HEMODYNAMIC DISORDERS - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 112
Title: HEMODYNAMIC DISORDERS
1
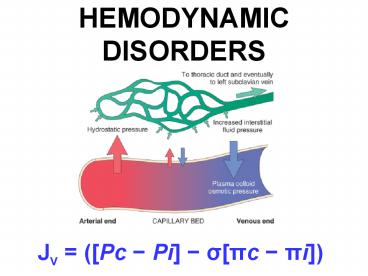
HEMODYNAMIC DISORDERS
Jv (Pc - Pi - spc - pi)
2
- Hemodynamic Disorders
- Thromboembolic Disease
- Shock
3
Overview
- Edema
- Hyperemia
- Congestion
- Hemorrhage
- Hemostasis
- Thrombosis
- Embolism
- Infarction
- Shock
4
EDEMA
- ONLY 4 POSSIBILITIES!!!
- Increased Hydrostatic Pressure
- Reduced Oncotic Pressure
- Lymphatic Obstruction
- Sodium/Water Retention
5
WATER
- 60 of body
- 2/3 of body water is INTRA-cellular
- The rest is INTERSTITIAL
- Only 5 is INTRA-vascular
- EDEMA is SHIFT to the INTERSTITIAL SPACE
- HYDRO-
- -THORAX, -PERICARDIUM, -PERICARDIUM
- EFFUSIONS, ASCITES, ANASARCA
6
INCREASED HYDROSTATIC PRESSURE
- Impaired venous return
- Congestive heart failure
- Constrictive pericarditis
- Ascites (liver cirrhosis)
- Venous obstruction or compression
- Thrombosis
- External pressure (e.g., mass)
- Lower extremity inactivity with prolonged
dependency - Arteriolar dilation
- Heat
- Neurohumoral dysregulation
7
REDUCED PLASMA ONCOTICPRESSURE (HYPOPROTEINEMIA)
- Protein-losing glomerulopathies (nephrotic
syndrome) - Liver cirrhosis (ascites)
- Malnutrition
- Protein-losing gastroenteropathy
8
LYMPHATIC OBSTRUCTION(LYMPHEDEMA)
- Inflammatory
- Neoplastic
- Postsurgical
- Postirradiation
9
Na RETENTION
- Excessive salt intake with renal insufficiency
- Increased tubular reabsorption of sodium
- Renal hypoperfusion?Increased renin-angiotensin-al
dosterone secretion
10
INFLAMMATION
- Acute inflammation
- Chronic inflammation
- Angiogenesis
11
Jv (Pc - Pi - spc - pi)
12
CHF EDEMA
- INCREASED VENOUS PRESSURE DUE TO FAILURE
- DECREASED RENAL PERFUSION, triggering of
RENIN-ANGIOTENSION-ALDOSTERONE complex, resulting
ultimately in SODIUM RETENTION
13
HEPATIC ASCITES
- PORTAL HYPERTENSION
- HYPOALBUMINEMIA
14
ASCITES
15
RENAL EDEMA
- SODIUM RETENTION
- PROTEIN LOSING GLOMERULOPATHIES (NEPHROTIC
SYNDROME)
16
EDEMA
- SUBCUTANEOUS (PITTING)
- DEPENDENT
- ANASARCA
- LEFT vs RIGHT HEART
- PERIORBITAL (RENAL)
- PULMONARY
- CEREBRAL (closed cavity, no expansion)
- HERNIATION of cerebellar tonsils
- HERNIATION of hippocampal uncus over tentorium
- HERNIATION, subfalcine
17
Pitting Edema
18
Transudate vs Exudate
- Transudate
- results from disturbance of Starling forces
- specific gravity lt 1.012
- protein content lt 3 g/dl
- Exudate
- results from damage to the capillary wall
- specific gravity gt 1.012
- protein content gt 3 g/dl
19
HYPEREMIA/(CONGESTION)
20
HYPEREMIA
- Active Process
CONGESTION Passive Process Acute or Chronic
21
CONGESTION
- LUNG
- ACUTE
- CHRONIC
- LIVER
- ACUTE
- CHRONIC
- CEREBRAL
22
ACUTE PASSIVE HYPEREMIA/CONGESTION, LUNG
?
