The Future of Electronic Commerce - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 18
Title:
The Future of Electronic Commerce
Description:
Notational money: ledger entries in Demand Deposit Accounts ... Example: NetBill, CompuServe, AOL, MSN. xx. The NetBill Concept ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:53
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: The Future of Electronic Commerce
1
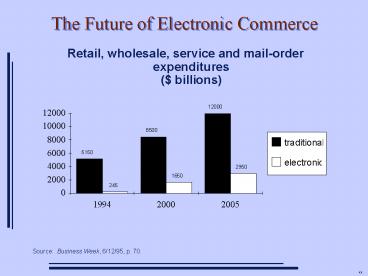
The Future of Electronic Commerce
- Retail, wholesale, service and mail-order
expenditures( billions)
Source Business Week, 6/12/95, p. 70.
2
Electronic Commerce
- Many phases to a commercial transaction
- learning about what goods are available
- finding potential suppliers
- negotiating price
- ordering goods
- goods delivery
- payment
- after sales support
3
The Internet and Information Markets
- The global reach of the Internet makes it the
leading network for disseminating information - There are many ways to organize a market for
information - The lack of payment mechanisms to date has
limited the variety of market structures
4
Payment Systems
- There are two kinds of money
- Token money tokens which represent value
- tokens can be exchanged for goods
- Notational money ledger entries in Demand
Deposit Accounts - money is transferred between accounts upon
instruction - e.g. by a check
- clearing required if accounts are at different
institutions - accounts may have negative balances
- e.g. credit card accounts
5
Payment Systems
- Payment System tradeoffs
- time
- setup cost
- transaction cost
- risk
6
Financial Transaction System-Cost Structure
7
Internet-Based Payment Models
- Secure transmission of credit card information
- Digital cash
- Digital checks
- Centralized online transactions
8
Credit Card Info Sent Direct to Merchant
(Netscape Model)
Merchant
Private Line
Credit Card Acquirer
Encrypted tunnel through the Internet
- Consumer sends card direct to merchant
- Similar to todays phone order
- Must trust merchant with card info
- High transaction costs
Internet
Consumer
9
Third Party Intermediary Model(CyberCash)
- Protects consumers card info
- Use Internet for reaching Cybercash gateway to
acquirers - Adds to credit card card cost
Merchant
Encrypted tunnel through the Internet
Internet
CyberCash
Consumer
10
Credit Card Acquirer On the Net (STTSEPPSET)
- Protects consumers card info
- Use Internet for reaching acquirer
- Still uses expensive credit card transactions
Merchant
Encrypted tunnel through the Internet
Internet
Consumer
11
Green Commerce Model(First Virtual)
- Messages sent in clear
- Credit card number stored at FV
- User must agree to pay after receiving
information goods - Credit Card transaction costs
Merchant
First Virtual
Internet
Consumer
12
Digicash Model
- 1- Consumer asks Bank for Digicash
- 2- Bank sends Digicash bits to consumer
- 3- Consumer sends Digicash to merchant in payment
- 4- Merchant checks that Digicash has not been
double spent - 5- Bank verifies that Digicash is valid
- Advantages
- Privacy, Scalability
- Disadvantages
- Complexity
- Detecting double spending
- Robustness against failure
- Accountability
Merchant
5
4
3
Bank
2
1
Consumer
13
Approach Digital Checks
- Consumers issue signed drafts on online bank
accounts - Merchants may do online or delayed clearing
- Examples NetCheque, FSTC NetAccount
14
Approach Online Transactions
- Funds transfer between accounts at a central
server - All accounts at the central server
- Prepaid or postpaid consumer accounts
- Advantages
- Low transaction overhead cost
- Disadvantages
- Scalability server may become a bottleneck
- Requires arrangement with accounting server
- Example NetBill, CompuServe, AOL, MSN
15
The NetBill Concept
- An electronic accounting server to enable network
based commerce - Accounts maintained at NetBill for rapid,
inexpensive payment clearing (1 transaction cost
for a 10 item)
Network
Service
Provider
End
User
NetBill
Server
Bank
16
Aggregation
- Users and Merchants create NetBill aggregation
accounts. - Each purchase transaction moves funds from the
users NetBill account to the merchants NetBill
account - Money transferred into or out of the aggregation
account using conventional money transfers - credit card charge
- ACH
- Fixed cost of conventional transfers amortized
over many microtransactions - Aggregation account can be run as a prepaid or as
a credit account - Prepaid conventional debit in advance of
micro-transaction - Credit charge user after aggregated
transactions reach a threshold
17
Issues of Trust in Electronic Commerce
- What does a merchant need to know about a
customer? - name? demographics?
- that the merchant will be (has been) paid?
- Who to trust
- financial intermediaries
- public key certificate authorities
- credential authorities
- The theory of reliable transactions has been
based on premise that errors are accidental not
deliberate. - New mechanisms needed to protect against errors
deliberately introduced with intent to defraud.
18
Summary
- The Internet is becoming the Global Information
Infrastructure - All phases of commerce can be supported by
networks - Organization of electronic information markets is
currently limited by lack of Internet payment
systems - Numerous payment models are being developed
- For information goods, delivery and payment
should be linked as a single atomic transaction
at low cost.