Introduction to Neuroanatomy - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Introduction to Neuroanatomy
Description:
Introduction to Neuroanatomy Structure-function relationships Localization of function in the CNS Non-invasive brain imaging CAT: structure, low resolution – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:1648
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Introduction to Neuroanatomy
1
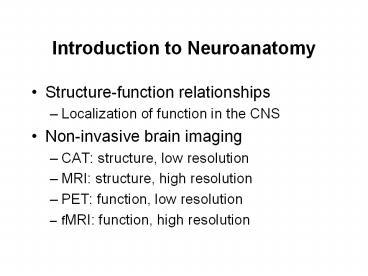
Introduction to Neuroanatomy
- Structure-function relationships
- Localization of function in the CNS
- Non-invasive brain imaging
- CAT structure, low resolution
- MRI structure, high resolution
- PET function, low resolution
- fMRI function, high resolution
2
Dual approach to learning neuroanatomy
- Functional anatomy
- Neural structures that serve particular
functions e.g., pain path from skin to cortex
for perception - Regional anatomy
- Localization of structures in particular brain
regions
3
Lecture objectives
- Overview of brain structures to demystify
anatomical content in Neural Science lectures - Survey brain structure-function relations to
provide background for first labs
First half of lecture
- Quick review of basic CNS organization
- Use development to understand principles of
structural organization of CNS
Second half Functional localization
4
Introduction to Neuroanatomy IRegional Anatomy
5
CNS Organizational Principles
- 1) Tubular organization of central nervous system
- 2) Columnar/longitudinal organization of spinal
and cranial nerve nuclei - 3) Complex C-shaped organization of cerebral
cortex and deep structures
6
Brief Overview of Mature CNS Neuroanatomy
- Tubular organization of central nervous system
- Columnar/longitudinal organization of spinal and
cranial nerve nuclei
7
SC
Dorsal surface
Dorsalroot
Ventralroot
Gray matter White matter
Spinal nerve
Ventral surface
NTA 1-4
8
Brief Overview of Mature CNS Neuroanatomy
- 1) Tubular organization of central nervous system
- 2) Columnar/longitudinal organization of spinal
and cranial nerve nuclei
- 3) Complex C-shaped organization of cerebral
cortex and nuclei and structures located beneath
cortex - Lateral ventricle
- Basal ganglia
- Hippocampal formation Fornix
9
Neural Induction
- Portion of the dorsal ectoderm becomes
committed to become the nervous system - Neural plate
10
Ectoderm
Neuralplate
Neuralgroove
Neuraltube
NTA 3-1
11
NT development
Brain vesicles
Rostral
Forebrain
Midbrain
Neural Tube Development
Hindbrain
Rostral neural tube forms the brain Caudal
neural tube forms the spinal cord
Spinal cord
Caudal
Cephalicflexure
NTA 3-2
12
3 5 ves stages
3-vesicle stage
5-vesicle stage
Cerebralhemisphere
Lateralventricle
Forebrain
Midbrain
Diencephalon
Midbrain
3rdventricle
Hindbrain
Pons Cerebellum
Cerebral aqueduct
Medulla
4thventricle
Spinal cord
Centralcanal
Cephalicflexure
by the 5 vesicle stage, all 7 major brain
divisions are present
NTA 3-2
13
MidsagBrain
The cephalic flexure persists into maturity
14
axes
NTA 1-13
15
Spinal cord brain stem have a similar
developmental plan
- Segmentation
- Nuclear organization columnar
16
SC dev
Dorsal horn
Alar plate
Sulcuslimitans
Central canal
Basal plate
Ventral horn
Dorsal horn
Central canal
Ventral horn
NTA 3-7
17
Dorsal horn
Dorsalroot
Ventralroot
Ventral horn
18
Similarities between SC and brain stem
development
Sulcus limitans separates sensory and motor
nuclei Nuclei have columnar shape
- Key differences
- 1) central canal enlargement motor medial and
sensory lateral - 2) migration away from ventricle
- 3) gtgt sensory and motor
19
BS dev
Alar plate andmigrating neuroblasts
Basal plate
NTA 3-8
20
Medulla development
4th Vent
Alar plate
Basal plate
Sulcus limitans
Inferior olivarynucleus
NTA 3-9
21
Pons development
4th Vent
Striated/branchio.
Alar plate
Striated/somite
Vestibular/auditory.
Somatic sensory.
Taste/viscerosensory
Autonomic.
Basal plate
Pontine nuclei
Sulcus limitans
Alar plate
Basal plate
NTA 3-10
22
Midbrain development
Cerebral aq.
Alar plate
Somatic sensory.
Autonomic.
Striated/somite
Red nucleus
Basal plate
Sub. nigra
Sulcus limitans
More like spinal Cord b/c fewer nuclear
classesand cerebral aqueduct
Basal plate
NTA 3-11
23
Similarities between forebrain and
hindbrain/spinal development
Tubular
- Key differences
- 1) CH more complex than BS/SC
- 2) Cortical gyri more complex anatomy than nuclei
- 3) Subcortical nuclei are C-shaped
- Confusing structure in two places on image
24
Diencephalon
- Thalamus
- Gateway to cortex
- Hypothalamus
- Control of endocrine and bodily functions
- Circadian rhythms
- Etc.
25
CH dev
NTA 3-14
26
Cerebral Cortex Development
27
Forebrain Development C-shaped Structures
- Cerebral cortex (NTA 3-15)
- Lateral ventricles (NTA 3-16)
- Striatum (NTA 3-16)
- Hippocampal formation and fornix (NTA 3-17)
28
Summary
- 7 Major components of the central nervous system
Ventricles - All present from 1st prenatal month
- Longitudinal organization of SC and BS nuclei
- Columns
- Anatomical and functional divisions
- C-shape organization of cerebral hemisphere
structures and diencephalic - Cerebral cortex
- Lateral ventricle
- Striatum
- Hippocampal formation and fornix

















![Introduction to Biopsychology [PSB 4002] PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/6377876.th0.jpg?_=20150404023)












