Problem Solving - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 32
Title:
Problem Solving
Description:
Web Hosting Issues. Bandwidth. Capabilities and specifications. Firewall ... Hosting the site. Obtaining a domain name. Graphics design and web site design ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:126
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Problem Solving
1
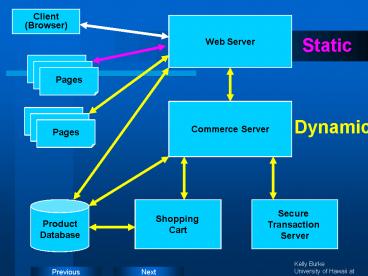
Client (Browser)
Web Server
Static
Commerce Server
Pages
Dynamic
Pages
Pages
Product Database
Shopping Cart
Secure Transaction Server
2
Client / Server Architecture
Three Tiered Client / Server
Client
Server (Business Logic)
Database
3
Active Server Pages Architecture
Input Form Passes Parameters
Client HTML Request
ASP Page VB Script SQL Query
Client HTML / ASP Dynamic Results
Access Database
4
How the Web WorksProtocols and Ports
- Clients / servers establish virtual connections
(conversations) via ports
5
How the Web WorksProtocols and Infrastructure
- Messages versus Packets
- i.e., connection vs connectionless
Message (example Page)
Packet 3
Packet 2
Packet 1
Packet
Packet
Packet
6
How the Web WorksProtocols and Infrastructure
- Server starts up an HTTP daemon
- HTTP daemon listens
- Forks a copy of itself to initiate a session
- can pre-fork
- Deamon continues to listen
- Copy services request
- reads request (request phase)
- serves response (response phase)
7
How the Web WorksProtocols and Infrastructure
- Request phase - client sends
- request method
- path (URL) of document (resource) requested
- version of HTTP being used
- header information (e.g., accept-file type, etc.)
- command
- GET (parameters passed in URL)
- http//www.company.com/orderform.asp?id2202namek
elly - HEAD (return header information of document)
- POST (treat as script and send data to it)
- PUT (replace contents of document with data)
- DELETE
8
How the Web WorksProtocols and Infrastructure
- Response phase - server sends
- protocol version
- status code
- 200 - 299 - success
- 300 - 399 - document moved
- 400 - 499 - client error
- 500 - up - internal sever error
9
How the Web WorksProtocols and Infrastructure
- Response phase - server sends
- response header (all optional except content
type) - server info
- location (of redirected messages)
- content length
- content type (e.g., text/html, text/plain,
image/jpeg, etc.) - content encoding (e.g., x-gzip, x-compress, etc.)
- transfer encoding (e.g., 7 bit, 8 bit, binary,
etc.) - the data
10
How the Web WorksProtocols and Infrastructure
- MIME (multi purpose mail extension)
- Browser needs to know what file type is in order
to know whether to - format and display (text/richtext)
- render as graphic (image/gif)
- pass to helper application to play through
speakers (audio/x-wav) - Accomplished via content type header info
11
How the Web WorksProtocols and Infrastructure
- HTTP/1.0 - stateless
- separate IP connection set-up and take-down for
each file / resource request - HTTP/1.1 - persistent
- pipelining HTTP requests
- keeping TCP connection open for multiple requests
- HTTP/NG
- asynchronous requests - multiplexed into same
connection - client doesnt need to wait for response before
sending out another request
12
Infrastructure Requirements
- Internet service
- Site content
- Site Design
- Site / Commerce functionality
- Database
13
Web Hosting Issues
- Bandwidth
- Capabilities and specifications
- Firewall system
- Wireless delivery
- Buy, rent, or lease
- Maintenance, upgrade, and service of the equipment
14
Developing e-Commerce Infrastructure
- Hosting the site
- Obtaining a domain name
- Graphics design and web site design
- Web site programming
- Secure transactions and purchasing
15
Hosting
- Where will the site be hosted?
- Your premises
- Leased space at an ISP
- Rack mounted server at a professional hosting
company - Managed host at a hosting co.
