Introduction to Enterprise Architecture - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Introduction to Enterprise Architecture
Description:
Introduction to Enterprise models and Architecture – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:28
Title: Introduction to Enterprise Architecture
1
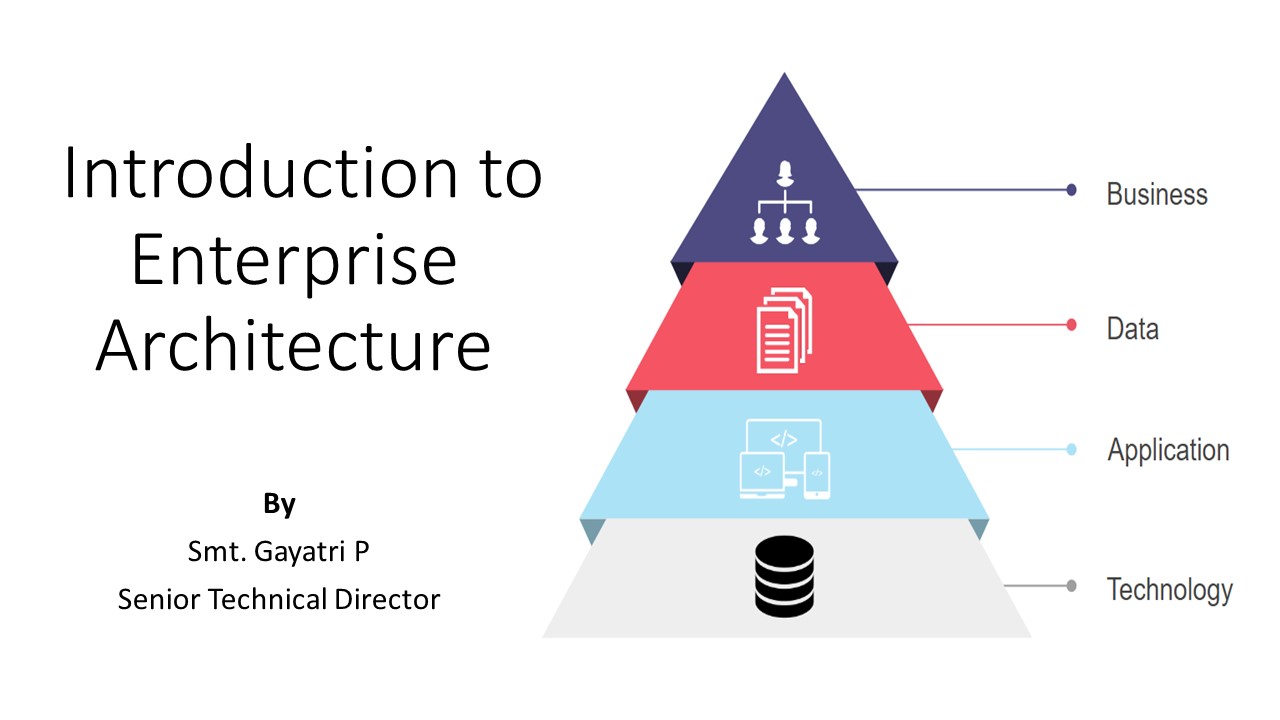
Introduction to Enterprise Architecture
By Smt. Gayatri P Senior Technical Director
2
Workshop scheduling
- Session 1 Introduction to Enterprise
Architecture - Session 2 Exploring various EA Frameworks
- Session 3 IndEA Framework
- Session 4 EA Case Study Land Hub Andhra
Pradesh - Session 4 EA Case Study University EA
Framework - Session 5 Interactive session involving question
and Answers about Enterprise Architecture and
associated
3
Agenda Session 1
- Understanding the nexus of Enterprise
Architecture - History Evolution of Enterprise Architecture
- Components of Enterprise Architecture
- Lifecycle of Enterprise Architecture
- Implementation of EA
- Enterprise Architecture Frameworks
- Zachman Framework
- ToGAF
- IndEA
4
Evolution of Government Observed
In the early days...
The next steps...
