Gprotein coupled receptor - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 34
Title:
Gprotein coupled receptor
Description:
MAPs = Mt-Associated Proteins (not tubulin) that bind to MTs for their function. ... Mt polymerizing. toward kinetochore. (plasma membrane) ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:58
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Gprotein coupled receptor
1
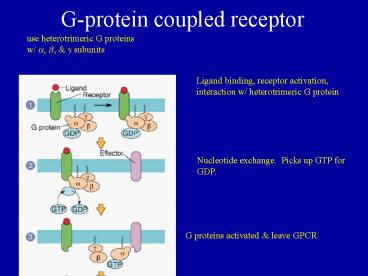
G-protein coupled receptor
use heterotrimeric G proteins w/ a, b, g
subunits
Ligand binding, receptor activation, interaction
w/ heterotrimeric G protein
Nucleotide exchange. Picks up GTP for GDP.
G proteins activated leave GPCR
2
activated subunit binds to effector
Effector (in this case) turns on and amplifies
signal
Hydrolyis of GTP inactivates G protein
G protein stops stimulating effector, waits for
next signal
3
Receptor tyrosine kinases dimerize when activated
function as kinases
4
Receptors activate a downstream series of events
5
Many of these cascades involve multiple steps
controlled by phosphorylation (by kinases)
dephosphorylation (by phosphatases)
6
(No Transcript)
7
Integrins and CAMs (cell adhesion molecules) link
the ECM (extracellular matrix) to the cytoplasm
8
Cadherins link cells to each other
9
Cells share gap junctions, tight junctions and
desmosomes
10
Cell-cell communications
- Gap junctions allow the movement of small
molecules between cells (cytoplasm to cytoplasm). - Tight junctions block diffusion from apical to
basolateral side of a tissue - Desmosomes connect cells in tissues to provide
strength
11
Cytoskeleton
Intermediate Filaments
Microtubules
Actin Filaments
eukaryotes, motility, support, organization
animals nuclei, support organization
12
Microtubules are polymers of a- b-tubulin
subunits
MAPs Mt-Associated Proteins (not tubulin) that
bind to MTs for their function.
13
Microtubules (MT) are organized from a MT
organizing center (MTOC)
MTOC
14
Interphase cell
MTOC w/ pair of centrioles
Mitotic cell
Spindle pole w/ pair of centrioles (an MTOC)
15
Centrioles are not found in plants or fungi
centriole
pericentriolar material
microtubule
16
Organelle transport uses motor proteins
RER to Golgi vesicle
Golgi to RER vesicle
Cytoplasm
-
Dynein
Kinesin
17
Cilia and flagella are made of microtubules use
dynein motors
18
Intermediate filaments are polymers of
filamentous proteins
Karp, 9.43
19
IFs give structural continuity to tissues.
20
Actin Filaments
Single actin monomer (white)
Single actin filament
Model of actin filament structure
TEM of actin filaments
Karp, 9.47
21
E.G. Myosin Cross-bridge Cycle
22
Actin filaments polymerize at the leading edge to
push the membrane forward in a crawling cell.
23
Withdraw from cell cycle ?
G0 (quiescent)
Three categories of cells in multicellular
animals 1. Highly specialized (differentiated)
cells that cannot divide. (i.e. nerve cells) 2.
Cells that do not normally divide, but can
divide if they need to. (i.e. liver cells) 3.
Cells that normally divide a lot. (i.e.
epithelial cells)
24
The division of cells occurs through mitosis and
cytokinesis.
- Mitosis is the division of the nucleus. We can
identify 5 phases of events in mitosis. - Prophase
- Prometaphase
- Metaphase
- Anaphase
- Telophase
- Cytokinesis is the division of the cytoplasm.
25
In prophase the interphase array of microtubules
is disassembled and reassembled into a spindle.
- Early in prophase duplicated centrosomes move
apart and become the spindle poles.
interphase
spindle pole
See Fig 14.16
prophase
26
In Prophase
- The chromosomes are condensed to make them easier
to move. - The nuclear envelope is broken up so its contents
can be redistributed to the 2 new cells. Some
cells like yeast keep their nuclear envelope
intact.
Fold chromosomes
(not to scale)
27
Structural components of a spindle
Polar mt
Spindle pole w/ 2 centrioles
Astral mt
-
-
kinetochore
Kinetochore mt
28
In prometaphase kinetochores of sister chromatids
must attach to microtubules from opposite poles.
Mt polymerizing toward kinetochore.
(plasma membrane)
- Prometaphase mts have high dynamic instability.
By randomly growing shrinking, mts from the
poles eventually contact and capture all
kinetochores.
29
Microtubules attach to chromatids at
kinetochores, which are complex protein structures
dynein
30
In metaphase, the chromosomes are aligned at the
equator.
- Kinetochores of sister chromatids are attached to
opposite poles via KMTs. - Metaphase/anaphase checkpoint prevents anaphase
until all chromosomes are aligned.
31
In anaphase
- Sister chromatids separate.
- ANAPHASE A Chromosomes move to opposite poles
on microtubules. - ANAPHASE B The spindle elongates.
32
Kinetochore MTs shorten at the kinetochore during
anaphase A
tubulin subunits released during depolymerization
33
In telophase
a. The chromosomes unwind (decondense)
c. Nuclear envelopes reform around the
chromosomes to make 2 new nuclei
34
In cytokinesis, a contractile ring of actin and
myosin constricts the plasma membrane.
A ring of actin/myosin directly below the plasma
membrane pulls in like a purse string.
Cell division completed (mitosis cytokinesis)