Geography and Demographics - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Geography and Demographics
Description:
6 republics: Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia-Herzegovinia, Serbia, ... and Croatia ... Not so Croatia. Serbia, plus Yugoslav National Army (JNA), fight ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:250
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Geography and Demographics
1
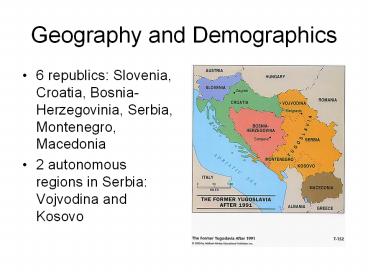
Geography and Demographics
- 6 republics Slovenia, Croatia,
Bosnia-Herzegovinia, Serbia, Montenegro,
Macedonia - 2 autonomous regions in Serbia Vojvodina and
Kosovo
2
Geography and Demographics
- Many ethnic groups Serbs, Croats, Slovenes, etc.
- Serbs largest in country, but not majority
- Complications boundaries of ethnic groups not
the same as boundaries of republics!
3
Geography and Demographics
4
Geography and Demographics
5
Ancient History
- Prior to WWI Area dominated by Austro-Hungarian
(in NW) and Ottoman (in SE) Empires. - No history of fighting, groups not enemies.
6
First Yugoslav State
- Formed at the end of WWI.
- Marriage of convenience, entered into willingly
by all parties.
7
First Yugoslav State
- BIG challenges
- Economic
- Political what would this new state look like?
- Serbs wanted strong, centralized state to
protect Serb minority populations in other
regions. - Others wanted decentralized state to protect
against Serb domination.
8
First Yugoslav State
- Solution a strong, centralized state
- Serb preferences won out (this time).
- Other groups not happy, but try to work together
to iron out problems.
9
WWII
- Hitler invades Yugoslavia in 1941
- Installs puppet regimes in Serbia and Croatia.
- Croat state (Ustasha) cleanse Croatia of Serbs.
- Serb paramilitaries (Chetniks) organize and fight
Ustasha. - Horrific fighting, bitter memories. Irony
Ustasha not popularly chosen.
10
WWII
- Tito and the Partisans
- Communists.
- Integrating force.
- Fought with Allies
- Fought civil war against Ustasha and Chetniks
- Won, took power at close of WWII
11
Titos Yugoslavia
- Inherited a tough situation
- Economic devastation
- Bitter memories of civil war
- Demographic snake pit what to do about Serbia?
12
Titos Yugoslavia
- Use the CP as an integrating force.
- Promote ideology of growth and development.
- Stomp out nationalism.
- Rely on personal popularity and charisma.
13
Titos Yugoslavia
- Give republics autonomy over own affairs, veto
power over central decisions. - Make Vojvodina and Kosovo autonomous regions,
give them veto power also. - Consociationalism keep the power of the largest
group (Serbs) in check.
14
Titos Yugoslavia
- Happy Days
- Country experienced economic growth into the
1970s. - Peace!
- But costs of stifling alternative political
voices, vacuum when Tito died.
15
(No Transcript)
16
Post-Tito
- 1980s Economic slowdown
- CP bureaucrats paralyzed by crisis
- What was good for one region was bad for another.
- Regions used veto in Federal Presidency to block
any policy that hurt them. - Stalemate!
17
Post Tito
- Political crisis also
- Serbian leaders unhappy about status of Kosovo
and Vojvodina. - Tried to address problem legally, but were
blocked by veto power of other republics. - Deadlock!
18
Moves by Serbia
- Serb politicians look for way around the
deadlock appeal to Serb grievances in Kosovo. - Serbs a minority in Kosovo (largely for economic
reasons). - Kosovo historical significance to Serbs.
- Politicians Serbs are being run out of their
homeland! (exaggerated claim, but effective).
19
Moves by Serbia
- Enter Slobodan Milosevic
- 1988 President of Serbia, Ivan Stambolic, sends
Milosevic to Kosovo to hear out the complaints of
the Kosovo Serbs - Was supposed to stick to CP anti-nationalist line.
20
Moves by Serbia
- Instead, took the side of the nationalists.
- Famous words, addressing crowd
- You will not be beaten again.
21
Moves by Serbia
- Rallies for Truth
- Orchestrated by politicians
- Demanded end of autonomy of Vijvodina and Kosovo
- Dramatized situation of Serbs in Kosovo
- Non-Serb leaders continue to refuse to negotiate
with Milosevic.
22
Moves by Serbia
- Milosevic topples leaders in Vojvodina, Kosovo,
and Montenegro, installs men loyal to him. - Radical effect on balance of power in Yugoslavia
Milosevic now controls 4 out of 8 votes in the
Federal Presidency.
23
Response of Slovenia and Croatia
- Leaders of Slovenia and Croatia very nervous, set
about trying to weaken the federal authority of
Yugoslav state. - Slovenia
- Backed Albanian resistance in Kosovo
- Refused to allow rally for truth
- Pulled out of Yugoslav CP
24
Response of Slovenia and Croatia
- Croatia
- At first try to broker compromise, preserve
Yugoslavia - Strategy changed abruptly with election of Franjo
Tudjman in May 1990.
25
Response of Slovenia and Croatia
- Tudjman and cronies provocative nationalists.
- Checkerboard flag.
- Serbs secondary minority status.
- Talked big about taking Croatia out of
Yugoslavia.
26
Escalation
- Serb minority in Croatia scared. Fears played
up by Serb politicians. - Summer 1990 Serbs in Krajina (area of Croatia)
armed themselves and declared self-rule. - Tudjman formed own paramilitaries
27
Escalation
- June 1991 Slovenia and Croatia declare
independence. - Serbia lets Slovenia go without fight.
28
Escalation
- Not so Croatia. Serbia, plus Yugoslav National
Army (JNA), fight to keep it in. - Large-scale war erupts in Croatia. Fighting
spread from there to Bosnia.
29
Implications for Ethnicity Theories
- Contrary to expectations of Primordialism, war in
Yugoslavia not the result of ancient hatreds.
Peace, not conflict, was norm. - And yet, the population responded quickly and
emotionally to the provocations of politicians.
Ethnicity was a hot button. Hard for
instrumentalism to explain why.
30
Implications for Conflict Theories
- Yes, grievances existed. However, they were
nothing new. Why did they suddenly flower into
conflict? Societal explanations important, but
insufficient.
31
Implications for Conflict Theories
- Politicians played a critical role whipped up
emotions, initiated conflict. - At national level, change in political leadership
important Tito suppressed nationalism, his
successors encouraged it.
32
Implications for Conflict Theories
- But also key the weakness of the Yugoslav state
after Tito. - Communist Party unable to cope with challenges.
- Veto power of republics gt deadlock.
- State unable to contain nationalist politicians,
gave them critical window of opportunity.