RADIATIONS - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 25
Title:
RADIATIONS
Description:
Roentgen - amount of x or gamma which produce 1 electrostatic unit of charge in 1 cm3 air. Roentgen Equivalent Man ( REM ) - unit absorbed energy x quality factor as ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:84
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: RADIATIONS
1
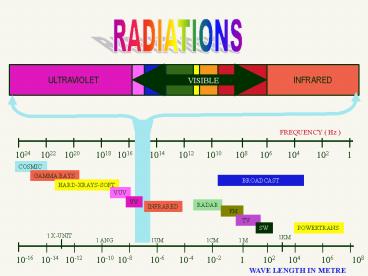
RADIATIONS
INFRARED
ULTRAVIOLET
VISIBLE
FREQUENCY ( Hz )
1024
1016
1014
1012
1010
108
106
1020
104
102
1022
1018
1
COSMIC
GAMMA RAYS
BROADCAST
HARD-XRAYS-SOFT
VUV
UV
RADAR
INFRARED
FM
TV
SW
POWERTRANS
1 X-UNIT
1KM
1CM
1 M
1UM
1 ANG
10-16
10-8
10-6
10-4
10-2
108
106
10-12
104
102
10-14
10-10
1
WAVE LENGTH IN METRE
2
IONIZING RADIATION
- Electromagnetic or particulate radiation capable
of producing ions, by interaction with matter.
3
IONIZING RADIATION
- COMMON TYPES
- Alpha particles
- Beta particles
- Neutrons
- Gamma radiation
- X-radiation
4
IONIZING RADIATION
- Alpha
- Originate from disintegration of radioactive
atoms - Positively charges ( 2 protons 2 neutrons )
- High Density ( Heavy ) Ionization
- Energy transfer - Short Distance
- Readily Shielded by piece paper / dead skin.
- Internal Radiation Hazards
- Beta
- Negatively charge
- Light High speed
- Penetrate tissues up to 1.5 cm
- Stopped by 12mm aluminium
5
IONIZING RADIATION
- X-rays
- Highly penetrating electromagnetic waves
- Electron bombardment of target materials.
- Gamma Rays
- Highly penetrating and present and external
radiation exposure hazards
6
SOURCE OF RADIATION
- Radioactive materials - emit one or more forms
of radiation - All radiation except x-rays originate from
radioactive materials. ( Cobalt-60 Radium 226
Cesium137 ). - X-ray is produce by x-ray machine
- High speed electrons suddenly slowed down on
striking target and losing energy in form of x-
radiation.
7
HEALTH EFFECTS
- ALPHA PARTICLES
- Interact electrically with human tissues and
other matter. Range 10 cm in air. - Hazardous when taking into the body.
- Tend to accumulate in kidney, lung, liver and
spleen. - No effect when outside the body.
8
HEALTH EFFECTS
- BETA PARTICLES
- Ejected from nuclei by disintegration of
Radioactive atoms. - Maximum range wood 4 cm
- Human body penetration 0.2 to 2.3 cm.
- High excessive dose may cause skin burns.
9
HEALTH EFFECTS
- NEUTRONS
- Release by nuclei disintegration of Radioactive
atoms. ( Fissionable isotopes ). - The range and extend of damage to human depend on
the characteristic of material they pass
through. - Human body penetration 0.6 cm approx.
depending on the neutron energy. - Emit secondary radiations ( alpha, beta, gamma.
etc) on collision with atoms.
10
HEALTH EFFECTS
- GAMMA RADIATION
- Similar to x-radiation
- Penetration depend on the wavelength
- The shorter wave length have greater penetrating
power and will penetrate several centimeters of
steel. - They are capable of penetrating deep into tissues
and cause ionizing.
11
HEALTH EFFECTS
- COMMON EFFECTS-
- Skin redness, Dermatitis, Skin Cancer, hair loss,
eyes inflammation. - Damage to the bone marrow resulting a blood
disease. - Damage the digestive systems
- Radiation Sickness
- Mutagenesis Carcinogenesis Teratogenesis
12
APPLICATION / USES
- X-rays Medicine Dentistry NDT
- Gamma- X-rays Medicine Sterilisations of
medical supplies. - Laboratories and Instrumentations
- Nuclear Power Generation
- Atomic weapons manufacturer.
13
UNITS
- Gray - 1 joule of absorbed energy/kg ( dose )
- Roentgen - amount of x or gamma which produce 1
electrostatic unit of charge in 1 cm3 air - Roentgen Equivalent Man ( REM ) - unit absorbed
energy x quality factor as compared with gamma
radiation. - Seivert ( SV ) - modern unit of absorbed dose. (
1 rem 10 mSV )
14
NCRP recommended limits
- Occupational exposure
- Annual 5 rem or 50 mSv
- Cumulative 1 rem x age or 10mSv x age
- Fetus exposure ( monthly )
- Equivalent dose limit 50 mrem or 0.5 mSv
15
CONTROL MEASURES
- Basic Protection Measures are associated with
- (1) Time - exposure by 1/2 Dose by half
- (2) Distance - 2x ( distance) 1/4 amount
- (3) Shielding - Thickness Radiation
16
RADIATION PROTECTION PROGRAMME
- Highly Specialised
- Includes following
- Controlled Area
- Tracking of source
- Monitoring of area
- Personal Monitoring
- Biological Monitoring
17
NON IONIZING RADIATION
- The electromagnetic rays that do not have
sufficient energy to dislodge electrons in the
body. - It does transmit energy to the atoms which give
rise to health effect. - The shorter wavelength have higher energies than
larger wave length.
18
ULTRAVIOLET
- Divided into three regions
- Near 400 - 300 nm ( UV-A )
- Far 300 - 200 nm ( UV-B )
- Vacuum 200 -100 nm (UV-C )
- Health Effects
- UV-A Pigmentation of skin
- UV-B Biological active Potentially harmful
- UV-C Bactericidal Germicidal
19
INFRARED
- IR region Visible red light ( 750nm ) to 0.3-cm
wavelength of microwaves. - Health Effects
- Increase tissue temperature upon exposure depend
on w/length. - IR - A 780 - 1400nm absorbed through
skin/cornea - IR - B 1400 -3000nm Absorbed all in
cornea/cataract - IR - C 3000 - 1mm Damage to skin/eyes
20
INFRARED
- HEALTH EFFECTS
- Short w/length Injured cornea, iris, retina and
lens. - Exposure to visible IR radiation from furnace -
Glass blower cataract / Heat Cataract.
21
MICROWAVES/RADIOWAVES
- Within broadspectrum of Radio frequencies (
approx 10-300,000 MHz ) - HEALTH EFFECTS
- Thermal effects
- lt 3000 MHz can penetrate skin and absorb by
underlying tissues. - Serious damage can occur when underlying tissues
such as eyes are exposed.
22
LASER
- Light Amplification by the Stimulated Emission of
Radiation. - Coherent Highly direction low divergence
- HEALTH EFFECTS
- Permanent eye damage and skin bruises can result
from exposure to powerful lasers.
23
RADIATION MONITORING
- To check - installation is safe
- To suggest ways to improve
- To enable safe working procedure
- To check amount of radiation received
- To monitor consequence of changes
24
PERSONAL MONITORING
- PURPOSE
- Radiation dose received
- Contamination and ingestion
- Film Badge - chest
- Gas ionisation Device - pocket
- Scintillation Counter - ingested / surface
25
ENVIRONMENT MONITORING
- Ionisation Chamber
- Scintillation Phosphors
- Geiger Counter
- Wipe test