active Transport
10
The Prokaryotic Cell Wall
In some cases recognized by host immune system.
Determines cell shape.
Prevents osmotic lysis.
Target for antibiotics.
In Bacteria, composed of Peptidoglycan.
Part of cell envelope.
11
Cell Wall
- Main structural component - Peptidoglycan
- Peptidoglycan
- repeating dissacharide units
- polypeptides
12
Gram-Pos vs. Gram-Neg
13
Budowa mureiny
14
Budowa mureiny
15
Gram-Positive Cell Envelope
16
(No Transcript)
17
Gram-Negative Cell Envelope
endotoxin
cell wall
18
Gram-Negative Cell Envelope
LPS Protection from antibiotics such as
penicillin plus against certain toxins.
Periplasm Site of preliminary nutrient
degradation.
19
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)
Carbohydrate has negative charge and provides
protection against some antibiotics some toxins
(e.g., detergents).
Lipid A Endotoxin
20
(No Transcript)
21
Mycoplasma lack Cell Walls
Note Pleomorphic
Mycoplasma pneumoniae causes Walking Pneumonia
22
Prokaryotic Cell Structure
- Glycocalyx - term to describe substances that
surround bacterial cells - 1. Capsule
- if substance is organized and firmly attached to
cell wall - 2. Slime Layer
- if substance is unorganized and loosely attached
to cell wall
23
Function of Capsule
1. Contribute to Virulence of bacteria by
preventing phagocytosis by WBCs
A. Streptococcus pneumoniae
B. Bacillus anthracis
24
Functions of Capsules
- 2. Prevents drying out or dessication
- 3. Allows bacteria to adhere to various surfaces
- Streptococcus mutans - enamel on teeth to cause
dental carries - Klebseilla pneumoniae - attaches to respiratory
tract
25
Glycocalyx
Protection (e.g., Streptococcus pneumoniae from
phagocytosis)
Attachment (e.g., Streptococcus mutans causing
dental plaques)
26
Capsule Staining
Capsules are more regular and gelatinous.
Slime Layers are less regular and more diffuse.
27
Flagellar Arrangements
Polar Flagellum
e.g., E. coli
also atrichous
28
Chemotaxis
Also Phototaxis, etc.
29
Fimbriae (a kind of pilli)
Tips are Adhesins, used to adhere, e.g., to
animal tissues
30
Motility
- Almost all Spiral bacteria are motile
- About 1/2 of Bacilli are motile
- Almost all Cocci are non-motile
31
Axial Filament - found only in spirochetes
(flexible spirals)
Treponema pallidum
32
Fimbriae
- Filamentous appendages that are shorter,
straighter and more numerous that flagella - found mostly in Gram (-) Bacteria
- used for attachment not motility
33
E. coli (pathogenic)
34
Nuclear area (nucleoid)
- 1 circular chromosome (ccDNA)
- attached to a mesosome
- segragation of DNA during Binary Fission
35
Plasmids
- Small circular, extra-chromosomal pieces of DNA
- 5 to 100 genes
- Code for auxiliary metabolic functions
- antibiotic resistance
- penicillase
- production of toxins
- E. coli 0157H7
36
Ribosomes - protein synthesis
- Prokaryotic Ribosome
- 70 S
- 50 S
- 30 S
- Eukaryotic Ribosomes
- 80 S
- 60 S
- 40 S
37
Selective Toxicity
- Some antibiotics are aimed at the 70 S ribosomes
of bacterial cells - Streptomycin, Neomycin, Erythromycin and
Tetracycline work by inhibiting protein synthesis
by disrupting the 70 S ribosome
38
Endospores - formed under periods of
environmental stress
- Only found in Gram () Bacteria
- Bacillus
- Bacillus cereus
- Bacillus anthracis
- Clostridium
- Clostridium tetani
- Clostridium botulinum
- Clostridium perfringens
39
Endospores
- Extremely resistant to heat, cold, chemicals,
lack of water, etc. - Most vegetative bacterial cells are killed at
temps. above 70 C (160 F) - Endospores can survive boiling water for several
hours (some for as long as 20 hours)
40
Endospores
- Spores can remain viable for weeks, months, years
- Thermoactinomyces vulgaris
- spores found in Minnesota were 7,500 years old
and still germinated
41
Endospores
Form inside of vegetative cells (hence endo).
Characteristic of many soil bacteria, e.g.,
Bacillus spp. Clostridium spp.
Highly resistant to heat, U.V., desiccation, etc.