23
Kerley B Air Bronch-ogram
24
(No Transcript)
25
(No Transcript)
26
CHRONIC PASSIVE HYPEREMIA/CONGESTION, LUNG
27
Acute Passive Congestion, Liver
28
Acute Passive Congestion, Liver
29
CHRONIC PASSIVE HYPEREMIA/CONGESTION, LIVER
30
(No Transcript)
31
(No Transcript)
32
HEMORRHAGE
- EXTRAVASATION beyond vessel
- HEMORRHAGIC DIATHESIS
- HEMATOMA (implies MASS effect)
- DISSECTION
- PETECHIAE (1-2mm) (PLATELETS)
- PURPURA lt1cm
- ECCHYMOSES gt1cm (BRUISE)
- HEMO- -thorax, -pericardium, -peritoneum,
HEMARTHROSIS - ACUTE, CHRONIC
33
EVOLUTION of HEMORRHAGE
- ACUTE? CHRONIC
- PURPLE? GREEN? BROWN
- HGB? BILIRUBIN? HEMOSIDERIN
34
(No Transcript)
35
(No Transcript)
36
(No Transcript)
37
(No Transcript)
38
(No Transcript)
39
HEMATOMAvs.CLOT
40
HEMOSTASIS
- OPPOSITE of THROMBOSIS
- PRESERVE LIQUIDITY OF BLOOD
- PLUG sites of vascular injury
- THREE COMPONENTS
- VASCULAR WALL, i.e., endoth/ECM
- PLATELETS
- COAGULATION CASCADE
41
SEQUENCE of EVENTSfollowing VASCULAR INJURY
- ARTERIOLAR VASOCONSTRICTION
- Reflex Neurogenic
- Endothelin, from endothelial cells
- THROMBOGENIC ECM at injury site
- Adhere and activate platelets
- Platelet aggregation (1 HEMOSTASIS)
- TISSUE FACTOR released by endothelium
- Activates coagulation cascade?thrombin?fibrin
(2 HEMOSTASIS) - FIBRIN polymerizes, TPA limits plug
42
PLAYERS
- ENDOTHELIUM
- PLATELETS
- COAGULATION CASCADE
43
ENDOTHELIUM
- NORMALLY
- ANTIPLATELET PROPERTIES
- ANTICOAGULANT PROPERTIES
- FIBRINOLYTIC PROPERTIES
- IN INJURY
- PRO-COAGULANT PROPERTIES
44
(No Transcript)
45
ENDOTHELIUM
- ANTI-Platelet PROPERTIES
- Protection from the subendothelial ECM
- Degrades ADP (inhib. Aggregation)
- ANTI-Coagulant PROPERTIES
- Membrane HEPARIN-like molecules
- Makes THROMBOMODULIN? Protein-C
- TISSUE FACTOR PATHWAY INHIBITOR
- FIBRINOLYTIC PROPERTIES (TPA)
46
ENDOTHELIUM
- PROTHROMBOTIC PROPERTIES
- Makes vWF, which binds Plats?Coll
- Makes TISSUE FACTOR (with plats)
- Makes Plasminogen inhibitors
47
ENDOTHELIUM
- ACTIVATED by INFECTIOUS AGENTS
- ACTIVATED by HEMODYNAMICS
- ACTIVATED by PLASMA
48
PLATELETS
- ALPHA GRANULES
- Fibrinogen
- Fibronectin
- Factor-V, Factor-VIII
- Platelet factor 4, TGF-beta
- DELTA GRANULES (DENSE BODIES)
- ADP/ATP, Ca, Histamine, Serotonin, Epineph.