Running business needs applications to be
integrated
- Moving from departmental stovepipes to citizen
centric approach in service delivery - Transforming and integrating the back office
- Collaborative working and information sharing
- Product and service innovation
- Citizen engagement and inclusion
- Networked form of organization model adding to
the complexity - Enhancing the economic infrastructure and
government Performance
Automation of manual tasks e.g. Payroll,
In-House Development
Application packages (Siloed Apps) e.g. HR,
Financial administration
5
Evolution of Government Observed
In the early days...
Now ..
6
How are we going to survive this Jungle?
- Problems
- Business KPIs are not aligned with Business
Vision/ Mission - Organization structure, functions and technology
do not align to meet the business goals - Accurate or complete operational data is
unavailable when required - Applications implemented do not integrate /
communicate properly - Business processes are ad-hoc and manual and
managing them is time consuming - Technology investments are ad-hoc and not cost
effective. - Decision making takes longer time
- Data is scattered across departments and
information is redundant
- Incompatibilities
- Data between applications
- User interfaces
- Terminologies
- Workflows
- Hardware and software
- platforms
- Business and IT !
7
Enterprise Architecture
Transformation
Alignment
Coherence
Agility
Interoperability
Robustness
Scalability
Ability to migrate
8
Defining Enterprise
Enterprise is a collection of organizations that
has a common set of goals. An enterprise could be
a Government agency, a corporation a single
department or a chain of geographically distant
organizations linked by a common ownership. An
extended enterprise frequently includes partners,
suppliers, and customers. If the goal is to
integrate an extended enterprise, then the
enterprise comprises the partners, suppliers, and
customers, as well as internal business units. A
Government consists of multiple ministries,
departments and agencies. All government
organizations, are unified under the common goal
to achieve Digital India vision. Hence, a
Government may be considered as an Enterprise of
Enterprise.
Enterprises
Enterprise of Enterprises
Source TOGAF
9
Defining Enterprise
10
Defining Architecture
Architecture in context of Enterprise
Architecture is fundamental organization of
system, embodied in its components, their
relationship to each other and the environment
and the principles governing its design and
evolution - ISO/IEC 420102007, Systems and
Software Engineering Recommended Practice for
Architectural Description of Software-Intensive
Systems
11
Defining Enterprise Architecture
12
Definition Enterprise Architecture (EA)
- An enterprise architecture (EA) is a conceptual
blueprint that defines the structure and
operation of an organization. - The intent of an enterprise architecture is to
determine how an organization can most
effectively achieve its current and perceived
future objectives.
13
Architecture transformation
- Which routes to follow?
- How to organize oneself?
- How to communicate?
- What are the main risks and how can they be
reduced?
14
What is Enterprise Architecture ?
What is Not Enterprise Architecture?
What is Enterprise Architecture?
- A shared business and IT vision for the
organization along with performance benchmarks - An interoperable and cost effective framework
which could transcend, be referenced and used for
inter-organization discovery and digital
collaboration for effective service delivery to
stakeholders - It ensures economies of scale by reusing Business
and Application Services, by the use of
consistent vocabulary in Business, Data,
Application and Technology layers by specifying
the interoperability requirements in terms of
open standards and open data formats - It ensures Single Source of Truth thereby
avoiding multiple data entry, data duplicity etc
15
Agenda
- Understanding the nexus of Enterprise
Architecture - History Evolution of Enterprise Architecture
- Components of Enterprise Architecture
- Lifecycle of Enterprise Architecture
- Implementation of EA
- Enterprise Architecture Frameworks
- Zachman Framework
- ToGAF
- IndEA
16
Evolution of Enterprise Architecture
17
Evolution of Enterprise Architecture Genesis
Business Systems Planning methodology
18
Evolution of Enterprise Architecture PRISM EA
Framework
19
Zachman Framework
20
Evolution of Enterprise Architecture from 90s
Year 1987 1994 1995 1996 2002 2003 2006 2009 2017
Activity Zachmans Enterprise Architecture TAFIM released TOGAF 1.0 Enterprise Edition released Clinger Cohen Bill passed FEA replaces FEAF TOGAF 8.0 Enterprise Edition released FEA completed () TOGAF 9 released IndEA released
The development of the above frameworks has paved
the way for multiple Nations (Korea, Singapore,
UAE, UK and USA) and Industry (Microsoft and
Oracle) to develop their own tailored enterprise
architecture frameworks which are being consumed
by enterprises.
