DSS PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 35
Title: DSS
1
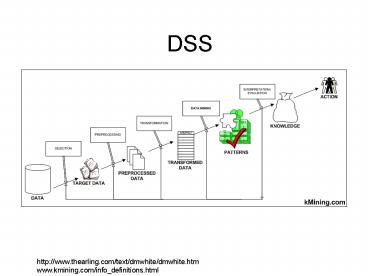
DSS
http//www.thearling.com/text/dmwhite/dmwhite.htm
www.kmining.com/info_definitions.html
2
Data Mining
- Data mining, the extraction of hidden predictive
information from large databases - Data mining tools predict future trends and
behaviors, allowing businesses to make proactive,
knowledge-driven decisions - Data mining tools can answer business questions
that traditionally were too time consuming to
resolve - They scour databases for hidden patterns, finding
predictive information that experts may miss
because it lies outside their expectations
3
Data Mining
- Forecasting sales
- Targeting mailings toward specific customers
- Determining which products are likely to be sold
together - Finding sequences in the order that customers add
products to a shopping cart
4
www.microsoft.com/.../tr/data-mining-addins.aspx
5
In the evolution from business data to business
information (each new step has built upon the
previous one)
Steps in the Evolution of Data Mining
6
- Data mining derives its name from the
similarities between searching for valuable
business information in a large database for
example, finding linked products in gigabytes of
store scanner data and mining a mountain for a
vein of valuable ore. Both processes require
either sifting through an immense amount of
material, or intelligently probing it to find
exactly where the value resides.
7
Data mining technology can generate new business
opportunities by providing these capabilities
- Automated prediction of trends and behaviors. A
typical example of a predictive problem is
targeted marketing. Data mining uses data on past
promotional mailings to identify the targets most
likely to maximize return on investment in future
mailings. Other predictive problems include
forecasting bankruptcy and other forms of
default, and identifying segments of a population
likely to respond similarly to given events. - Automated discovery of previously unknown
patterns. An example of pattern discovery is the
analysis of retail sales data to identify
seemingly unrelated products that are often
purchased together. Other pattern discovery
problems include detecting fraudulent credit card
transactions and identifying anomalous data that
could represent data entry keying errors.
8
How Data Mining Works
- How exactly is data mining able to tell you
important things that you didn't know or what is
going to happen next? The technique that is used
to perform these feats in data mining is called
modeling. Modeling is simply the act of building
a model in one situation where you know the
answer and then applying it to another situation
that you don't. For instance, if you were looking
for a sunken Spanish galleon on the high seas the
first thing you might do is to research the times
when Spanish treasure had been found by others in
the past. You might note that these ships often
tend to be found off the coast of Bermuda and
that there are certain characteristics to the
ocean currents, and certain routes that have
likely been taken by the ships captains in that
era. You note these similarities and build a
model that includes the characteristics that are
common to the locations of these sunken
treasures. With these models in hand you sail off
looking for treasure where your model indicates
it most likely might be given a similar situation
in the past. Hopefully, if you've got a good
model, you find your treasure.
9
- For example, say that you are the director of
marketing for a telecommunications company and
you'd like to acquire some new long distance
phone customers. You could just randomly go out
and mail coupons to the general population - just
as you could randomly sail the seas looking for
sunken treasure. In neither case would you
achieve the results you desired and of course you
have the opportunity to do much better than
random - you could use your business experience
stored in your database to build a model. As the
marketing director you have access to a lot of
information about all of your customers their
age, sex, credit history and long distance
calling usage. The good news is that you also
have a lot of information about your prospective
customers their age, sex, credit history etc.
Your problem is that you don't know the long
distance calling usage of these prospects (since
they are most likely now customers of your
competition). You'd like to concentrate on those
prospects who have large amounts of long distance
usage. You can accomplish this by building a
model.
