Design of Prosthetic Vascular Grafts - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 14
Title:
Design of Prosthetic Vascular Grafts
Description:
Arteries transport blood away from the heart whereas ... Knitted/Woven Polyesters. Application. Material. S. Waldman. MECH 393. Advantages and Disadvantages ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:1933
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Design of Prosthetic Vascular Grafts
1
Design of Prosthetic Vascular Grafts
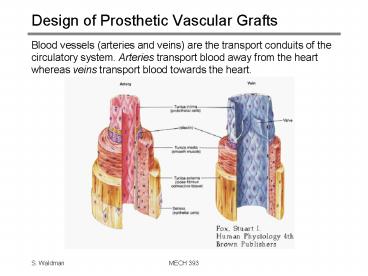
- Blood vessels (arteries and veins) are the
transport conduits of the circulatory system.
Arteries transport blood away from the heart
whereas veins transport blood towards the heart.
2
Cardiovascular Disease
Majority of cardiovascular diseases are disorders
involving the blood vessels. Two primary blood
vessels disorders are aneurysms and
atherolsclerosis. An aneurysm is a gradual
dilation of the arterial wall over a period of
time. If left untreated, the vessel will
eventually rupture. Atherosclerosis is
deposition of fatty substances, cholesterol and
other substances in the inner lining of an artery
(plaque) causing a restriction in blood flow.
3
Treatment Options
- Unless the disease state is severe (i.e.
seriously affecting quality of life), medication
is the best alternative. - Typically, surgical procedures are first used to
mitigate or correct the damage associated with
the disease (e.g. angioplasty, by-pass surgery).
However, in some cases, it is necessary to
implant a mechanical device to restore proper
blood flow in order for the patient to lead a
normal life. - The two main prosthetic options are
- Prosthetic Blood Vessels
- Stents
4
Prosthetic Vascular Grafts
- Vascular grafts may be used to either by-pass or
completely replace an occluded or aneurysmal
vessel, or inside an aneurysmal artery in such a
way as to exclude the aneurysm from the blood
flow. - Types of by-pass grafts
- Side-to-side anastomosis (by-pass of damaged
vessel segment) - End-to-end anastomosis (replacement of damaged
vessel segment)
5
Prosthetic Vascular Grafts
The first prosthetic vascular graft was implanted
in 1958 to repair to the narrowing of an artery
caused by atherosclerosis. The graft was
constructed out of a woven fabric polyester
(Dacron).
6
Prosthetic Vascular Graft Materials
This design has not changed much since its
inception however, various different polymeric
materials have been used over the years for
different applications.
7
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages The main advantages of prosthetic
vascular grafts over autografts include the
ability to manipulate size, reliability, and high
tensile and fatigue strength. Disadvantages The
major disadvantage of prosthetic vascular grafts
is the blood incompatibility of the materials
used. Most materials are somewhat thrombogenic
which can lead to poor long-term patency.
Improper matching of graft mechanical properties
with the parent vessel can lead to other problems
such as suture line stresses and development of
backflow and/or turbulence due to compliance
mismatching.
8
Future of Prosthetic Vascular Grafts
- The development of the next generation of
prosthetic vascular grafts have focused on
improving long-term patency through - materials that have less thrombogenic surfaces
- recruitment endothelial cells
- coatings to provide controlled release of
anti-coagulants - development of degradable grafts that can
replaced by native or seeded tissue to regenerate
damaged vessels - Several attempts have been made to line
prosthetic grafts with endothelial cells. These
techniques have been shown to improve graft
performance in animals, but success has been
limited in human clinical trials. In one study of
peripheral bypass grafts, only 38 of cell seeded
PTFE grafts remained patent at 30 months,
compared to 92 of autologous grafts.
9
Stents
- Stents are metallic wire meshes used to hold open
occluded arteries (partially or fully occluded)
or other vascular grafts. The architecture of the
metallic wire mesh is arranged such that the
stent itself may be squeezed into a tube of very
low radius. The stent with a balloon inside is
inserted in the occluded vessel and then the
balloon is expanded causing the stent to push
open the vessel wall. The wire mesh has
sufficient radial rigidity to resist closing
back, thus permanently dilating the vessel to
allow normal blood flow to resume.
10
Stents
11
Stent Materials
- All stents to-date have been made from metal
alloys as the design relies on the development of
plastic strains (non-recoverable) in the material
to function. - Commonly used materials include
- stainless steels
- cobalt-chromium alloys
12
Stents
- Stents have also been used as a lining for
vascular grafts during the repair of aneurysms.
Grafts for aortic aneurysms require greater
radial stiffness and the presence of a stent
around the (inside of the) graft provides that
additional radial rigidity. Some designs
incorporate the stent directly into the graft for
this purpose.
13
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages The main advantages of using a stent
(over by-pass surgery) is that the procedure is
minimally invasive. Disadvantages Some problems
with stents are inadequate (or degrading) radial
strength of the stent causing it to collapse,
thromobosis (as most metals are thromogenic), and
reoccurrence of atherosclerosis (process of
plaque formation is not affected). In addition,
stents are not usually used in severe cases of
atherosclerosis, except when the patient is not a
candidate for conventional by-pass surgery (age,
other health risks, etc.).
14
Future of Stent Design
- The development of the next generation of stents
have focused on the use of better materials and
incorporation of other features - shape memory alloys
- less thrombogenic metals (e.g. magnesium)
- drug eluting stents (controlled release of
anti-proliferative agents) - bioresorbable stents