The Zachman Framework
The Open Group Architectural Framework
The Gartner Methodology
The Federal Enterprise Architecture
The Zachman Framework is an Enterprise Ontology
which provides a formal and structured way of
viewing and defining an enterprise.
The Open Group Architecture Framework (TOGAF) is
a framework for enterprise architecture which
provides an approach for designing, planning,
implementing, and governing an enterprise
information technology architecture
Gartner Methodology is based on the amalgamation
of Gartner framework and Meta architecture
development process.
A federal enterprise architecture (FEA) provides
a common approach for the integration of
strategic, business and technology management as
part of organization design and performance
improvement
Source TOGAF and A comparison of top four EA
methodologies, 2007 by Microsoft
21
Agenda
- Understanding the nexus of Enterprise
Architecture - History Evolution of Enterprise Architecture
- Components of Enterprise Architecture
- Lifecycle of Enterprise Architecture
- Implementation of EA
- Enterprise Architecture Frameworks
- Zachman Framework
- ToGAF
- IndEA
22
Components of Enterprise Architecture
23
Agenda
- Understanding the nexus of Enterprise
Architecture - History Evolution of Enterprise Architecture
- Components of Enterprise Architecture
- Lifecycle of Enterprise Architecture
- Implementation of EA
- Enterprise Architecture Frameworks
- Zachman Framework
- ToGAF
- IndEA
24
Life Cycle of Enterprise Architecture
25
Life Cycle of Enterprise Architecture
Illustration of a government project
26
Agenda
- Understanding the nexus of Enterprise
Architecture - History Evolution of Enterprise Architecture
- Components of Enterprise Architecture
- Lifecycle of Enterprise Architecture
- Implementation of EA
- Enterprise Architecture Frameworks
- Zachman Framework
- ToGAF
- IndEA
27
Ecosystem of Enterprise Architecture I
28
Ecosystem of Enterprise Architecture II
29
Enterprise Architecture helps to align the vision
of the project to the implementability
30
(No Transcript)
31
Business Layer Illustrative
32
EA implementation benefits
Impact Description
Clarity on long term goals EA focusses on enterprises developing strategic capabilities. It provides a long-term view of the organizations processes, systems and technologies. This roadmap and blueprint is enabled through strong Governance and Coordination teams which help the sub-enterprises to achieve the desired state.
Strategic, responsive and optimized IT investments EA enables IT investments to be optimized, strategic, responsive, promote alignment, standardization and re-use of IT assets. This in turn mandates that IT looks at future requirements and capabilities and is designed to maximize reuse and reduce duplication.
Agile EA is viewed as a key enabler by creating, communicating and improving the key requirements, principles and models that describe an enterprises future state and enable its evolution.
Source Enterprise Architecture by Open Group
and MIT white paper on Enterprise Architecture
Landscape in Singapore Government Agencies
published on February 2013
33
Increasing the need for Enterprise Architecture
and the roles and responsibilities of an
Enterprise Architect
34
Need for an Enterprise Architecture
35
Roles and Responsibilities of an EA
36
Roles and Responsibilities of an EA
37
Risks associated with Enterprise Architecture
38
Risks associated with Enterprise Architecture
- Inability to rapidly respond to new requirements
- Lack of focus on enterprise requirements
- Lack of common direction and synergies
- Incomplete visibility of the current and future
vision - Inability to predict impacts of future changes
- Increased gaps and architecture conflicts
- Lack of commonality and consistency
- Rigidity, redundancy and lack of scalability and
flexibility in the deployed solutions - Lack of integration, compatibility and
interoperability between applications - Piece-meal and ad hoc software development driven
by a tactical and reactive approach
39
Challenges to EA implementation
Component Description
Awareness and understanding of EA Multiple definitions and EA frameworks are currently existing with their own definitions and frameworks. EA has evolved from IT hence there is a confusion on whether EA is to solve IT specific technical problems which enterprises face.
Measuring tangible benefits out of EA US Government Accountability Office (US GAO) identifies EA benefits under lower costs, enhanced productivity, improved management, and greater interoperability. Benefits of EA implementation will cut across ministries and departments which leads to difficulty in establishing the overall benefits. EA implementation and maturity requires significant time to realize improvements in overall enterprise architecture.
