Results from Probe Synthesis - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 14
Title: Results from Probe Synthesis
1
Results from Probe Synthesis
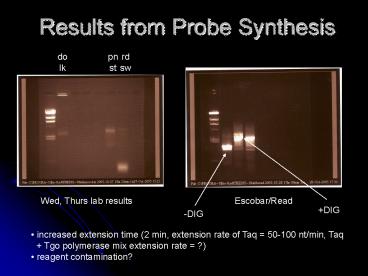
pn st
rd sw
do lk
Wed, Thurs lab results
Escobar/Read
DIG
-DIG
- increased extension time (2 min, extension rate
of Taq 50-100 nt/min, Taq - Tgo polymerase mix extension rate ?)
- reagent contamination?
2
Southern Analysis
- Hybridization, Washing, and Detection
3
Broad and Long Term Objective
To determine the copy number of Myb transcription
factor genes in the genome of the model plant
Arabidopsis thaliana
4
Research Plan
Isolate Genomic DNA
Digest Genomic DNA with Various Restriction
Enzymes
Agarose Gel Electrophoresis and Southern Transfer
Southern Blot
Make Non-Radioactive Myb Probe
Hyribidize Probe to Southern Blot
Washes and Colorimetric Detection
Data Analysis
5
Todays Laboratory Objectives
- To become familiar with a Southern Hybridization,
Washing and Detection Methods - a. Mechanics and trouble spots
- b. What variables can be manipulated to
enhance signal - Data Analysis and Interpretation
- Positive control- efficacy of probe and
hybridization conditions - Negative control- stringency of hybridization
- Experimental signal- identify restriction
fragments harboring myb genes
6
Theoretical Basis of SouthernHybridization and
Washing
Prehybridization prehybridization solution
contains a mix of proteins and nucleic acids that
will bind to the membrane, covering regions where
there is no fixed DNA (membrane blocking). This
prevents the single stranded probe from binding
nonspecifically to the membrane. Hybridization
Heat denatured probe is then added to the
prehybridization solution and incubated
overnight. On a fully blocked membrane, probe can
associate with the membrane only by hybridizing
with complementary ssDNA sequences fixed to the
membrane. Washing removes probe molecules that
are weakly associated with the surface of the
membrane or the genomic DNA.
7
Stringency of Hybridization
- The incubation conditions during the
hybridization and washing steps can be varied to
require greater or lesser complementarity between
probe and bound DNA (stringency) - Stringency is determined primarily by salt
concentration, temperature, and the
presence/absence of organic solvents (esp.
formamide) - Successful hybridization between probe and a
target DNA is determined by the Tm - Tm (ºC) 81.5 16.6 log10 (Na/1.0
0.7Na) 0.41(GC) 500/n 1( mismatch) - n length of duplex (bp)
- Applicable for sequences gt15 bp
8
DIG Detection Principle
- DIG labeled probes that hybridized to a target
sequence are detected with an anti-DIG antibody
that is covalently attached to a phosphatase
enzyme. - If the blot is incubated with suitable reagents
like NBT and BCIP, phosphatase activity is
detected by a color reaction.
9
Color Development
- Substrate BCIP and NBT form a redox system
- BCIP is oxidized by the alkaline phosphatase to
indigo by release of a phosphate group - NBT is reduced to diformazan
- Reaction products form a water insoluble dark
blue to brownish precipitate, depending on the
type of membrane.
10
Theoretical Basis of Colorimetric Detection
- Blocking performed with BSA to prevent
non-specific binding of antibody - Antibody Wash antibody binds to DIG portion of
DIG-dUTP incorporated during amplification of
Myb61 gene probe - Colorimetric Detection phosphatase enzyme
conjugated to anti-DIG antibody reacts with
substrate when phosphate is removed blue/purple
precipitate is formed
11
Flow Diagram of Colorimetric Detection with
NBT/BCIP
- Reaction Solution Time
- Washing 2X SSC, 0.1 SDS 2 x 5 min
- Washing 0.5X SSC, 0.1 SDS 2 x 15 min
- Rinse 0.1 M Tris (pH 7.5), 0.15 M NaCl 1 min
- Blocking 0.1 M Malate, 0.15 M NaCl,0.5 30 min
- Blocking Reagent
- Antibody Blocking Reagent, 150 mU/ml 30 min
- Anti-Dig Antibody
- Washing 0.1 M Malate, 0.15 M NaCl, 0.3 2 x 15
min - Tween 20
- Detection 0.1 M Tris, 0.1 M NaCl, 1/50 vol 1-12
hr - NBT/BCIP stock solution
12
Data Analysis
- What information do your positive and negative
controls provide? - How many hybridizing fragments for each
restriction enzyme- what does this indicate about
Myb gene copy number? - How homologous is Myb61 to other gene sequences?
(BLASTn) From your blot, does it appear that
these sequences hybridized with the Myb61 probe?
Evidence for a single copy gene
13
Troubleshooting
- Poor signal
- Probe specific activity too low
- Inadequate depurination
- Inadequate transfer buffer
- Not enough target DNA
- Transfer time too short
- Inefficient transfer system
- Probe concentration too low
- Incomplete denaturation of probe and/or target
DNA - Final wash too stringent
- Hybridization time too short
- Inappropriate membrane
14
Troubleshooting
- High Background
- Insufficient Blocking
- Membrane allowing to dry out during hybridization
or washing - Membranes adhered during hybridization or washing
- Bubbles in hybridization bag
- Walls of hybridization bag collapsed on to
membrane - Not enough wash solution
- Hybridization temperature too low
- Labeled probe molecules are too short
- Probe Concentration too high
- Inadequate prehybridization
- Probe not denatured
- Not enough SDS in wash solution








![Chemical synthesis through oxidation of graphite[9-9] PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/6520210.th0.jpg?_=201505010412)





