- With endothelium, form TISSUE FACTOR
49
(No Transcript)
50
NORMAL platelet on LEFT, DEGRANULATING ALPHA
GRANULE ON RIGHT AT OPEN WHITE ARROW
51
(No Transcript)
52
PLATELET PHASES
- ADHESION
- SECRETION (i.e., release or activation or
degranulation) - AGGREGATION
53
PLATELET ADHESION
- Primarily to the subendothelial ECM
- Regulated by vWF, which bridges platelet surface
receptors to ECM collagen
54
PLATELET SECRETION
- BOTH granules, a and d
- Binding of agonists to platelet surface receptors
AND intracellular protein PHOSPHORYLATION
55
PLATELET AGGREGATION
- ADP
- TxA2 (Thromboxane A2)
- THROMBIN from coagulation cascade also
- FIBRIN further strengthens and hardens and
contracts the platelet plug
56
PLATELET EVENTS
- ADHERENCE to ECM
- SECRETION of ADP and TxA2
- EXPOSE phospholipid complexes
- Express TISSUE FACTOR
- PRIMARY?SECONDARY PLUG
- STRENGTHENED by FIBRIN
57
COAGULATION CASCADE
- INTRINSIC(contact)/EXTRINSIC(TissFac)
- Proenzymes?Enzymes
- Prothrombin(II)?Thrombin(IIa)
- Fibrinogen(I)?Fibrin(Ia)
- Cofactors
- Ca
- Phospholipid (from platelet membranes)
- Vit-K dep. factors II, VII, IX, X, Prot. S, C, Z
58
(No Transcript)
59
COAGULATION TESTS
- (a)PTT INTRINSIC (HEP Rx)
- PT (INR) EXTRINSIC (COUM Rx)
- BLEEDING TIME (PLATS) (2-9min)
- Platelet count (150,000-400,000/mm3)
- Fibrinogen
- Factor assays
60
THROMBOSIS
- Pathogenesis
- Endothelial Injury
- Alterations in Flow
- Hypercoagulability
- Morphology
- Fate
- Clinical Correlations
- Venous
- Arterial (Mural)
61
THROMBOSIS
- Virchows TRIANGLE
ENDOTHELIAL INJURY
ABNORMAL FLOW (NON-LAMINAR)
HYPER- COAGULATION
62
ENDOTHELIAL INJURY
- Jekyll/Hyde disruption
- any perturbation in the dynamic balance of the
pro- and antithrombotic effects of endothelium,
not only physical damage
63
ENDOTHELIUM
- ANTI-Platelet PROPERTIES
- Protection from the subendothelial ECM
- Degrades ADP (inhib. Aggregation)
- ANTI-Coagulant PROPERTIES
- Membrane HEPARIN-like molecules
- Makes THROMBOMODULIN? Protein-C
- TISSUE FACTOR PATHWAY INHIBITOR
- FIBRINOLYTIC PROPERTIES (TPA)
64
ENDOTHELIUM
- PROTHROMBOTIC PROPERTIES
- Makes vWF, which binds Plats?Coll
- Makes TISSUE FACTOR (with plats)
- Makes Plasminogen inhibitors
65
ABNORMAL FLOW
- NON-LAMINAR FLOW
- TURBULENCE
- EDDIES
- STASIS
- DISRUPTED ENDOTHELIUM
- ALL of these factors may bring platelets into
contact with endothelium and/or ECF
66
1 HYPERCOAGULABILITY(INHERITED)
- COMMONEST Factor V and Prothrombin defects
- Common Mutation in prothrombin gene, Mutation in
methyltetrahydrofolate gene - Rare Antithrombin III deficiency, Protein C
deficiency, Protein S deficiency - Very rare Fibrinolysis defects
67
(No Transcript)
68
2 HYPERCOAGULABILITY(ACQUIRED)
- Prolonged bed rest or immobilization
- Myocardial infarction
- Atrial fibrillation
- Tissue damage (surgery, fracture, burns)
- Cancer (TROUSSEAU syndrome, i.e., migratory
thrombophlebitis) - Prosthetic cardiac valves
- Disseminated intravascular coagulation
- Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia
- Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome (lupus
anticoagulant syndrome) - Lower risk for thrombosis
- Cardiomyopathy
- Nephrotic syndrome
- Hyperestrogenic states (pregnancy)
- Oral contraceptive use
- Sickle cell anemia
- Smoking, Obesity
69
MORPHOLOGY
- ADHERENCE TO VESSEL WALL
- HEART (MURAL)
- ARTERY (OCCLUSIVE/INFARCT)
- VEIN
- OBSTRUCTIVE vs. NON-OBSTRUCTIVE
- RED, YELLOW, GREY/WHITE
- ACUTE, ORGANIZING, OLD
70
MURAL THROMBI, HEART
71
FATE of THROMBI
- PROPAGATION (Downstream)
- EMBOLIZATION
- DISSOLUTION
- ORGANIZATION
- RECANALIZATION
72
(No Transcript)
73
OCCLUSIVE ARTERIAL THROMBUS
74
D.V.T.