Lack of EA sponsorship EA implementation requires support of the senior leadership of an enterprise. Typically this would involve direct reporting to CEO (for private entities) and Cabinet Division / Prime Minister / President (for nations). Without the support from senior leadership, the mandate for reforms and transformations through EA is not implementable.
Sustainability Standards and policies associated with EA are linked to the underlying technology and platforms. With technology refresh, it is important to establish a habit for continuous review and improvement of the existing EA practices without which the entire process would fail in three years.
40
Current Challenges in Enterprise Architecture
41
Agenda
- Understanding the nexus of Enterprise
Architecture - History Evolution of Enterprise Architecture
- Components of Enterprise Architecture
- Lifecycle of Enterprise Architecture
- Implementation of EA
- Enterprise Architecture Frameworks
- Zachman Framework
- ToGAF
- IndEA
42
Enterprise Architecture Frameworks
Gartner
IndEA
FEA
43
Countries who have adopted EA
Document Name Australian Government Architecture Reference Models NSW Government Enterprise Architecture Strategy Administration on the NetThe ABC guide of eGovernment in Austria FedICT e-gov Bhutan e-Government Master Plan Government of Canada Enterprise Architecture White Paper on Enterprise Architecture Working Group Standards and Architectures for eGovernment Applications Government Enterprise Architecture Oman eGovernment Architecture Framework (OeGAF) - A Quick Glance Andhra Pradesh State Enterprise Architecture (e-Pragati)
Sr. No. Parameters Australia New South Wales (Southeastern Australian state) Austria Belgium Bhutan Canada Denmark Germany New Zealand Oman India
1 Architecture Type Federated Federated Federated Federated NA Federated Federated NA Federated NA Federated
2 Methodology FEA TOGAF SOA Paradigm SOA Paradigm TOGAF TOGAF Zachman RM-ODP TOGAF TOGAF
3 Architecture Ref Models Vision/Mission Y Y Y NA Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
4 Architecture Ref Models Performance Ref Model Y N NA NA N NA NA NA Y N Y
5 Architecture Ref Models Business Ref Model Y Y NA NA Y Y NA Y Y Y Y
6 Architecture Ref Models Service Ref Model Y N NA NA N NA NA Y N N Y
7 Architecture Ref Models Data Ref Model Y Y NA NA Y Y NA Y Y Y Y
8 Architecture Ref Models Application Ref Model N Y NA NA Y Y NA Y Y Y Y
9 Architecture Ref Models Technology Ref Model Y Y NA NA Y Y NA Y Y Y Y
10 Architecture Ref Models Security Ref Model N N NA NA N NA NA Y Y N Y
11 Architecture Ref Models Governance Ref Model N Y NA NA Y Y NA NA NA NA Y
44
Popular EA Frameworks
45
EA Frameworks
- Focus areas of the four Enterprise Architecture
Frameworks - TOGAF Process Centric
- FEA Implementation Centric
- Zachman Taxonomy/Framework Centric
- Gartner Practice/outcome Centric
Each of the frameworks follow different
philosophies as presented in the above table. It
is up to the implementing agency to choose bits
and pieces from each of the methodologies, modify
and merge them as per their unique set of
requirements.
Source TOGAF and Gartner Report September 2014
46
Methods for implementing Enterprise Architecture
- In an EA project, Enterprise Architect must
select a framework and an implementation
methodology. There are multiple frameworks
available, it is important to select one and
model it to the organizations requirements
Covered in this session
47
Zachman Framework
48
Zachman Framework Overview
The Zachman Framework is a schema - the
intersection between two historical
classifications that have been in use for
literally thousands of years. The first is the
fundamentals of communication found in the
primitive interrogatives What, How, When, Who,
Where, and Why. It is the integration of answers
to these questions that enables the
comprehensive, composite description of complex
ideas. The second is derived from the
transformation of an abstract idea into an
instantiation that was initially postulated by
ancient Greek philosophers and is labeled in the
Zachman Framework Identification, Definition,
Representation, Specification, Configuration and
Instantiation
The Zachman Framework typically is depicted as a
bounded 6 x 6 matrix with the Communication
Interrogatives as Columns and the levels of
abstractions Transformations as Rows. The
Framework classifications are represented by the
Cells, that is, the intersection between the
Interrogatives and the Transformations. This
matrix would necessarily constitute the total set
of descriptive representations that are relevant
for describing something... anything in
particular an enterprise
Sourcehttps//www.zachman.com/about-the-zachman-f
ramework
49
View Points
50
The Zachman Framework Matrix
Planner's ViewContextual Owner?'s
ViewConceptual Designer?'s ViewLogical Build
er'?s Viewphysical Integrator's View User's
View.
