Nucleotide Binding - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 11
Title:
Nucleotide Binding
Description:
The NAD-binding domain of the dehydrogenases, which is composed of 2 - a- - a ... Ions and electrons steric complementarity doesn't mean as much. ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:83
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Nucleotide Binding
1
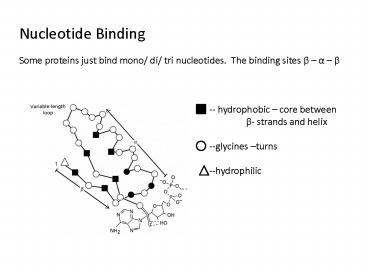
Nucleotide Binding Some proteins just bind mono/
di/ tri nucleotides. The binding sites ß a ß
-- hydrophobic core between ß- strands and
helix --glycines turns --hydrophilic
2
The NAD-binding domain of the dehydrogenases,
which is composed of 2 ß- a- ß- a- ß
nucleotide-binding units. Nucleotides are
generally bound on the right, near the carboxyl
ends of the ß- strands.
3
Small Ligands Ions and electrons steric
complementarity doesnt mean as much. Not shape,
small charged blobs. In general, ion-binding
sites are internal and use several binding groups
simultaneously in a cooperative manner. Some
intrinsic affinity Ca2 -- likes oxygens Zn2
-- likes sulfurs and imidazole Ns in His Fe2 /
Fe3 -- like sulfurs in Cys Internal binding
sites Cu2 -- thiols or imidazoles Mg2 -- bind
with phosphate groups of ligands
4
Ca2 Binding Love it buffers or sensors. Used
extensively to trigger muscle contraction and
control the release of neurotransmitters and
hormones. Very common structural motif known as
an EF hand
5
Asps bind with Oxygens Others are hydrophobic EF
hands come in pairs ? can be identified by
sequence Calmodulin sensor- binds Ca2 , rolls
into ball, and recognizes sequence
6
O2 binding proteins Ferrous heme groups of the
globins 2 Fe2 held by His, Glu Myoglobin
7
2 Cu2 ions held close by 6 His side chains In
the case of myoglobin and hemoglobin, O2 (and CO)
associate and dissociate rapidly though the
binding site is in the interior of the protein.
Fluctuations of the protein structure are thought
to allow this movement. Some other random
examples TATA box binding protein
(TBP) A DNA sequence rich in As and Ts
located 25 base pairs upstream of the
transcription site. Involved in the regulation
of transcription in eukaryotes.
8
A ß sheet in TBP forms the DNA binding
site Two homologous repeats, each of 88 amino
acids, at both ends of the TBP DNA-binding domain
form two structurally very similar motifs. Each
comprises an anti-parallel ß sheet of 5 strand
and 2 helices. It is referred to as a molecular
saddle. The underside of the saddle forms a
concave surface built up by the central 8 strands
of the ß sheet. Side chains form this side of
the ß sheet, as well as residues from the
stirrups, form the DNA-binding site. No a
helices are involved in the interaction area.
9
DNA bends significantly The interaction is
mainly hydrophobic (-- not a major groove deal)
and sometimes mediated by water. 15 side chains
from the ß- strands make hydrophobic contacts
with the phosphate sugar backbone of the DNA.
The phosphate groups are H-bonded to Ars and Lys
side chains at the end of the interaction
area. About 110o bend
10
Some leucine zippers have 2 parts The part we
see here, and then at the end they have a charged
basic region.
11
Here is the sequence
Zipper
Transition
It grips the DNA