10
- To best apply these data mining techniques, they
must be fully integrated with a data warehouse as
well as flexible interactive business analysis
tools. Many data mining tools currently operate
outside of the warehouse, requiring extra steps
for extracting, importing, and analyzing the
data. Furthermore, when new insights require
operational implementation, integration with the
warehouse simplifies the application of results
from data mining. The resulting analytic data
warehouse can be applied to improve business
processes throughout the organization, in areas
such as promotional campaign management, fraud
detection, new product rollout, and so on
11
illustrates an architecture for advanced analysis
in a large data warehouse
12
Some successful application areas include
- A pharmaceutical company can analyze its recent
sales force activity and their results to improve
targeting of high-value physicians and determine
which marketing activities will have the greatest
impact in the next few months. The data needs to
include competitor market activity as well as
information about the local health care systems.
The results can be distributed to the sales force
via a wide-area network that enables the
representatives to review the recommendations
from the perspective of the key attributes in the
decision process. The ongoing, dynamic analysis
of the data warehouse allows best practices from
throughout the organization to be applied in
specific sales situations.
13
- A credit card company can leverage its vast
warehouse of customer transaction data to
identify customers most likely to be interested
in a new credit product. Using a small test
mailing, the attributes of customers with an
affinity for the product can be identified.
Recent projects have indicated more than a
20-fold decrease in costs for targeted mailing
campaigns over conventional approaches.
14
- A diversified transportation company with a large
direct sales force can apply data mining to
identify the best prospects for its services.
Using data mining to analyze its own customer
experience, this company can build a unique
segmentation identifying the attributes of
high-value prospects. Applying this segmentation
to a general business database such as those
provided by Dun Bradstreet can yield a
prioritized list of prospects by region.
15
- A large consumer package goods company can apply
data mining to improve its sales process to
retailers. Data from consumer panels, shipments,
and competitor activity can be applied to
understand the reasons for brand and store
switching. Through this analysis, the
manufacturer can select promotional strategies
that best reach their target customer segments.
Each of these examples have a clear common
ground. They leverage the knowledge about
customers implicit in a data warehouse to reduce
costs and improve the value of customer
relationships. These organizations can now focus
their efforts on the most important (profitable)
customers and prospects, and design targeted
marketing strategies to best reach them.
16
OLAP
- On-line analytical processing. Refers to
array-oriented database applications that allow
users to view, navigate through, manipulate, and
analyze multidimensional databases.
17
http//www.filebuzz.com/software_screenshot/full/6
1412-RadarCube_OLAP_ASP_NET_Direct.jpg
18
http//farm3.static.flickr.com/2154/2497588470_07f
9d36ca6.jpg
19
OLAP
- Until the mid-nineties, performing OLAP analysis
was an extremely costly process mainly restricted
to larger organizations (the major OLAP vendor
are Hyperion, Cognos, Business Objects,
MicroStrategy). This has changed as the major
database vendor have started to incorporate OLAP
modules within their database offering -
Microsoft SQL Server 2000 with Analysis Services,
Oracle with Express and Darwin, and IBM with DB2.
Cont...
http//www.dwreview.com/OLAP/Introduction_OLAP.htm
l
20
OLAP
- OLAPs are designed to give an overview analysis
of what happened. Hence the data storage (i.e.
data modeling) has to be set up differently. The
most common method is called the star design. - The central table in an OLAP start data model is
called the fact table. The surrounding tables are
called the dimensions. Using the above data
model, it is possible to build reports that
answer questions such as - The supervisor that gave the most discounts.
- The quantity shipped on a particular date, month,
year or quarter. - In which zip code did product A sell the most.
- To obtain answers, such as the ones above, from a
data model OLAP cubes are created (or
multi-dimensional expressions).
21
OLAP Example
http//www.rittmanmead.com/2005/04/positioning-ora
clebi-discoverer-for-olap-2/
22
OLAP Example
http//www.rittmanmead.com/2005/04/positioning-ora
clebi-discoverer-for-olap-2/
23
OLAP Example
http//www.cimconcepts.com/svcs_rpt.shtml
24
Data Mining vs OLAP
- Both data mining and OLAP are two of the common
Business Intelligence (BI) technologies. Business
intelligence refers to computer-based methods for
identifying and extracting useful information
from business data. - Data mining deals with extracting interesting
patterns from large sets of data. It combines
many methods from artificial intelligence,
statistics and database management. - OLAP is a compilation of ways to query
multi-dimensional databases.