Identification, Definition,
Representation, Specification,
Configuration Instantiation
Why
When
Who
What
Where
How
Sourcehttps//www.zachman.com/about-the-zachman-f
ramework
51
Zachman Framework Rules
Sourcehttps//www.zachman.com/about-the-zachman-f
ramework
52
The Zachman Framework
- The Zachman Framework is a metamodel and unlike
a methodology, does not imply anything about - Whether you do Architecture or whether you simply
build implementations that is, whether you build
Primitive Models, the ontological,
single-variable intersections between the
Interrogatives and the Transformations or whether
you simply build ad hoc, multi-variable,
composite models made up of components of several
Primitive Models - How you do Architecture top-down, bottom-up,
left to right, right to left, where to start,
etc., etc - The long-term/short-term trade-off relative to
instantiating the expression of the components of
the object that is, what is formalized in the
short-term for implementation purposes versus
what is engineered for long-term reuse - How much flexibility you want for producing
composite models (Enterprise implementations)
from your Enterprise Architecture (primitive
models), that is, how constrained (little
flexibility) or unconstrained (much flexibility)
you make the horizontal, integrative
relationships between the Cell components across
the Rows and the vertical, transformational
relationships of the Cell components down the
Columns. - Although these are significant, identifiable,
methodological choices, they are not
prescriptions of the Framework structure
Sourcehttps//www.zachman.com/about-the-zachman-f
ramework
53
TOGAF Framework
54
Overview
TOGAF- The Open Group Architecture Framework
- The Open Group Architecture Framework (TOGAF) is
a framework for enterprise architecture which
provides an approach for planning, designing,
implementing, and governing an enterprise
information technology architecture
Source TOGAF 9.1
55
9 Components
TOGAF- The Open Group Architecture Framework
56
Architecture Development Method (ADM)
TOGAF- The Open Group Architecture Framework
The TOGAF Architecture Development Method (ADM)
provides a tested and iterative process for
developing EA. It comprises instituting an
architectural framework, transitioning,
developing architecture contents, and governing
the comprehension of architectures.
57
TOGAF Architecture Domains
TOGAF-The Open Group Architecture Framework
Architecture Domains Description
Business Architecture Business Strategy, Governance, Organization and key Business Process
Data Architecture Structure of Organizations logical and physical data assets and data management resources
Application Architecture A blueprint of individual application systems to be deployed, their interactions, and their relationships to the core business processes of the organization
Technology Architecture Software and Hardware capabilities that are required to support the deployment of business, data and application services. This includes IT infrastructure, middle ware, networks, communications, processing and standards
Source TOGAF 9.1
58
4 Iteration cycles, based on a grouping of phases
TOGAF- The Open Group Architecture Framework
(Architecture Capability )
Architecture governance
(Architecture development)
(Transition planning)
59
Enterprise Continuum
TOGAF- The Open Group Architecture Framework
60
Architecture Content Framework
TOGAF- The Open Group Architecture Framework
61
Enterprise Repository
TOGAF- The Open Group Architecture Framework
Eight Reference Models of IndEA
62
ADM Guidelines and Techniques
TOGAF- The Open Group Architecture Framework
- Guidelines for Adapting the ADM Process
- Ways to apply iteration to the ADM,
- Applying the ADM at different levels of the
enterprise, - Security considerations for the different phases
and - Supporting SOA
- Techniques for Architecture Development
- Architecture Principles,
- Stakeholder Management,
- Architecture Patterns,
- Business Scenarios,
- Gap Analysis,
- Migration Planning Techniques
- Interoperability Requirements,
- Business Transformation Readiness Assessment,
- Risk Management,
- Capability-Based Planning
63
TOGAF Capability Framework
TOGAF-The Open Group Architecture Framework
Source TOGAF 9.1
64
TOGAF-The Open Group Architecture Framework
Source TOGAF
65
IndEA Framework
66
India Enterprise Architecture (IndEA)
- IndEA is a framework for developing a holistic