- D. (CALF, THIGH, PELVIC) V.T.
- CHF a huge factor
- INACTIVITY!!!
- Trauma
- Surgery
- Burns
- Injury to vessels,
- Procoagulant substances from tissues
- Reduced t-PA activity
75
ARTERIAL/CARDIAC THROMBI
- ACUTE MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION OLD ATHEROSCLEROSIS
FRESH THROMBOSIS - ARTERIAL THROMBI also may send fragments
DOWNSTREAM, but these fragments may contain
flecks of PLAQUE also - LODGING is PROPORTIONAL to the of cardiac
output the organ receives, i.e., brain, kidneys,
spleen, legs, or the diameter of the downstream
vessel
76
ATHEROEMBOLI
- CHOLESTEROL clefts are components of
atherosclerotic plaques, NOT thrombi!!!
77
Disseminated Intravascular CoagulationD.I.C.
- OBSTETRIC COMPLICATIONS
- ADVANCED MALIGNANCY
- NOT a primary disease
- CONSUMPTIVE coagulopathy, e.g., reduced
platelets, fibrinogen, F-VIII and other
consumable clotting factors, brain, heart, lungs,
kidneys, MICROSCOPIC ONLY
78
(No Transcript)
79
EMBOLISM
- Pulmonary
- Systemic (Mural Thrombi and Aneurysms)
- Fat
- Air
- Amniotic Fluid
80
PULMONARY EMBOLISM
- USUALLY SILENT
- CHEST PAIN, LOW PO2, S.O.B.
- Sudden OCCLUSION of gt60 of pulmonary
vasculature, presents a HIGH risk for sudden
death, i.e., acute cor pulmonale, ACUTE right
heart failure - SADDLE embolism often/usually fatal
- PRE vs. POST mortem blood clot
- PRE Friable, adherent, lines of ZAHN
- POST Current jelly or chicken fat
81
(No Transcript)
82
(No Transcript)
83
SYSTEMIC EMBOLI
- PARADOXICAL EMBOLI
- 80 cardiac/20 aortic
- Embolization lodging site is proportional to the
degree of flow (cardiac output) that area or
organ gets, i.e., brain, kidneys, legs
84
OTHER EMBOLI
- FAT (long bone fxs )
- AIR (SCUBA bends)
- AMNIOTIC FLUID, very prolonged or difficult
delivery, high mortality
85
(No Transcript)
86
(No Transcript)
87
INFARCTION
- Defined as an area of necrosis secondary to
decreased blood flow - HEMORRHAGIC vs. ANEMIC
- RED vs. WHITE
- END ARTERIES vs. NO END ARTERIES
- ACUTE?ORGANIZATION?FIBROSIS
88
INFARCTION FACTORS
- NATURE of VASCULAR SUPPLY
- RATE of DEVELOPMENT
- SLOW (BETTER)
- FAST (WORSE)
- VULNERABILITY to HYPOXIA
- MYOCYTE vs. FIBROBLAST
- CHF vs. NO CHF
89
(No Transcript)
90
(No Transcript)
91
HEART
92
SHOCK
- Pathogenesis
- Cardiac
- Septic
- Hypovolemic
- Morphology
- Clinical Course
93
SHOCK
- Definition CARDIOVASCULAR COLLAPSE
- Common pathophysiologic features