- Custom outsourced site
- Template outsourced site (e.g. Yahoo
storefront)
16
Hosting Doing it Yourself
- Buy servers and network equipment and lease
bandwidth (pipes) from Telco - Advantages
- Complete control over all aspects of site,
including security, functionality, integration
with existing business systems - Cost savings once level of online commerce
reaches a certain threshold - Disadvantages
- IT costs to manage equipment, systems
- Initial capital investment
- Physical infrastructure impact
17
Hosting Lease Space at an ISP
- Rent space for your equipment to be hosted at an
ISP - Pay bulk bandwidth charges to ISP
- Advantages
- Complete control over site
- Smaller start up expenses
- Disadvantages
- Must manage your own systems, usually remotely
- Cost of purchasing equipment
- Harder to integrate with existing business systems
18
HostingLease Equipment at Hosting Vendor
- Rent equipment at a professional hosting company
- Pay bulk bandwidth charges (sometimes rolled into
hosting package) - Advantages
- Aging equipment is not your problem
- Smaller start up costs
- Disadvantages
- Must manage your own system
19
Hosting Managed Host at Hosting Vendor
- Rent use of a system at a hosting vendor
- System is managed for you
- Can mix and match services (web, email, ordering,
etc.) - You are responsible for site content
- Advantages
- System is managed for you
- You maintain control over site design,
functionality - Disadvantages
- Ongoing expenses
20
Hosting Custom Outsourced Site
- Outsource the development of the web site
- May be a different entity than hosting co. (e.g.
consultant) - Advantages
- Custom designed site
- No web development or system management required
on your part - Disadvantages
- Less control over costs
21
Hosting Template Outsourced Site
- Use pre-designed templates for building site
from dot-coms catering to small business owners - Advantages
- Very low cost (some free!)
- Disadvantages
- Cookie-cutter feel to sites
- Little control over site or design
- Customer service?
22
Web Programming Implementing the Software
Infrastructure
- Most e-Commerce sites are not a static collection
of web pages, but dynamic interactive systems - Need to develop the software infrastructure that
drives the site databases, business rules,
secure ordering, web user interfaces, etc. - Q Do you need to interface your site to your
existing IT infrastructure? Database?
23
Web Programming Implementing the Software
Infrastructure
- There are turnkey solutions for implementing
some of this software infrastructure - Unless you have a simple business, these probably
wont be satisfactory - Reality check custom software development takes
time and money - Programmers are not artists, and vice versa!
Dont hire programmers to write web pages and
dont hire webmasters to write sophisticated
software. - Dont hire either one to design your corporate
image!
24
Web Programming Implementing the Software
Infrastructure
- Electronic storefront must contain
- A merchant system or storefront that provides the
merchants catalog with products, prices and
promotions - A transaction system for processing orders and
payments and other aspects of the transaction - A payment gateway that routes payments through
existing financial systems primarily for the
purpose of credit card authorization and
settlement
25
Web Programming Implementing the Software
Infrastructure
- Purchase a suite of software that claims to
integrate storefront functions into a single box - iCat Corp.s Electronic Commerce Suite and
Commerce Publisher - MIVAs Merchant 4
- http//www.miva.com
- Microsoft Corp.s Site Server Commerce Edition
- IBM Corp.s Net. Commerce Pro
- Saqqara Systems StepSearch Professional
26
Web Programming Implementing the Software
Infrastructure
- Electronic Commerce Suites
- Offer merchants greater flexibility,
specialization, customization and integration in
supporting complete front and back-office
functionality
Catalog Database
Catalog Application
Customer Management, Registration, Profiles,
Service
Customer Database
Order Database
Order Capture, Completion
Fulfillment Systems
Web Browser
Web Server
Payment Processing (SET Purchase Order)
Payment Database
Financial Network
Open Market e-Commerce Server Architecture
27
Web Programming Implementing the Software
Infrastructure
- Making a Web catalog into a multimedia
extravaganza - Not easy and expensive
- Lower end systems begin at 25,000
- High end systems 250,000 to 2 million
28
Secure Transactions and Ordering
- Payment handling one of the easiest things to
outsource - To handle it on your own web server, you need to
obtain a certificate from a Certificate Authority
(CA) - Certificates allow authenticated, encrypted,
trusted connections - Certificates expire and must be renewed for an
annual fee - You probably should be concerned about secure
transactions even if payment handling is
outsourced
29
Review ofe-Commerce Infrastructure
- Hosting the site
- Obtaining a domain name
- Graphics design and web site design
- Web site programming
- Secure transactions and purchasing
30
Review ofe-Commerce Infrastructure
- Putting together a successful e-Commerce web site
requires different skills from different people - Graphics designer
- Webmaster
- Programmer(s)
- Other business entities marketing, etc.
- Few people have all these effective skills
31
Review ofe-Commerce Infrastructure
- The good newsthere are many choices for hosting
and outsourcing the infrastructure development - Your choices will depend on
- How central is the e-Commerce aspect of your
business to the core focus of your business? - What is your current investment in IT and
existing infrastructure? - What are your available resources for capital
investment? - What are your e-Commerce objectives?
32
Outsourcing Pros and Cons
- Pros
- Faster
- Resources readily available
- Competitive - many alternatives
- You can focus on what you do best
- Youll learn as you go
- Cons
- Can be costly
- Always risky need to do research before and
monitor performance during and after