architecture treating the Government as a single
enterprise or more realistically, as an
Enterprise of Enterprises, which are functionally
inter-related - IndEA is a structured combination of several
Reference Models that, together, enable a
boundary-less flow of information across the
length and breadth of the government and
facilitate the delivery of integrated services to
the stakeholders - It is an authoritative reference providing an
integrated, consistent and cohesive view of
strategic goals, business services and enabling
technologies across the entire organization
67
IndEAWhole of Government WoG Level
68
IndEAAgency Level
69
IndEASolution Level
70
IndEA vis-à-vis State Enterprise Architecture in
the National Context
71
Comparison of a few EA frameworks
72
Comparison of the frameworks
Sr Criteria Description of Criteria Preferred Framework
1 Taxonomy Completeness How well you can use the methodology to classify the various architectural artifacts? Zachman
2 Process Completeness How fully the methodology guides you through a step-by-step process for creating an enterprise architecture? TOGAF
3 Reference-model Guidance How useful the methodology is in helping you build a relevant set of reference models.? FEA, TOGAF
4 Practice Guidance How much the methodology helps you assimilate the mind-set of enterprise architecture into your organization and develop a culture in which it is valued and used? Gartner
5 Maturity Model How much guidance the methodology gives you in assessing the effectiveness and maturity of different organizations within your enterprise in using enterprise architecture? FEA
6 Business Focus Whether the methodology will focus on using technology to drive business value, in which business value is specifically defined as either reduced expenses and/or increased income? Gartner
7 Governance Guidance How much help the methodology will be in understanding and creating an effective governance model for enterprise architecture? FEA, Gartner
8 Partitioning Guidance How well the methodology will guide you into effective autonomous partitions of the enterprise, which is an important approach to managing complexity? FEA
9 Prescriptive Catalog How well the methodology guides you in setting up a catalogue of architectural assets that can be reused in future activities? FEA
10 Vendor Neutrality How likely you are to get locked-in to a specific consulting organization by adopting this methodology? TOGAF
11 Information Availability Amount and quality of free or inexpensive information about this methodology. TOGAF
12 Time to Value Length of time you will likely be using this methodology before you start using it to build solutions that deliver high business value. Gartner
Source A comparison of top four EA
methodologies, 2007 by Microsoft
73
Comparison between EAIM
Concepts EA concepts are important for Enterprises 1.Alignment between Business and IT 2.Importance of Repository 3.Association Communication among artefacts 4. EAIM Strategy 5. Governance
Modeling EA concepts provide basis for EAIM. Modeling of different perspectives of enterprise are significant part of modelling 1.Easy to Use 2.Easy to learn 3.Traceability 4.Consistency 5.Different Views 6.Complexity
Process The activities and steps that guide Enterprise Architects in EA implementation 1.Requirement 2.Step by Step 3.Detailed Design 4.Implementation 5.Guidelines 6.Maintenance
Major Aspects of EAIM ( Enterprise Architecture
Implementation Methodologies )
74
Comparison between EAIM
Concept TOGAF DODAF Gartner FEA
Alignment between Business and IT M M M L
Association Communication among artefacts H M M M
Governance H M M L
Importance of Repository M M M M
EAIM Strategy H H M H
Modeling TOGAF DODAF Gartner FEA
Easy to Use L M M M
Easy to learn L M M M
Traceability H L L M
Consistency H L L M
Different Views M M L M
Complexity L L L L
Legend Legend
L low consideration or high level description
M Medium consideration or little description
H high consideration or detailed and clear description
75
Comparison between EAIM
Process TOGAF DODAF Gartner FEA
1.Requirement H L L L
2.Step by Step M M M M
3.Detailed Design M M M M
4.Implementation M M M M
5.Guidelines H M L H
6.Maintenance M L L M
Legend Legend
L low consideration or high level description
M Medium consideration or little description
H high consideration or detailed and clear description
76
Thank you