- INADEQUATE CARDIAC OUTPUT and/or
- INADEQUATE BLOOD VOLUME
94
GENERAL RESULTS
- INADEQUATE TISSUE PERFUSION
- CELLULAR HYPOXIA
- UN-corrected, a FATAL outcome
95
TYPES of SHOCK
- CARDIOGENIC (Acute, Chronic Heart Failure)
- HYPOVOLEMIC (Hemorrhage or Leakage)
- SEPTIC (ENDOTOXIC shock, 1 killer in ICU)
- NEUROGENIC (loss of vascular tone)
- ANAPHYLACTIC (IgE mediated systemic vasodilation
and increased vascular permeability)
96
CARDIOGENIC shock
- MI
- VENTRICULAR RUPTURE
- ARRHYTHMIA
- CARDIAC TAMPONADE
- PULMONARY EMBOLISM (acute RIGHT heart failure or
cor pulmonale)
97
HYPOVOLEMIC shock
- HEMORRHAGE, Vasc. compartment?H2O
- VOMITING, Vasc. compartment?H2O
- DIARRHEA, Vasc. compartment?H2O
- BURNS, Vasc. compartment?H2O
98
SEPTIC shock
- OVERWHELMING INFECTION
- ENDOTOXINS, i.e., LPS (Usually Gm-)
- Gm
- FUNGAL
- SUPERANTIGENS, (Superantigens are polyclonal
T-lymphocyte activators that induce systemic
inflammatory cytokine cascades similar to those
occurring downstream in septic shock, toxic
shock antigents by staph are the prime example.)
99
SEPTIC shock events(overwhelming infection)
- Peripheral vasodilation?
- Pooling?
- Endothelial Activation?
- DIC
- Think of this as a TOTAL BODY inflammatory
response
100
ENDOTOXINS
- Usually Gm-
- Degraded bacterial cell wall products
- Also called LPS, because they are
Lipo-Poly-Saccharides - Attach to a cell surface antigen known as CD-14
101
ENDOTOXINS
102
SEPTIC shock events(linear sequence)
- SYSTEMIC VASODILATION (hypotension)?
- ? MYOCARDIAL CONTRACTILITY?
- DIFFUSE ENDOTHELIAL ACTIVATION?
- LEUKOCYTE ADHESION?
- ALVEOLAR DAMAGE? (ARDS)
- DIC
- VITAL ORGAN FAILURE? CNS
103
CLINICAL STAGES of shock
- NON-PROGRESSIVE
- PROGRESSIVE
- IRREVERSIBLE
104
NON-PROGRESSIVE
- COMPENSATORY MECHANISMS
- CATECHOLAMINES
- VITAL ORGANS PERFUSED
105
PROGRESSIVE
- HYPOPERFUSION
- EARLY VITAL ORGAN FAILURE
- OLIGURIA
- ACIDOSIS
106
IRREVERSIBLE
- HEMODYNAMIC CORRECTIONS of no use
107
PATHOLOGY
- MULTIPLE ORGAN FAILURE
- SUBENDOCARDIAL HEMORRHAGE (why?)
- ACUTE TUBULAR NECROSIS (why?)
- DAD (Diffuse Alveolar Damage, lung) (why?)
- GI MUCOSAL HEMORRHAGES (why?)
- LIVER NECROSIS (why?)
- DIC (why?)
108
ARDS/DAD
109
MYOCARDIAL NECROSIS
110
ATN
111
DIC
112
CLINICAL PROGRESSIONof SYMPTOMS
- Hypotension ?
- Tachycardia ?
- Tachypnea ?
- Warm skin? Cool skin? Cyanosis
- Renal insufficiency?
- Obtundance
- Death