The Atmosphere - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 17
Title: The Atmosphere
1
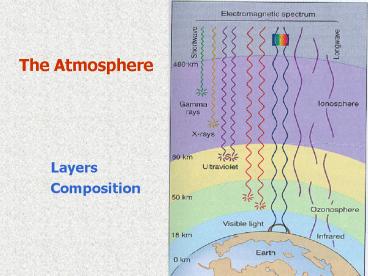
The Atmosphere
- Layers
- Composition
2
Composition of air - Whats in it?
- Stable Components
- N2 78
- O2 21
- CO2 lt 1
- 100
3
- Variable Components
- H2O Vapor highly variable (0 to 4)
- O3 - photochemical reactions
4
Layers of the Atmosphere
- Troposhpere
- Where we live
- Weather
- 90 of total mass of atmosphere
5
- Stratosphere
- Contains O3
- Absorbs ________??
6
- Mesosphere
- Coldest layer
- Meteor dust act as cloud nuclei
- Thermosphere
- Warmest layer
- Ionosphere
- Absorbs cosmic rays, gamma rays, x-rays,
shortest UV
7
(No Transcript)
8
(No Transcript)
9
Effect of Atmosphere on EMR
- All solar emr passes through space to reach top
of atmosphere, but not all reaches Earth's
surface. - Atmosphere scatters, absorbs and reflects a
portion of in-coming solar radiation. - Earth scatters, absorbs and reflects solar
radiation that gets transmitted through the
atmosphere. - Finally - atmosphere scatters, absorbs and
reflects the electromagnetic radiation that is
reflected off the Earth's surface back toward the
sensor.
10
- Atm. Gases
- Critical to earth's energy balance through
absorption and emission. - Determines solar radiation reaching surface
- "windows"
- atm. effects are minimal
- allows ground-based measurements of celestial
objects, and satellite-based measurements of
earth's surface/atm.
11
- Signal reaching the sensor may include reflection
off Earth's surface that contains information,
but it also includes in-coming and reflected EMR
that has been scattered by the atmosphere. - This can result in a loss of detail in the
resulting images, making interpretation more
difficult.
12
Challenges of Remote Sensing
- 4 of in-coming solar radiation is reflected back
from Earth's surface. - 5 re-radiated after absorption as thermal IR.
- These two components are the focus of most
terrestrial remote sensing.
13
Challenges of Remote Sensing
- Only selected wavelengths are able to penetrate
Earth's atmosphere and be reflected back to
sensor. - Thus, only some wavelengths are available for
analysis and some objects of interest may not
have unique spectral signatures within the set of
available wavelengths.
14
- Composition of atmosphere is important in
understanding the role it plays in remote sensing
and in interactions with electromagnetic
radiation. - largely a mixture of gases
- some with fairly constant concentrations
- others are variable in space and time.
- In addition - suspended particles (e.g. aerosol,
smoke, ash etc.) and hydrometeors (e.g. cloud
droplets, raindrops, snow, ice crystals, etc). - About 99 of the mass lies below an altitude of
30km.
15
Table 1 composition of atmosphere below 100km.
16
Main gases which absorb radiation.ultraviolet
(UV), visible, infrared (IR) and microwave
wavelengths.main spectral regions ("windows")
for which atmospheric absorption is small, are
listed at the bottom of the table.
17
(No Transcript)