Ch' 2 Musculoskeletal System - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 22
Title:
Ch' 2 Musculoskeletal System
Description:
Axial bones = skull, pelvis. IE 552. 3. BONE STRUCTURE - 1. Cortical/compact. Cancellous/spongy. Marrow - blood. Trabeculae 3D lattice structure ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:50
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Ch' 2 Musculoskeletal System
1
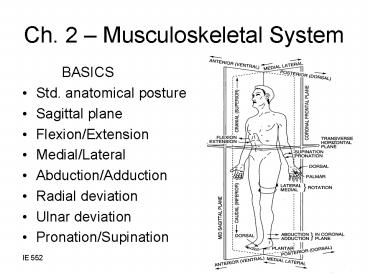
Ch. 2 Musculoskeletal System
- BASICS
- Std. anatomical posture
- Sagittal plane
- Flexion/Extension
- Medial/Lateral
- Abduction/Adduction
- Radial deviation
- Ulnar deviation
- Pronation/Supination
2
SKELETAL SYSTEM
- Rigid links for muscles
- Internal protection
- 200 bones
- Long bones limbs
- Axial bones skull, pelvis
3
BONE STRUCTURE - 1
- Cortical/compact
- Cancellous/spongy
- Marrow - blood
- Trabeculae 3D lattice structure
- Wolffs law form follows function
4
BONE STRUCTURE - 2
- Cells (2)
- Osteoblasts - form
- Osteocytes - reabsorb
- Extracellular matrix collagen fibers
- Ground substance hydroxy apatite (Ca)
- Lamellar structure
- Canal system
5
Ex. 2.1 Bending moments of hollow tubes (bones)
6
STRESS-STRAIN CURVES
7
COMPACT BONE STRENGTH
8
LOADING MODES
9
BONE PROPERTIES - 1
Running
10
BONE PROPERTIES - 2
Why?
11
BONE PROPERTIES - 3
- Daily loading
- Shear fractures
- Bending moments
- Dynamic effects
- Astronauts
- Traction
- Aging
12
SOFT CONNECTIVE TISSUE
- Tendons muscle to bone
- Ligaments bone to bone
- Fascia covers organs, skin
- Cartilage articular joints
13
FIBERS Collagen, Elastin, Reticulin
14
TYPES OF JOINTS
- Fibrous joints connect fixed bones, e.g. skull
- Cartilaginous joints found between
intervertebral discs - Articular joints at the articulating (moving)
end of bones
15
ARTICULAR JOINTS
- Synovial capsule surrounds joint
- Synovial fluid, µ0.002
- Meniscus distributes forces
- Poor blood supply
- Poor regeneration
16
ARTICULAR (HYALINE) CARTILAGE
- Cells Chondrocytes (2)
- Fibers Collagen (60)
- Ground substance Proteoglycan gel (40)
- Hyaluronic acid water
17
ARTICULAR CARTILAGE STRUCTURE 1
- Zonal pattern of cells and fibers parallel,
random, and perpendicular - Tidemark transition to bone, anchor
18
ARTICULAR CARTILAGE STRUCTURE 2
- Hydrophilic proteoglycan gel
- Movement of water absorb, squeeze out
19
ARTICULAR CARTILAGE MECHANICAL PROPERTIES
- Collagen solid elastic
- Proteoglycan liquid viscoelastic
20
JOINT LUBRICATION
- Hydrostatic loading forces out fluid
- Hydrodynamic motion causes a wedge effect
- Squeeze-film fluid forced out, moves from high
to low pressure
21
ARTICULAR CARTILAGE MECHANICAL PROPERTIES
- Wear
- Damage to collagen
- Disruption of proeteoglycan gel
- Impairment of interface
- Limited repair, minimal blood flow
- Osteoarthritis secondary inflammation
22
CARTILAGINOUS JOINTS
- Between intervertebral discs
- Cartilage end plate
- Annulus fibrosus (A) fibrous outer layer
- Nucleus pulposus (N) gel center
- Dynamic fluid exchange
- Drying, hardening
- Disc herniation