Double recombination Yeast integration in Pichia pastoris - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 24
Title:
Double recombination Yeast integration in Pichia pastoris
Description:
CHO Chinese hamster ovary. Cos Monkey cells with makingSV40 replication proteins ... His6-X HA-Y ; Bind to nickel ion column, elute, Western with HA Ab ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:1165
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Double recombination Yeast integration in Pichia pastoris
1
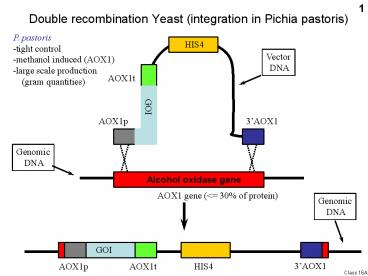
Double recombination Yeast (integration in Pichia
pastoris)
P. pastoris-tight control-methanol induced
(AOX1)-large scale production (gram
quantities)
Alcohol oxidase gene
2
Half-genes
Linearized viral genome
Restriction site
Gene of interest
Strong polyhedron promoter
(Fall army worm)
Baculovirus as a vector
in insect cells
3
Linearized viral genome
Constitutive early to late promoter
Strong polyhedron promoter
Gene of interest
Re-built ORF1629, required for viral growth
Re-built functional lacZ (blue)
Gene of interest
4
Baculovirus cont.
Enterokinase
5
Clone gene of interest behind the strong
polyhedron protein promoter.
Co-transfect Sf9 cells with linearized
baculovirus genome
Recombinant virus produced but at low titer.
Harvest recombinant virus and re-grow to high
titer.
Infect at high multiplicity and harvest protein
after transient infection. Yield can be 30 of
total protein synthesis
6
Baculovirus - Selection Plus
7
In vitro translation following in vitro
transcription
Transcription via the T7 promoter T7 pol
Add energy source, tRNAs, amino acids, label
(35S-met), May need to add RNase to remove
endogenous mRNA
VECTOR
cDNA
T7 RNA polymerase binding site (17-21 nt)
ACCATGG..
8
Expression in mammalian cells HEK293 Human
embyonic kidney HeLa Human cervical
carcinoma\ CHO Chinese hamster
ovary Cos Monkey cells with makingSV40
replication proteins BHK Baby hamster
kidey HepG2 Human hepatoma 3T3 Mouse or human
exhibiting regulated (normal-like)
growth GH3 Rat pituitary cells PC12 Mouse
neuronal-like tumor cells MCF7 Human breast
cancer various others, many differentiated to
different degrees AND Primary cells cultured
with a limited lifetime. E.g., MEF mouse
embryonic fibroblasts HDF Human diploid
fibroblasts
9
Expression in mammalian cells HEK293, HeLa, CHO,
cos, popular mammalian cell promoters
- SV40 LargeT Ag (Simian Virus 40)
- RSV LTR (Rous sarcoma virus)
- MMTV (steroid inducible) (Mouse mammary tumor
virus) - HSV TK (low expression) (Herpes simplex virus)
- Metallothionein (metal inducible, Cd)
- CMV early (Cytomegalovirus)
- Inducible / repressible tet, ecdysone,
glucocorticoid (tet tetracycline)
10
Tetracycine-responsive promoter (engineered)
VP16 transcriptional activator domain
Keep tet (dox) in to keep the gene off
(tet off)
tTA, tet trans activator protein
TetR tet repressor protein gene
VP VP16, a transcriptional activator domain
Remove tet (dox) to turn on the gene
Gene of interest
Repressor element
Dox doxicycline (like tetracycline but more
effective)
U. Arizona
11
system
(tet on)
Gene of interest
Note that in both systems, what was originally
the tet repressor element is functioning here as
the target for an inducer of transcription
U. Arizona
12
In vitro site-specific mutagenesis
(of coli DNA polymerase)
M13 strand
M13 single stranded bacteriophage
50 WT
50 mutant
13
Get rid of WT genome
Enzyme that removes U from U-containing DNA
Dut deoxyuracil phophotransferase. Dut- cells
accumulate dUTP, ? DNA Ung uracil
Nglycosylase. Ung- mutants do
not excise uracil from DNA Growth of plasmid
template plasmid on dut- ung- E. coli double
mutant cells ? U in DNA Synthesize mutant DNA
using T. Transfect heteroduplex into dutung E.
coli. U gets removed from WT template strand,
leaving apyrimidinic sites, these cannot
replicate. Mutant synthetic strand survives
normally.