Cont...
http//www.differencebetween.com/difference-betwee
n-data-mining-and-vs-olap/ixzz1JjXKPFqe
25
- Data mining usually deals with following four
tasks clustering, classification, regression,
and association. Clustering is identifying
similar groups from unstructured data.
Classification is learning rules that can be
applied to new data and will typically include
following steps preprocessing of data, designing
modeling, learning/feature selection and
evaluation/validation. Regression is finding
functions with minimal error to model data. And
association is looking for relationships between
variables. Data mining is usually used to answer
questions like what are the main products that
might help to obtain high profit next year in
Wal-Mart. - Typically OLAP is used for marketing, budgeting,
forecasting and similar applications. a matrix is
used to display the output of an OLAP. The rows
and columns are formed by the dimensions of the
query. They often use methods of aggregation on
multiple tables to obtain summaries. For example,
it can be used to find out about the sales of
this year in Wal-Mart compared to last year? What
is the prediction on the sales in the next
quarter? What can be said about the trend by
looking at the percentage change?
Cont...
26
- Although it is obvious that Data mining and OLAP
are similar because they operate on data to gain
intelligence, the main difference comes from how
they operate on data. OLAP tools provides
multidimensional data analysis and they provide
summaries of the data but contrastingly, data
mining focuses on ratios, patterns and influences
in the set of data. That is an OLAP deal with
aggregation, which boils down to the operation of
data via addition but data mining corresponds
to division. Other notable difference is that
while data mining tools model data and return
actionable rules, OLAP will conduct comparison
and contrast techniques along business dimension
in real time.
27
GIS
http//www.boluarastirma.gov.tr/index.php?sayfaic
erikid44main_menu37
28
GIS
- A geographic information system (GIS) allows us
to view, understand, question, interpret, and
visualize data in many ways that reveal
relationships, patterns, and trends in the form
of maps, globes, reports, and charts.
http//gis.com/
29
What Can You Do with GIS?
- 1. Map Where Things Are
- Mapping where things are lets you find places
that have the features you're looking for, and to
see where to take action. Finding
patternsLooking at the distribution of features
on the map instead of just an individual feature,
you can see patterns emerge.
Cont...
30
What Can You Do with GIS?
- 2. Map Quantities
- People map quantities, like where the most and
least are, to find places that meet their
criteria and take action, or to see the
relationships between places. For example, a
catalog company selling children's clothes would
want to find ZIP Codes not only around their
store, but those ZIP Codes with many young
families with relatively high income. Or, public
health officials might not only want to map
physicians, but also map the numbers of
physicians per 1,000 people in each census tract
to see which areas are adequately served, and
which are not.
Cont...
31
What Can You Do with GIS?
- 3. Map Densities
- While you can see concentrations by simply
mapping the locations of features, in areas with
many features it may be difficult to see which
areas have a higher concentration than others. A
density map lets you measure the number of
features using a uniform areal unit, such as
acres or square miles, so you can clearly see the
distribution. Mapping density is especially
useful when mapping areas, such as census tracts
or counties, which vary greatly in size. On maps
showing the number of people per census tract,
the larger tracts might have more people than
smaller ones. But some smaller tracts might have
more people per square milea higher density.
Cont...
32
What Can You Do with GIS?
- 4. Find What's Inside
- Use GIS to monitor what's happening and to take
specific action by mapping what's inside a
specific area. For example, a district attorney
would monitor drug-related arrests to find out if
an arrest is within 1,000 feet of a school--if
so, stiffer penalties apply.
Cont...
33
What Can You Do with GIS?
- 5. Find What's Nearby (Map Change)
- Map the change in an area to anticipate future
conditions, decide on a course of action, or to
evaluate the results of an action or policy. - By mapping where and how things move over a
period of time, you can gain insight into how
they behave. For example, a meteorologist might
study the paths of hurricanes to predict where
and when they might occur in the future. - Map change to anticipate future needs. For
example, a police chief might study how crime
patterns change from month to month to help
decide where officers should be assigned. - Map conditions before and after an action or
event to see the impact. A retail analyst might
map the change in store sales before and after a
regional ad campaign to see where the ads were
most effective.
Cont...
34
GIS example
http//demo.dtsagile.com/wildfire/
35
GIS example
http//www.esri.com/industries.html