Mutant E. coli allows U to persist in DNA
DpnI sites
Apyrimidinic DNA formed and will not replicate
14
Use of DpnI to get rid of WT template.
Template WT methylated DpnI sites
DpnI
Synthesis
Newly synthesized mutant strand its DpnI sites
are not methyated,.
DpnI treatment selectively destroys the
hemimethylated WT strand
Mutant strand greatly enriched.
15
RS1
RS2
PCR ? fragment ? subsequent cloning in a plasmid
Cut with RE 1 and 2
Ligate into similarly cut vector
16
PCR-ligation-PCR mutagenesis
Site to mutate
Note you can easily create an internal deletion
this way.
Ali SA, Steinkasserer A., Biotechniques. 1995
May18(5)746-50.
17
Random mutagenesis but in a limited
region Cassette mutagenesis by error-prone PCR
Original sequence coding for, e.g., an enhancer
--------------------------------------------------
-------------------------------------------------
-------------------
PCR fragment with high Taqpolymerase and Mn
instead of Mg
-------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------
-----------------
Cut in primer sites and clone upstream of a
reporter.
Pick colonies Analyze phenotypes Sequence
18
Cassette mutagenesis by doped synthesis Target
e.g., an enhancer element
--------------------------------------------------
-------------------------------------------------
-------------------
Original enhancer sequence
---------------------------------------------
-------- ----------------------------------
-----------------
Buy 2 doped oligos anneal
Clone upstream of a reporter.
Doping e.g., 85 G, 5 A, 5 C, 5
T at each position
Pick colonies Analyze phenotypes Sequence
19
Measuring protein-protein interactions in
vitro Xone protein Y another protein
Binding between (almost) purified
proteins- His6-X HA-Y Bind to nickel ion
column, elute, Western with HA Ab GST-X HA-Y
Bind to glutathione ion column, elute, Western
with HA Ab His6-X 35S-Y (made in vitro)
Bind Ni column, elute, gel autoradiography.
(HA flu hemagglutinin)
BIAcore (or several other measurements)
20
The binding events are monitored in real-time and
it is not necessary to label the interacting
biomolecules.
http//home.hccnet.nl/ja.marquart/BasicSPR/BasicSp
r01.htm
21
Reflectance is lessened at a critical angle due
to interaction of photons with delocalized
electrons in the thin gold layer. The angle at
which this occurs is dependent on the refractive
index difference at the opposite side of the gold
layer. The RI difference is dependent on the
surface properties at this opposite surface.
SURFACE PLASMON RESONANCE
1- Glass 2- Gold 3- Polymer Circle- Protein Y-
Binding protein
R photodiode
22
Surface plasmon resonance Detects binding of
protein or nucleic acids to molecules immobilized
on the opposite surface. Suitable for protein
protein interaction, measure kinetics, binding
constants. Use small amount (ug) and even ligands
in crude extracts Popular instrument Biacore
23
Protein-protein interactions in
cells Co-immunoprecipitation (co-IP) from
extracts 2-hybrid formation FRET (Fluorescence
resonance energy transfer) Complementation
readout
24
Co-immunoprecipitation Most times not true
precipitation, which requires about equivalent
concentrations. of antigen and antibody Use
protein A immobilized on beads (e.g.,
agarose) Protein A from Staphylococcus aureus
binds tightly to Immunoglobulin G (IgG) from many
species.
incubate
anti-X IgG
Cell extract
Protein A
Wash by centrifugation Elute with SDS Detect X, Y
by Western blotting